
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
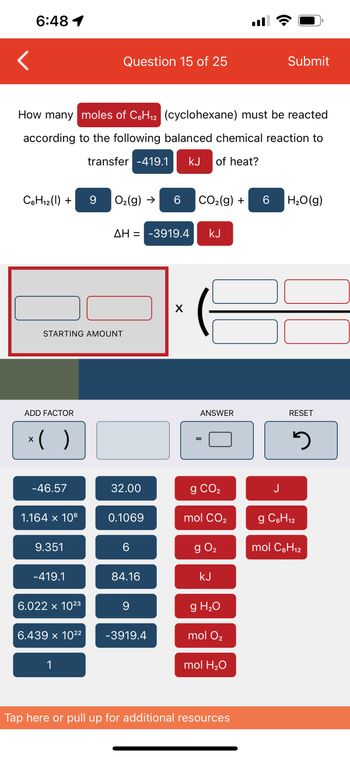
Transcribed Image Text:6:48 1
C6H₁2 (1) +
How many moles of C6H₁2 (cyclohexane) must be reacted
according to the following balanced chemical reaction to
transfer -419.1 kJ of heat?
ADD FACTOR
STARTING AMOUNT
x( )
-46.57
1.164 x 106
9.351
-419.1
6.022 × 10²3
6.439 x 10²²
Question 15 of 25
1
9 O₂(g) → 6 CO₂(g) +
ΔΗ = -3919.4 KJ
32.00
0.1069
6
84.16
9
-3919.4
X
ANSWER
=
g CO₂
mol CO₂
g 0₂
kJ
g H₂O
mol O₂
mol H₂O
Tap here or pull up for additional resources
Submit
6 H₂O(g)
J
RESET
2
g C6H₁2
12
mol C6H₁2
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- At constant volume, the heat of combustion of a particular compound, compound A, is −3520.0 kJ/mol.−3520.0 kJ/mol. When 1.439 g1.439 g of compound A (molar mass =112.71 g/mol)=112.71 g/mol) is burned in a bomb calorimeter, the temperature of the calorimeter (including its contents) rose by 6.391 ∘C.6.391 ∘C. What is the heat capacity (calorimeter constant) of the calorimeter?arrow_forwardYou wish to find the enthalpy for the reaction 6 Gel (s) + 14 NH:1 (s) → 3 Ge:H6 (1) + 7 N2 (g) + 38 HI (g) kJ/mol Given the following equations Equation 1: 2 Ge (s) + 3 H2 (g) → Ge:H6 (1) AH = 137.3 kJ/mol Equation 2: Ge (s) + 4 HI (g) – Gel: (s) + 2 H2(g) AH = -247.8 kJ/mol Equation 3: 2 NH&| (s) → N2 (g) + 2 HI (g) + 3 H2(g) AH = 455.8 kJ/mol 2 4 C What would be the enthalpy change, in kJ/mol, for 6 Gel4 (s) + 12 H2(g) - 6 Ge (s) + 24 HI (g)? 7 8 9. +/- x 100 3. 1,arrow_forwardTitanium reacts with iodine to form titanium(III) iodide, emitting heat, via the following reaction: 2Ti(s)+3I2(g)→2TiI3(s), ΔHrxn=−839kJ Determine the mass of titanium that reacts if 1.53×103 kJ of heat is emitted by the reaction. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Determine the mass of iodine that reacts if 1.53×103 kJ of heat is emitted by the reaction. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.arrow_forward
- The overall reaction in commercial heat packs can be represented as the reaction below. 4 Fe(s) + 3 O2(g) → 2 Fe2O3(s), ΔH = -1652 kJ How much heat is released when 4.24 mol iron is reacted with excess O2? How much heat is released when 1.16 g iron is reacted with excess O2? How much heat is released when 10.80 g Fe and 1.76 g O2 are reacted?arrow_forwardgiven the following reaction (see image) the enthalpy of the reaction of the nitrogen to produce nitic oxide isarrow_forwardDetermine the enthalpy of reaction: 2NH3+2CH4+302=2HCN+6H2Oarrow_forward
- Consider these reactions: Reaction 1: H₂(g) + Cl₂ (g) 2HCl(g) AH-184.6 kJ Reaction 2: 20F2(g) O₂(g) + 2 F₂ (g) AH = -49.4 kJ Reaction 3: N₂(g) + 2O₂(g) · 2NO₂(g) AH = +66.4 kJarrow_forwardWhen methanol, CH, OH, is burned in the presence of oxygen gas, O₂, a large amount of heat energy is released. For this reason, it is often used as a fuel in high performance racing cars. The combustion of methanol has the balanced, thermochemical equation CH₂OH(g) + O₂(g) → CO₂(g) + 2 H₂O(1) AH = -764 kJ How much methanol, in grams, must be burned to produce 983 kJ of heat? mass: garrow_forward1. Determine the mass of CO2 produced by burning enough of methane to produce 1.00×10^2kJ of heat. CH4(g)+2O2(g)→CO2(g)+2H2O(g) ΔH∘rxn=−802.3kJmol−1 Express your answer using three significant figures. 2. Determine the mass of CO2 produced by burning enough of propane to produce 1.00×10^2kJ of heat. C3H8(g)+5O2(g)→3CO2(g)+4H2O(g) ΔH∘rxn=−2217kJmol−1 Express your answer using three significant figures.arrow_forward
- Consider the following equation for the combustion of acetone (C3H6O), the main ingredient in nail polish remover. C3H6O(l)+4O2(g)→3CO2(g)+3H2O(g) ΔHrxn=−1790kJ if a bottle of nail polish remover contains 161 g of acetone, how much heat would be released by its complete combustion?arrow_forwardAccording to the equation below, do the products have stronger or weaker bonds than the reactants? C (s) + 2H (g) → CH4 (g), ΔHrxn = -74.86 kJ/molarrow_forwardAccording to the reaction below, determine the amount heat (in kJ) that can be generated from the combustion of 1.42 grams of C3H8? C3H8(g) + 5O2(g) ⟶⟶ 3CO2(g) + 4H2O(g) Δ?=−2043.2??arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY