
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
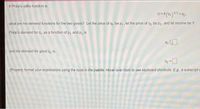
Transcribed Image Text:If Philip's utility function is
U=4 (41) 05+42.
0.5
what are his demand functions for the two goods? Let the price of q, be p,, let the price of q, be p2, and let income be Y.
Philip's demand for q, as a function of p, and p, is
91
and his demand for good q, is
(Properly format your expressions using the tools in the palette. Hover over tools to see keyboard shortcuts. Eg, a subscript o
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What is the marginal rate of substitution (MRS) for the utility function U(x, y) = x² + y²? The marginal rate of substitution of good x for good y is MRS = (Properly format your expression using the tools in the palette. Hover over tools to see keyboard shortcuts. E.g., a superscript can be created with the ^ character.) (Note: Be sure to use the Greek letter rho provided in the tool palette in your response.)arrow_forward10arrow_forwardSuppose your utility for goods x1 and x2 is represented by the following utility function: U(x1,x2)= x11/5 x24/5 a) What is your marginal rate of substitution, MRS12? b) If the price for good x1 is p1 = 2, the price for good x2 is p2 = 4, and your available income is m = 20, write down your budget constraint. c) Using the prices and income given at b) above, find your optimal consumption choice bundle (Marshallian demand) and its corresponding utility level. d) Illustrate your optimal consumption choice on a graph. e) For the prices given in b), what income would you need to achieve a utility level of 25?arrow_forward
- Consider the following Marshallian Demand Function derived from the utility maximization problem, X = a M P where X is the quantity consumed, Mis income of the consumer, P is the price of the good, and α is some number between 0 and 1 which represents the relative importance of the good. Does this demand function satisfy the law of demand? (_ Why or why not? (*arrow_forwardLet U(x, y) = 3x + y be the utility function of a consumer, whohas a budget of I. As a function of I, find the consumer’s Walrasian demand when the prices are px = py = 1. The price of good x increases to 2, find the new Walrasian demand for the new prices px = 2 and py = 1. Decompose this change into an income and a substitution effect.arrow_forwardPlease can I get step by step helparrow_forward
- (2) Lisa can buy either whole chickens or chicken wings at her local supermarket. Her utility function over whole chickens and chicken wings is U(xc,Xw) = 2xc + Xw, where x, and xw are chickens and chicken wings, respectively. What is her demand function xc (pc, Pw, m) for chickens?arrow_forwardSuppose your utility for goods x1 and x2 is represented by the following utility function: U(x1,x2)= x11/5 x24/5 a) What is your marginal rate of substitution, MRS12? b) If the price for good x1 is p1 = 2, the price for good x2 is p2 = 4, and your available income is m = 20, write down your budget constraint. c) Using the prices and income given at b) above, find your optimal consumption choice bundle (Marshallian demand) and its corresponding utility level. d) Illustrate your optimal consumption choice on a graph. e) For the prices given in b), what income would you need to achieve a utility level of 25? PLEASE ONLY ANSWER PART C, D AND Earrow_forwardSuppose the demand curves for goods A, B, and C have the following functional forms, where Q denotes quantity demanded, P denotes price, and M denotes income: QA = 120 - 3.5PA - 6PB + 14M QB = 100 - 2PB + 3PC + 1.1M Qc = 1500 -0.5Pc - 300M. Based on these demand curves, which of the following goods are known to be normal goods? A, B and C B A and B only C Aarrow_forward
- (In this question we denote income by Y, not by W as in the lecture notes). The following figure shows the consumption of x and y for two market situations. We can conclude that: x is a normal good for all market situations. py is greater than px. It is not conclusive. x is an inferior good for some market situation. y is an inferior good for some market situation.arrow_forwardBased on Nick's willingness to sell, plot his supply curve as a step function on the following graph using the orange points (square symbol). Be sure to plot your first point at (0, 0). Price of Water 10 9 100 8 7 8 10 3 2 1 0 0 2 3 Quantity of Water Suppose the price of a bottle of water is $4. In this case, Nick receives $ 5 If the price rises to $6, Nick now sells Nick's Supply Price = $4 Use the black line (plus symbol) to draw a price line at $4. Next use the grey point (star symbol) to indicate how many bottles of water Nick will produce and sell at that price. Finally, use the purple point (diamond symbol) to shade the area that represents Nick's producer surplus. bottles of water. This Quantity Sold Producer Surplus in producer surplus from his water sales. his producer surplus to $arrow_forwardSuppose that i's preferences over goods x and y are represented by the following utility function U₁(x, y)=x45¹5. Let m denote the consumer's income, p denote the price of good x and let the price of good y equal 1. A) Find the Marshallian demand functions for goods x and y. B) Show how each of the demand function is affected by a change in the price of good x. C) Which of the goods is an inferior good?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education