
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
I have gotten this wrong repeatedly
![### Determining the Molality and Molarity of a Sodium Chloride Solution
In this educational exercise, you will determine the molality and molarity of a sodium chloride (NaCl) solution. The solution is prepared by adding 216.0 grams of solid NaCl to 612.0 grams of water. The density of the resultant saline solution is 1.1972 grams per milliliter (g/mL).
**Given Data:**
- Mass of NaCl = 216.0 g
- Mass of water = 612.0 g
- Density of saline solution = 1.1972 g/mL
**Formulas to Use:**
1. **Molality (m)**:
\[
\text{molality (m)} = \frac{\text{moles of solute}}{\text{mass of solvent (kg)}}
\]
2. **Molarity (M)**:
\[
\text{molarity (M)} = \frac{\text{moles of solute}}{\text{volume of solution (L)}}
\]
To find these quantities, follow these steps:
1. **Calculate the Moles of NaCl**:
- Molar mass of NaCl = 58.44 g/mol
- Moles of NaCl = \(\frac{216.0 \text{ g}}{58.44 \text{ g/mol}}\)
2. **Convert the Mass of Water to Kilograms**:
- Mass of water (kg) = \(\frac{612.0 \text{ g}}{1000}\)
3. **Determine the Volume of the Solution**:
- Total mass of solution = mass of NaCl + mass of water
- Volume of solution (mL) = \(\frac{\text{total mass}}{\text{density}}\)
- Convert volume from mL to L
4. **Calculate Molality**:
\[
\text{molality (m)} = \frac{\text{moles of NaCl}}{\text{mass of water (kg)}}
\]
5. **Calculate Molarity**:
\[
\text{molarity (M)} = \frac{\text{moles of NaCl}}{\text{volume of solution (L)}}
\]
**Input Fields:**
- **](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/7eaef044-20a7-420f-b57c-5d0c5f8d0743/5b6585ee-73db-4cff-99d4-25c4da29cd9d/4lms3k8_thumbnail.jpeg)
Transcribed Image Text:### Determining the Molality and Molarity of a Sodium Chloride Solution
In this educational exercise, you will determine the molality and molarity of a sodium chloride (NaCl) solution. The solution is prepared by adding 216.0 grams of solid NaCl to 612.0 grams of water. The density of the resultant saline solution is 1.1972 grams per milliliter (g/mL).
**Given Data:**
- Mass of NaCl = 216.0 g
- Mass of water = 612.0 g
- Density of saline solution = 1.1972 g/mL
**Formulas to Use:**
1. **Molality (m)**:
\[
\text{molality (m)} = \frac{\text{moles of solute}}{\text{mass of solvent (kg)}}
\]
2. **Molarity (M)**:
\[
\text{molarity (M)} = \frac{\text{moles of solute}}{\text{volume of solution (L)}}
\]
To find these quantities, follow these steps:
1. **Calculate the Moles of NaCl**:
- Molar mass of NaCl = 58.44 g/mol
- Moles of NaCl = \(\frac{216.0 \text{ g}}{58.44 \text{ g/mol}}\)
2. **Convert the Mass of Water to Kilograms**:
- Mass of water (kg) = \(\frac{612.0 \text{ g}}{1000}\)
3. **Determine the Volume of the Solution**:
- Total mass of solution = mass of NaCl + mass of water
- Volume of solution (mL) = \(\frac{\text{total mass}}{\text{density}}\)
- Convert volume from mL to L
4. **Calculate Molality**:
\[
\text{molality (m)} = \frac{\text{moles of NaCl}}{\text{mass of water (kg)}}
\]
5. **Calculate Molarity**:
\[
\text{molarity (M)} = \frac{\text{moles of NaCl}}{\text{volume of solution (L)}}
\]
**Input Fields:**
- **
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Molality is equal to the number of moles of solute dissolved in per kg of solvent.
It is denoted by m.
Its SI unit is mol/kg.
