
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
1. identify the presence of a peptide bonds in your structure by putting a star/highlighting at the appropriate bond(s). If you have none explain why?
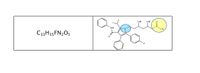
Transcribed Image Text:OH
OH
NH
OH
C33H35FN2O5
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider the peptide below, and indicate which of the following would accurately select all that apply. describe the peptide. H₂NⓇ CH- CH₂ CH-CH3 CH3 -CH- CH₂ N- CH- CH₂ CH₂ CH 3 00 One of the residues is capable of forming disulfide linkages. It is hydrophobic. It would easily cross-link with another peptide with the same structure. If it was mixed into a mixture of hexane (an organic solvent) and water, it would probably partition into the hexane layer. It would have a "net charge" of 0 at pH 7.arrow_forward4. *** Consider an a-helix with the following sequence:arrow_forwardPlese fins the attachementarrow_forward
- Hello I need the answer of question attached. Thanksarrow_forwardNot sure how to do the expanded structure for these… (if you can only answer one, can you do letter E?) All of them would be awesome though! Thank you!arrow_forwardDraw the protein given by the sequence TIP and circle any chiral carbons. 6arrow_forward
- Imagine the main chain of a protein bends back on itself, so that two amino acid residues R₁ and R₂ come close to each other. In the table below are four possibilities for what R₁ and R2 might be. In each case, decide whether a specific interaction could form between the residues. If a specific interaction could form, give the name of the interaction. R₁ R₂ specific interaction? name of specific interaction x yes alanine valine O no isoleucine asparagine ○ yes O no yes lysine glutamate ☐ O no yes threonine asparagine O noarrow_forward(Anyone) Can you please help me with this Chemistry problems? (all of them)arrow_forwardGive detailed Solution with explanation neededarrow_forward
- Which peptides is more likely to take up on alpha-helical structure? Explain. Top: Leu-Lys-Ala-Glu-Asn-Asp-Glu-Ala-Ala-Arg-Ala-Met-Ser-Glu-Ala Bottom: Cys-Arg-Ala-Gly-Gly-Phe-Pro-Trp-Asp-Gln-Pro-Gly-Tyr-Ser-Asnarrow_forwardOnly typed solutionarrow_forwardRefer to the bar graph below, Explain why the n→π* interactions contributes more to the overall stabilization of the protein than all the other interactions(C-H-O hydrogen bond,π-π interactions, C5 Hydrogen Bonds, Cation-π interactions, Sulfur-arene interactions, Anion-π interactions, Chalcogen bonds, X-H-π interactions) even though n→π* is the weaker interaction. Explain why that's the case for EACH of the bonds. I.e Why n→π* interactions contribute more to the overall stabilization of the protein than C-H-O hydrogen bonds, even though n→π* is the weaker interaction. Why n→π* interactions contribute more to the overall stabilization of the protein than π-π interactions even though n→π* is the weaker interaction. Why n→π* interactions contribute more to the overall stabilization of the protein than C5 Hydrogen Bonds, even though n→π* is the weaker interaction. Why n→π* interactions contribute more to the overall stabilization of the protein than Cation-π interactions, even though…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY