
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Identify the stereogenic carbon in (S)- and (R)-limonene, rank the substituents around it and rationalize the assignment of their stereochemical configurations. Hint: When ranking carbons that have multiple bonds, consider the bolded carbon of C=C being connected to 2 carbons and the bolded carbon of C≡C being connected to 3 carbons.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
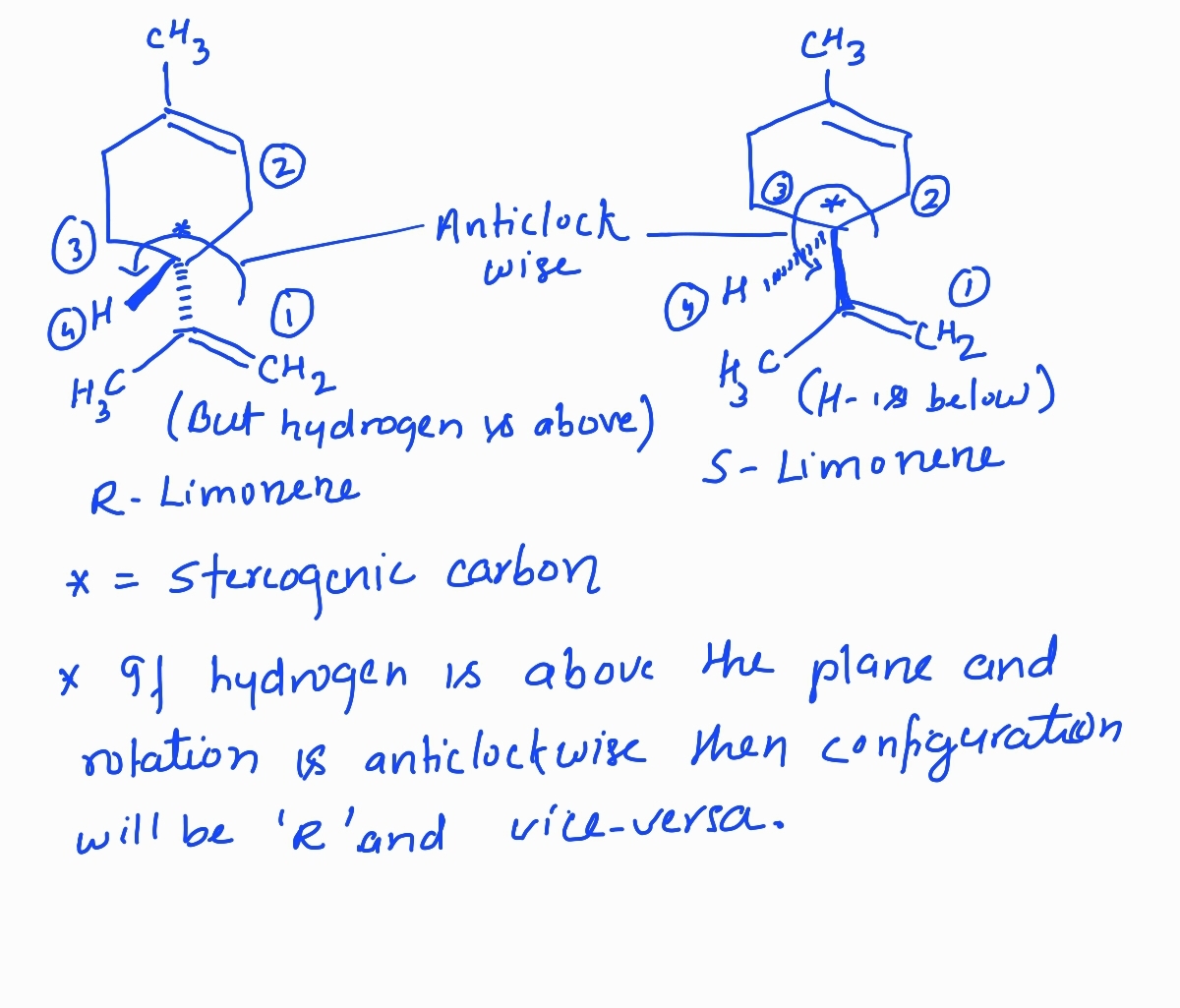
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Using a planar pentagon representation for the cyclopentane ring, draw structural formula for trans-1,2-dimethylcyclopentane. • Use the wedge/hash bond tools to indicate stereochemistry where it exists. • Include H atoms at chiral centers only. • In cases where there is more than one answer, just draw one. • Do not include lone pairs in your answer. They will not be considered in the grading. opy aste C. O O O- [* ChemDoodle I...arrow_forward1) Draw the molecule to which the Newman plot below belongs. 2) a) Draw the Newman projection of the most unstable and stable conformations based on the C2-C3 carbons of butane. b) Draw the most stable conformation of cis-1-methyl-3-ethylcyclohexane. 3) Which of the following molecules are structural isomers with each other?arrow_forwardHow many degrees of unsaturation for C9H15NO2?arrow_forward
- Compounds 1 and 2 were prepared, and the difference in their heats of combustion was found to be 17.2 kJ/mol (J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1961, 83, 606-614): H H 1 Shown below are the lowest-energy conformations of compounds 1 and 2. Identify which drawing matches which compound, and identify which compound has the larger heat of combustion. H H H H |||I 2 H 4 H H The first drawing is compound 1, and compound 1 has a larger heat of combustion because it is the less stable compound. O The first drawing is compound 2, and compound 2 has a larger heat of combustion because it is the less stable compound. The first drawing is compound 2, and compound 2 has a larger heat of combustion because it is the more stable compound. The first drawing is compound 1, and compound 1 has a larger heat of combustion because it is the more stable compound.arrow_forwardAnswer parts b and Carrow_forward5. For the molecules below assign the stereochemical configuration of the selected tetrahedral carbon chiral centers (R, S or N (not a chiral center)) and the alkene (E, Z or N (not a stereocenter)) that are indicated by the arrows (note that you do not have to assign the configuration of every chiral center in the molecule). If the atom in question is not a chiral center or is not a stereocenter circle N for neither. b) RSN RSN HO" RSN EZ N RSN НО. H₂N HO HO OH HO OH RSN RSN CH3 НИ H3 CH₂ RSN RSN RSN EZ N RSNarrow_forward
- Draw a skeletal (bond-line) structure of (R)-2,2,3- trimethylhexane. Use a dash or wedge bond to indicate stereochemistry of substituents on asymmetric centers, where applicable.arrow_forwardDraw the sold/dashed wedge structures (skeletal structure) for all stereoisomers of 3,4-dichloro 4-methylhexane. Label each structure with the proper R/S notation Label enantiomers and diastereomersarrow_forward2. Draw Newman projections (= 60° increments) of the conformations of 2R-bromobutane from C2-C3. Indicate anti, gauche and eclipsed conformations. Indicate the most and least stable conformations.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY