
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
If cylinder E has a mass of 20 kg and each cable segment can sustain a maximum tension of 400 N, determine the following:
3.1 The largest mass of cylinder F that can be supported by the system is ______ kg.
3.2 The sag yC is equal to ______ m.
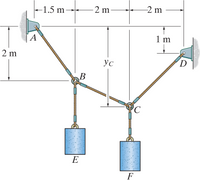
Transcribed Image Text:2 m
2 m
+1.5 m
-
1 m
A
2 m
Ус
В
E
F
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- QB2: Determine the force in members GH, GB, and BC, and state whether each of these three members is in tension (T) or compression (C), or whether it is a zero-force member (ZFM). Solve this problem using the Method of Sections. [Туре C for LO 3.2, 3.4] 3 kN 3 kN 3 kN 1 kN 1 kN 45° 4m 1m 3 m 3 m 3 m 3 marrow_forwardA 12.0 kg weight hangs from a 7.50 m pole as illustrated in the diagram. The pole has a mass of 8.0 kg. Determine the tension in the cable, and the "Frictional" and "Normal" forces felt from the wall.arrow_forwardFour sets of flexible cables, spaced at 120° intervals, are used to stabilize a 400-ft communications tower. The tower and one cable from each set is shown in Fig. The weight of each tower is 40 lb/ft, and the communica- tions equipment at the top weighs 2000 lb. Determine the axial forces transmitted by transverse cross sections at points A, B, C, and D of the tower. 50 ft 30 1500 lb 100 ft B 40° 1250 lb 100 ft 50° 1000 lb 100 ft 50 ft 60 750 Ibarrow_forward
- A "scale" is constructed with a 4.1-ft-long cord and the 13-lb block D. The cord is fixed to a pin at A and passes over two small pulleys at B and C. Determine the weight of the suspended block at B if the system is in equilibrium. Add your answer 7 1n B 1.50arrow_forwardThe traffic light shown in (Figure 1) has a mass of21 kg . Take h= 3.5 mm.arrow_forward2-Determine the magnitude ( P) of the B W=30 N horizontal force required to initiate motion of the block of mass (m.) for the cases : a-Pis applied to the right. b-Pis applied to the lift. u=0.5 30° P(a) mg P(barrow_forward
- 1. The rectangular plate is suspended from verti- cal cables and is in equilibrium. The mass, m, of the plate and the dimension d are given. The weight of the plate acts through the center of the rectangle. What are the tensions T4, T; and Tc in each of the three cables? 1.5d B 2.5d 10.75d d Harrow_forwardQ.2) A plate is supported by a rope and two hinges as shown in figure. Assume that hinges do not exert couples on the plate, and the hinge at A does not exert a force on the plate in the direction of the hinge axis. If the plate is uniform with 50 kg mass, determine the tension in the 240 mm 240 mm гope. 400 mín 400 mm 200 mm! 200 mm B 480 mmarrow_forwardQuestion 1 Member ABC of negligible weight is supported by a pin and bracket at B and by an inextensible cord attached at A and C and passing over a frictionless pulley at D. For the loading shown and neglecting the size of the pulley, calculate the tension in the cord ,the horizontal and vertical reactions at point B. (X,XX,XXX represents the last digits number of your IC). 1 257mm 75 N 167mm B 127 mmarrow_forward
- Q2. Determine the stretch in each spring for equilibrium of the block of mass M. The springs are shown in the equilibrium position Given: M = 2 kg a - 3 m b = 3 m C - 4 m kAB - 30 kAC = 20 kAD - 40 g- 9.81 www Darrow_forward3. For a frictionless pulley and cable, tensions in the cable (T₁ and T₂) are related as a. b. T₁ > T₂ c. T₁ = T₂ d. T₁ < T₂ e. T₁ = T₂ sin 8 T₂ T₁arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY