
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
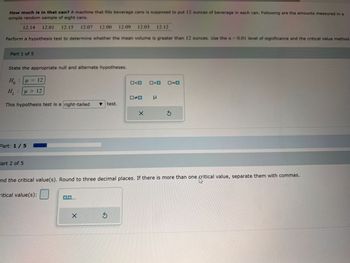
Transcribed Image Text:How much is in that can? A machine that fills beverage cans is supposed to put 12 ounces of beverage in each can. Following are the amounts measured in a
simple random sample of eight cans.
12.14 12.01 12.15 12.07 12.00 12.09 12.03 12.12
Perform a hypothesis test to determine whether the mean volume is greater than 12 ounces. Use the a=0.01 level of significance and the critical value method
Part 1 of 5
State the appropriate null and alternate hypotheses.
H: μ = 12
H₁ μ> 12
:
This hypothesis test is a right-tailed ▼ test.
Part: 1 / 5
Part 2 of 5
0,0,...
X
<D
S
#D
X
>O 0=0
ind the critical value(s). Round to three decimal places. If there is more than one critical value, separate them with commas.
us
ritical value(s):
μ
S
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 7 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Assume that a simple random sample has been selected from a normally distributed population. State the final conclusion.Test the claim that the mean lifetime of car engines of a particular type is greater than 220,000 miles. Sample data are summarized as n = 23, and s = 11,500 miles. Use a significance level of α = 0.01.H0: μ = 220,000 HA: μ > 220,000State your conclusion about H0. Choose the best answer below: A. Reject HA B. Do not reject H0 C. Do not reject HA D. Reject H0 E. Cannot draw a conclusion for information givenarrow_forwardWhere are the deer? Random samples of square-kilometer plots were taken in different ecological locations of a national park. The deer counts per square kilometer were recorded and are shown in the following table. Mountain Brush Sagebrush Grassland Pinon Juniper 30 20 5 25 59 10 25 16 2 24 19 4 Shall we reject or accept the claim that there is no difference in the mean number of deer per square kilometer in these different ecological locations? Use a 5% level of significance. (a) What is the level of significance?State the null and alternate hypotheses. Ho: ?1 = ?2 = ?3; H1: Exactly two means are equal.Ho: ?1 = ?2 = ?3; H1: At least two means are equal. Ho: ?1 = ?2 = ?3; H1: All three means are different.Ho: ?1 = ?2 = ?3; H1: Not all the means are equal. (b) Find SSTOT, SSBET, and SSW and check that SSTOT = SSBET + SSW. (Use 3 decimal places.) SSTOT = SSBET = SSW = Find d.f.BET, d.f.W, MSBET, and MSW. (Use 2 decimal places for MSBET, and MSW.)…arrow_forwardUse the following ANOVA table to answer the question. Source Regression Error Total MS SS 355.22 76.38 431.60 DF 177.61 7 10.91 What is the value of s?? O 177.61 10.91 76.38 335.05arrow_forward
- Listed below are the lead concentrations (in ug/g) measured in different Ayurveda medicines. Ayurveda is a traditional medical system commonly used in India. The lead concentrations listed here are from medicines manufactured in the United States. Assume that a simple random sample has been selected. Use a 0.01 significance level to test the claim that the mean lead concentration for all such medicines is less than 14.0 µg /g. 2.96 6.45 5.99 5.51 20.53 7.45 11.97 20.46 11.52 17.54 D Identify the null and alternative hypotheses. Ho: H1: (Type integers or decimals. Do not round.) Identify the test statistic. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Identify the P-value. (Round to three decimal places as needed.) State the conclusion about the null hypothesis, as well as the final conclusion that addresses the original claim. V the null hypothesis. There sufficient evidence at the 0.01 significance level to V the claim that the mean lead concentration for all Ayurveda medicines…arrow_forwardThe EPA tests cars for city miles per gallon (mpg). For one model, a sample of 16 cars were tested for mpg, the results follow. 28 25.7 25.8 28 28.5 29.8 30.2 30.4 26.9 28.3 29.8 27.2 26.7 27.7 29.5 28 1) What is point estimate of the mean mpg?arrow_forwardThe accompanying data table lists the magnitudes of 50 earthquakes measured on the Richter scale. Test the claim that the population of earthquakes has a mean magnitude greater than 1.00. Use a 0.01 significance level. Identify the null hypothesis, alternative hypothesis, test statistic, P-value, and conclusion for the test. Assume this is a simple random sample Magnitude of Earthquake 0.720 0.740 0.640 0.390 0.700 2.200 1.980 0.640 1.220 0.200 1.640 1.320 2.950 0.900 1.760 1.010 1.260 0.000 0.650 1.460 1.620 1.830 0.990 1.560 0.410 1.280 0.830 1.320 0.540 1.250 0.920 1.000 0.780 0.790 1.440 1.000 2.240 2.500 1.790arrow_forward
- Listed below are the lead concentrations (in µg/g) measured in different Ayurveda medicines. Ayurveda is a traditional medical system commonly used in India. The lead concentrations listed here are from medicines manufactured in the United States. Assume that a simple random sample has been selected. Use a 0.05 significance level to test the claim that the mean lead concentration for all such medicines is less than 14.0 µg/g. 5.98 5.50 20.54 3.03 6.46 Identify the null and alternative hypotheses. Ho: H 14 H₁: μ 14 (Type integers or decimals. Do not round.) Identify the test statistic. = (Round to two decimal places as needed.) 7.45 12.01 20.47 11.48 17.53 D S Vi I. (1,0) Morearrow_forwardUse technology to help you test the claim about the population mean, µ, at the given level of significance, a, using the given sample statistics. Assume the population is normally distributed. Claim: u> 1290; a= 0.03; o = 196.18. Sample statistics: x= 1310.04, n= 200 Identify the null and alternative hypotheses. Choose the correct answer below. O A. Ho: u2 1290 O B. Ho: u>1310.04 Ha: H 1310.04 Hap> 1290 Ο Ε. Ho με 1310.04 F. Ho: u> 1290 Ha: H< 1310.04 Ha us1290arrow_forwardChoose the appropriate statistical test. When computing, be sure to round each answer as indicated. A dentist wonders if depression affects ratings of tooth pain. In the general population, using a scale of 1-10 with higher values indicating more pain, the average pain rating for patients with toothaches is 6.8. A sample of 30 patients that show high levels of depression have an average pain rating of 7.1 (variance 0.8). What should the dentist determine? 1. Calculate the estimated standard error. (round to 3 decimals). [st.error] 2. What is thet-obtained? (round to 3 decimals). 3. What is the t-cv? (exact value) 4. What is your conclusion? Only type "Reject" or Retain"arrow_forward
- Do males have a significantly lower mean on the ACT test than females? n st. dev 12pt ✓ I 50 Paragraph Males Females What is the appropriate statistical test that should be used to test for significance? Calculate the standard error, the test statistic, and the degrees of freedom? What is the critical score? Do males score significantly lower than females? Edit View Insert Format Table mean 25 18.8 21.3 4.5 3.0 ✓ T²✓ E✓ EV SV B I UAV 2 ✓ T²V T田 √x + ✓arrow_forwardEat your cereal: Boxes of cereal are labeled as containing 14 ounces. Following are the weights, in ounces, of a sample of 12 boxes. It is reasonable to assume that the population is approximately normal. 13.03 14.98 13.12 13.13 13.11 13.03 13.16 14.98 13.06 13.05 13.12 13.13 The quality control manager is concerned that the mean weight is actually less than 14 ounces. Based on the confidence interval, is there a reason to be concerned? Explain.arrow_forwardUse technology to help you test the claim about the population mean, u, at the given level of significance, a, using the given sample statistics. Assume the population is normally distributed Claim: 1180; a=0.06: a202.19. Sample statistics x= 1208.77, n=300 Identify the null and alternative hypotheses. Choose the correct answer below. OA H 1208.77 H1208.77 OC. H₂>1208.77 H:Hs 1208.77 OE H:1208.77 H₂>1208.77 Calculate the standardized test statistic The standardized test statistic in (Round to two decimal places as needed) Determine the P-value P= (Round to three decimal places as needed.) Determine the outcome and conclusion of the test Ho. At the 6% significance level, there enough evidence to OB. Hop21180 H₂1180 OD. Hus 1180 H₂>1180 OF H₂1180 Hps 1180 the claimarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman