
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
10 If it is not in long-run equilibrium, what will happen in this industry to restore long-run equilibrium?
11 In long-run equilibrium, what is the firm's profit-maximizing quantity?
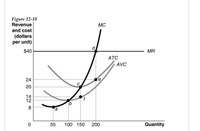
Transcribed Image Text:Figure 12-18
Revenue
MC
and cost
(dollars
per unit)
d
$40
MR
ATC
AVC
24
C
20
14
12
8
a
55
100 150
200
Quantity
.......
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 11. Consider a competitive market where firms have U-shaped cost curves. Which of the following is true? a. The long run market supply curve for a constant cost industry is upward sloping, and, the short run supply curve of each firm is upward sloping. b. The long run market supply curve for an increasing cost industry is upward sloping, and, the short run supply curve of each firm is upward sloping. c. The long run market supply curve for a decreasing cost industry is upward sloping, and, the short run supply curve of each firm is upward sloping. d. The long run market supply curve for an increasing cost industry is downward sloping, and, the short run supply curve of each firm is horizontal. e. None of the above.arrow_forward4. The demand for an individual firm's output depends on the demand for the industry's output, the number of firms in the industry, and the structure of the industry. O a. True Ob. Falsearrow_forward3. Suppose a perfectly competitive firm is operating at a level of output such that P> MC. Would you advise this firm to keep producing at this level or should it increase or decrease its output? Why? (Hint: it will help you to draw a graph for a perfectly competitive firm in short run equilibrium. The level of profit in equilibrium does not matter).arrow_forward
- 11. The graph below shows the marginal revenue, marginal cost, and average total cost at different quantities for a firm in a perfectly competitive market. If this firm chooses to produce no output in the short run, what must the market price be? A-Below $20 $21-$30 $31-$40 $41-$50 Above $50 7. firm's implicit costs are $10,000, explicit costs are $5,000, and its total revenue is $10,000. This firm is earning A-normal accounting profit B-positive accounting profit of $5,000 C-positive economic profit of $5,000 D-normal economic profit E-negative accounting profit of $5,000arrow_forwardLooking to see how to resolvearrow_forward7 A local tavern in a perfectly competitive market was in a long-run equilibrium. Then, a scientific breakthrough determines that beer prevents heart attacks, resulting in an increase in demand for beer. Describe the market processes that affect the tavern in both the short run and the new long-run equilibrium.arrow_forward
- 7. Short-run supply and long-run equilibrium Consider the competitive market for ruthenium. Assume that no matter how many firms operate in the industry, every firm is identical and faces the same marginal cost (MC), average total cost (ATC), and average variable cost (AVC) curves plotted in the following graph. COSTS (Dollars per pound) 100 90 80 70 40 30 20 10 0 0 MC D 5 10 ATC 15, 15 AVC ☐ 15 20 25 30 35 QUANTITY (Thousands of pounds) 40 + 45 50 The following graph plots the market demand curve for ruthenium. (?)arrow_forward22. Which of these is a valid difference between firms in competitive price-searcher and price-taker markets? Price-taker firms advertise their products, while price-searcher firms do not. Price-searcher firms advertise their products, while price-taker firms do not. Price takers earn economic profit in the short run, while price searchers do not. Price searchers earn economic profit in the long run, while price takers do not.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education