Formula used:
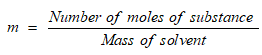
Molarity is equal to the number of moles of solute dissolved in per litre of solution.
It is denoted by M.
Its SI unit is mol/L.
Formula used:
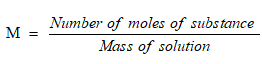
arrow_forward
Step 2
To determine molaltiy of NaCl solution.
Mass of solvent = 612g =0.612kg.
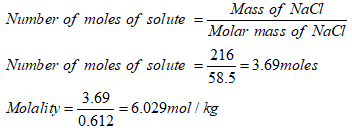
Answer: Molality of the NaCl solution is 6.029mol/kg
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 9 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- In the picture below, determine how many circles with a radius of 0.5" can fit into a 5.0" box. r=0.5") 5.0"arrow_forwardme of Cones Practice Session - PeriodibsTable x 84.studyisland.com/cfw/test/practice-session/a2166?CFID=0487f3b7-46be-4e10-aa17-5c7ee16a463d&CFTOKEN=0&cratelD=a2166&packl. < ☆ Login O Mail -Keidy A Mun.. PowerSchool Learn.. Salir de ASNEF No.. Home-Study Island Desmos | Scientific. F Meet-mythhou-dih able 1. The halogens are the elements of group 17 on the periodic table. Halogens combine easily-with elements from group 1. When a halogen reacts with a metal, what type of compound is formed? A. noble gas OB. potassium Oc. alloy OD salt Reset Submit Session Score: 0% (0/0)arrow_forwardLargest radius K+ Са2+ p3- s2- Cl- Smallest radius Answer Bankarrow_forward
- If 1.5 x 1022 carbon atoms were placed side-by-side in a line, how long would that line be (in feet) if the radius ofa carbon atom is 77 pm? Set up and solve a single step dimensional analysis problem that includes all necessaryfactors.arrow_forward= 8 E 10 An electric current of 463.0 mA flows for 43.0 minutes. Calculate the amount of electric charge transported. Be sure your answer has the correct unit symbol and the correct number of significant digits. Continue O 2020 McGraw-Hill Education. Al I n p3.jpg Calc Fin p1jpg Type here to search 080 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 F8 F9 F10 F11 F12 Pr z' DIO Scr Lk S- %23 & 4. 6. 7 W %24arrow_forward3D16283.34693 16.3 mapbe -> 2. The volume of a cylinder is calculated as V= r?h where nr2 is the area of the circle. If a gallon of kerosene were spilled on a still lake and the height of the slick is, 1.386 nm, what would be the area in m? of the oil slick on the surface of the pond? 1 gal = 3.8 L; 1 nm = 1 x 10-9 m; 0.81 kg = 1 L; 1 kg = 2.206 Ibs; %3D %3D %3D %3D 1000 cm3 = 1.0 liter %3D 1.386nm |1X10-m Inm Aluminum has a density of 2.70 g/cm3. What would the volume be in in3 of a piece of alarrow_forward
- Examine the following IR spectra. Assign the characteristic peaks/vibrations (use v, 8, t, y). Then, tell (in words) all you can about the compound producing these spectra.arrow_forwardThis question was rejected, but this question is part of a practice set and as you can see it is out of zero points. Other practice questions from this set were answered.arrow_forwardNeed help on all of them. It is mu first time taking chemistry so I am stuck on what to do. Thank youarrow_forward
- The solution calls for an exponent. How would I write that?arrow_forwardI know you don't answer graded questions and I am not looking for you to straight up give me the answer to this but how do I even start? like I said before I know that the highest peak is 16amu which is Oxygen but do I just the vertical bar as a ratio? Like the next bar to the left (15amu?) is like 90% intensity? so like 9:10 ratio? There isn't even a 15amu element so please just give me some idea where to start. The place in the book it tells you to go to read has nothing about this stuff, its about finding empirical formulas from mass or percentages.... please help me!arrow_forwardSolve for C:F = 1.8C + 32 %3D PV Solve for P: = R %3D nTarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY