
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
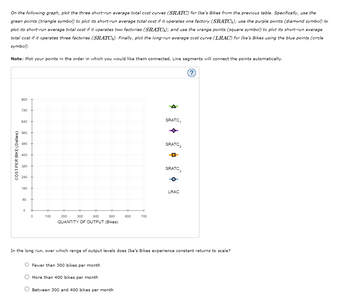
Transcribed Image Text:On the following graph, plot the three short-run average total cost curves (SRATC) for Ike's Bikes from the previous table. Specifically, use the
green points (triangle symbol) to plot its short-run average total cost if it operates one factory (SRATC₁); use the purple points (diamond symbol) to
plot its short-run average total cost if it operates two factories (SRATC₂); and use the orange points (square symbol) to plot its short-run average
total cost if it operates three factories (SRATC3). Finally, plot the long-run average cost curve (LRAC) for Ike's Bikes using the blue points (circle
symbol).
Note: Plot your points in the order in which you would like them connected. Line segments will connect the points automatically.
COST PER BIKE (Dollars)
800
720
640
560
480
400
320
240
160
80
0
0
100
200
300
400
500
QUANTITY OF OUTPUT (Bikes)
O Fewer than 300 bikes per month
More than 400 bikes per month
600
Between 300 and 400 bikes per month
700
SRATC,
SRATC₂2
SRATC
In the long run, over which range of output levels does Ike's Bikes experience constant returns to scale?
LRAC
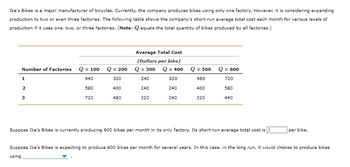
Transcribed Image Text:Ike's Bikes is a major manufacturer of bicycles. Currently, the company produces bikes using only one factory. However, it is considering expanding
production to two or even three factories. The following table shows the company's short-run average total cost each month for various levels of
production if it uses one, two, or three factories. (Note: Qequals the total quantity of bikes produced by all factories.)
Number of Factories Q = 100
440
1
2
3
580
720
Q = 200
320
400
480
Average Total Cost
(Dollars per bike)
Q = 300 Q = 400
240
320
240
320
240
240
Q
= 500
480
400
320
Q = 600
720
580
440
Suppose Ike's Bikes is currently producing 600 bikes per month in its only factory. Its short-run average total cost is
per bike.
Suppose Ike's Bikes is expecting to produce 600 bikes per month for several years. In this case, in the long run, it would choose to produce bikes
using
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A small company produces organic cookies. When the price is $9.00 per dozen, the average daily sales has been 84 dozen cookies. When the price was decreased to $6.00 per dozen, the average daily sales increased to 110 dozen cookies. Assume that daily cookie sales is linearly related to price per dozen. Each dozen cookies has a variable cost of 70 cents to make, plus additional daily fixed costs of $55.00arrow_forwardCan you assist in filling out this chart?arrow_forwardThe production function is f (L, M ) = 5L1/2M 1/2, where L is the number of units of labor and M is the number of machines. If the amounts of both factors can be varied and if the cost of labor is $9 per unit and the cost of using machines is $64 per machine, then what is the total cost of producing 12 units of output?arrow_forward
- 1. If the average cost of a plant to produce a "q" unit is explained by the functions below this: C = 0.0003q2 - 0.001q + 4 + 20.000/q a. What is the marginal cost function of product q?b. What is the marginal cost when producing 10 units?c. What is the marginal cost when producing 50 units? 2. If the average cost of a plant to produce a "q" unit is explained by the functions below this: C = 0.0001q2 - 0.002q + 5 + 10.000/q a. What is the marginal cost function of product q?b. What is the marginal cost when producing 20 units?c. What is the marginal cost when producing 100 units?arrow_forwardFirm A produces 1,000 units of output at a cost of $16.84 each. Firm A sells 600 units to Firm B for a price of $24.53 each. They sell the remaining units to consumers for a price of $25.21 each. Firm B produces 100 units of output using the 600 units that it purchased from Firm A. The total cost of producing the 100 units was $77 per unit. Firm B sold 90 units to consumers for $101 each and did not sell the remaining units this year. What is the value of consumption spending? Enter a number rounded to two decimal places. ASUS 10 & 5 6arrow_forwardE Let the demand function for a product be given by the function D(q) = -1.65g + 270, where q is the quantity of items in demand and D(q) is the price per item, in dollars, that can be charged when q units are sold. Suppose fixed costs of production for this item are $4, 000 and variable costs are $3 per item produced. If 96 items are produced and sold, find the following: A) The total revenue from selling 96 items (to the nearest penny). Answer: $ B) The total costs to produce 96 items (to the nearest penny). Answer: $ C) The total profits to produce 96 items (to the nearest penny. Profits may or may not be negative.). Answer: $ Question Help: C ME PE Video 66°F Mostly cloudyarrow_forward
- In Bushville, residents typically either work as salaried employees or owns small business on Central Square. Salaried employees on average earn $56,000 per year. All of the stores are rented by real estate companies who own the buildings. Currently the typical store brings in $325,000 of revenue per year. The typical variable costs needed to run a store in Bushville (paying for labor, buying material, etc.) are $210,000 year. a) What is the opportunity cost of running a store? Explain how you know this. b) Given this opportunity cost, what rent will the real estate companies charge? Explain. c) Suppose that a new highway brings more visitors to town, and stores on Central Square now brings in $472,000 of revenue per year with modest increase in variable costs to $236,000. What will happen to rents? Who will benefit – shop owners or the real estate companies?arrow_forwardSuppose a firm's total cost and marginal cost are given by TC= 200 + 100+90 and MC = 10 + 180. The output level that minimizes average total cost is 18 22.22 10 20 0000arrow_forwardA company produces very unusual CD's for which the variable cost is $ 15 per CD and the fixed costs are $ 50000. They will sell the CD's for $ 79 each. Let a be the number of CD's produced. Write the total cost C as a function of the number of CD's produced. C =$ Write the total revenue R as a function of the number of CD's produced. R=$ Write the total profit P as a function of the number of CD's produced. P=$ Find the number of CD's which must be produced to break even. The number of CD's which must be produced to break even is Question Help: Video Submit Questionarrow_forward
- 7. Costs in the short run versus in the long run Ike's Bikes is a major manufacturer of bicycles. Currently, the company produces bikes using only one factory. However, it is considering expanding production to two or even three factories. The following table shows the company's short-run average total cost each month for various levels of production if it uses one, two, or three factories. (Note: Q equals the total quantity of bikes produced by all factories.) Number of Factories Q = 100 440 580 720 1 2 3 Q = 200 320 400 480 Average Total Cost (Dollars per bike) Q = 300 Q = 400 240 320 240 240 320 240 Q = 500 480 400 320 Q = 600 720 580 440 Suppose Ike's Bikes is currently producing 600 bikes per month in its only factory. Its short-run average total cost is $ per bike. Suppose Ike's Bikes is expecting to produce 600 bikes per month for several years. In this case, in the long run, it would choose to produce bikes using On the following graph, plot the three short-run average total…arrow_forwardIke's Bikes is a major manufacturer of bicycles. Currently, the company produces bikes using only one factory. However, it is considering expanding production to two or even three factories. The following table shows the company's short-run average total cost (SRATC) each month for various levels of production if it uses one, two, or three factories. (Note: Q equals the total quantity of bikes produced by all factories.) NOTE: the options for the blank question is this Suppose Ike's Bikes is expecting to produce 500 bikes per month for several years. In this case, in the long run, it would choose to produce bikes using _______ (once factory OR two factory OR three factory)arrow_forwardA toll road commission is planning to locate garages for tow trucks along a 94-mile circular highway. Each garage has a fixed cost of $4,500 per day. Towing jobs are equally likely along any point of the highway, and cost per mile towed is $47. If there were 4,500 towing jobs per day, what number of garages would minimize the sum of the fixed costs and towing costs? Instructions: Enter your answer as a whole number. garagesarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education