
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
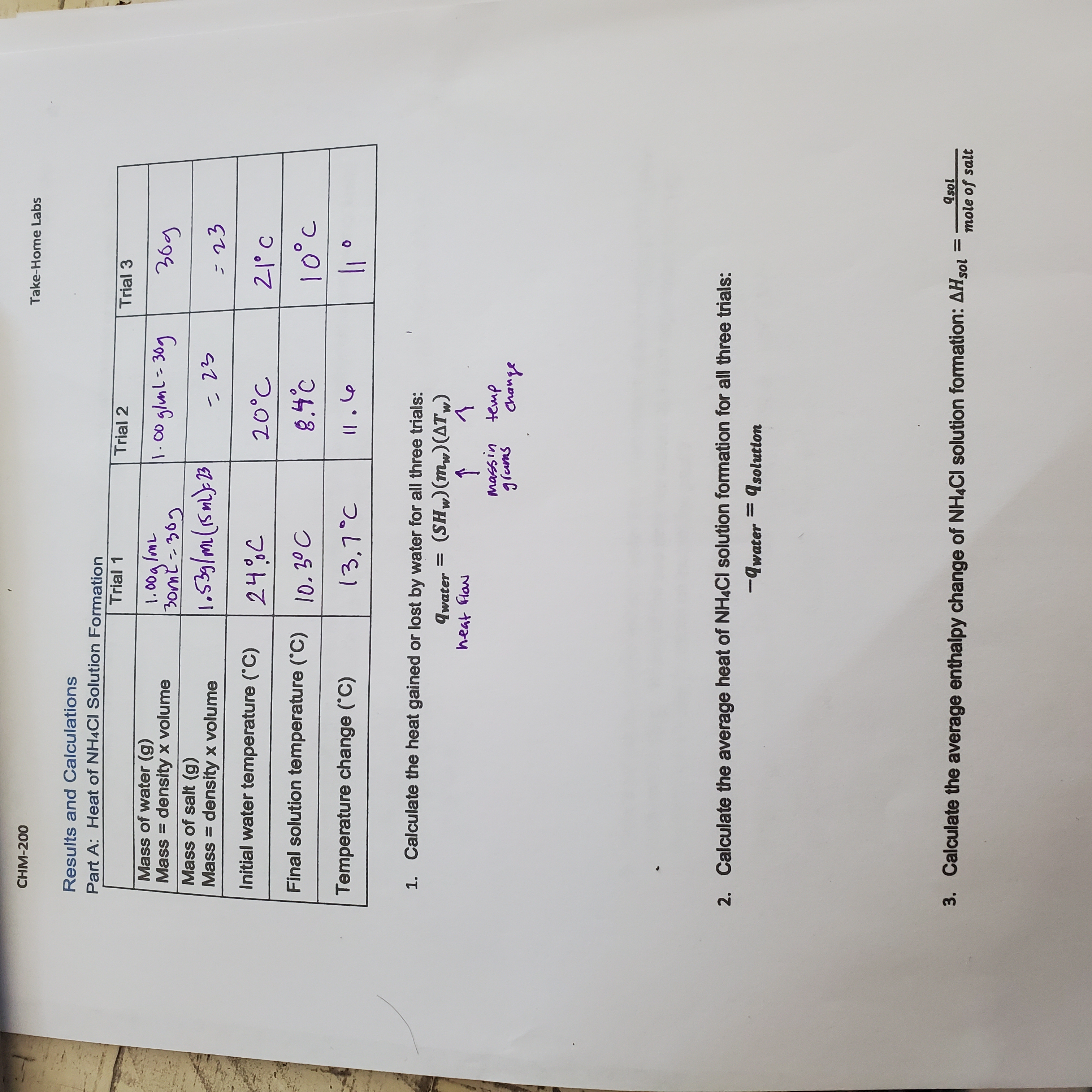
I need help with this experiment. First I need help understanding what this equation is asking: Insturctor wants me to calcultat the heat gaied or lost by water for all three trials
qwater = (SHw) (mw)( ATw)
would like to understand this formula and I will share my worksheet where I am stuck.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- (Figure 1) Enthalpy diagram illustrating Hesa's law. The net reaction is the same as in Figure 5.21 in the textbook, but here we imagine different reactions in our two-step version. As long as we can write a series of equations that add up to the equation we need, and as long as we know a value for AHF for all intermediate reactions, we can calculate the overall AH Figure thalpy Figure Enthalpy CH₂(g) + 2O₂(g) ΔΗ, = -890 kJ AH₁ = -890 kJ AH₂=-607 kJ CO(g) + 2 H₂O(l) + O₂(g) AH. = -283 kl CH₂(g) + 2O₂(8) AH3= -283 kJ CO₂(g) + 2 H₂O(1) Part A Suppose the overall reaction wore modified to produce 2H₂O(g) rather than 2H₂O(1). Would any of the values of AH in the diagram stay the same? O yes O no Submit Provide Feedback AH₂ = -607 kJ CO(g) + 2 H₂O(1) + O₂(8) Request Answer 4 1 of 1 Next > Prarrow_forwardthermometer- A 54.2 g sample of polystyrene is put into a calorimeter (see sketch at right) that contains 100.0 g of water. The polystyrene sample starts off at 92.7 °C and the temperature of the water starts off at 21.0 °C. When the temperature of the water stops insulated container changing it's 32.6 °C. The pressure remains constant at 1 atm. water Calculate the specific heat capacity of polystyrene according to this experiment. Be sure your answer is rounded to the correct number of significant digits. sample- a calorimeter J g.°Carrow_forwardPlease don't provide handwritten solution ....arrow_forward
- Make a scatter plot of temperature vs time (x-axis). Then determine the initial temp of the water inside the calorimeter, the final temperature of the water and the calorimeter and indicate the time of mixing on the plot.arrow_forwardConsider the following thermochemical equations (Note: HA is a weak acid)H+(aq) + OH-(aq) → H2O(l) ΔH1HA(aq) → H+(aq) + A-(aq) ΔH2HA(aq) + OH-(aq) → A-(aq) + H2O(l) ΔH3Choose the equation that shows the correct relationship between their enthalpy changes.arrow_forwardFor the questions of the Experiment of Heat and Temperature: The Law of Dulong and Petit, the following data were obtained for the unknown element. specific heat (S) of unknown element (J/g⚫K) Aw of unknown element (g/mol) 0.339 63.96 b) Calculate the atomic heat (C) in J/mol K for the unknown element. 1) In this case, your answer should be in decimal notation (for example, 0.123, not 1.23*10^-1) with the correct number of significant figures. Also follow the unit specified in each question. Do NOT put its unit in your answer because its unit is shown already in the questions. 2) It means students shouldn't include any letters or text in the "Numeric answers", because otherwise it'll be marked wrong even if the numbers are correct. Type your answer...arrow_forward
- The following are equations of interest in a laboratory similar to your current exercise. Your goal is to find the enthalpy change (deltaH) for reaction 1. Mg(s) + 1/2O2(g) --> MgO(s) deltaH1 = ? Mg(s) + 2H+(aq) --> Mg2+(aq) + H2(g) deltaH2 = +10.1 kJ/mol MgO(s) + 2H+(aq) --> Mg2+(aq) + H2O(l) deltaH3 = -5.0 kJ/mol 1/2O2(g) + H2(g) --> H2O(l) deltaH4 = -286.0 KJ/mol To arrive at equation 1 from the others... match the following equations with what you would need to do in order to add up properly to equation 1. You will also be asked to calculate the deltaH1 in an upcoming question. (hint: write it out on scrap paper, signs change if an equation is reversed.)arrow_forwardCalcium oxide (CaO) is used to remove sulfur dioxide generated by coal-burning power stations: 2CaOs + 2502i) + O21) → 2CaSO4s) What is the heat (in kJ) involved for this removal process if 6.6 g of SO2 (64.07 g/mol) is converted? AH (Cao) = -635.6 kJ/mol AH; (SO2) = -296.1 kJ/mol AH?(CasOa) = -1432.7 kJ/molarrow_forwarda) How would you find the molar enthalpy (in kJ/g) for each fuel and would they compare with each other? b) what are two other factors that can be used to evaluate the fuelsarrow_forward
- Please help me, double and triple check your answers previous tutors got it wrong,arrow_forwardnot sure what i did wrong says incorrect i need helparrow_forward© Macmillan Learning For a particular isomer of Cg H₁8, the combustion reaction produces 5108.7 kJ of heat per mole of Cg H₁8 (g) consumed, under standard conditions. Cg H18 (g) + 25/ 0₂(g) → 8 CO₂(g) + 9 H₂O(g) What is the standard enthalpy of formation of this isomer of Cg H₁g (g)? AH; = esc 1 TOOLS X10" 2 # 3 с $ 4 AHxn=-5108.7 kJ/mol G Search or type URL L 5 MacBook Pro % < 6 & kJ/mol 8arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY