
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
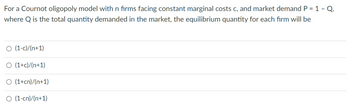
Transcribed Image Text:For a Cournot oligopoly model with n firms facing constant marginal costs c, and market demand P = 1 - Q.
where Q is the total quantity demanded in the market, the equilibrium quantity for each firm will be
O (1-c)/(n+1)
O (1+c)/(n+1)
O (1+cn)/(n+1)
O (1-cn)/(n+1)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
How does it go from qi = (1 - q1 - q2 - ... - qn - c)/2 to q = (1 - cq)/(n + 1) via the substitution in the last step?
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
How does it go from qi = (1 - q1 - q2 - ... - qn - c)/2 to q = (1 - cq)/(n + 1) via the substitution in the last step?
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Q4arrow_forwardProblem 3 Consider the infinitely repeated game with the discount factor & € (0, 1) of the following Cournot duopoly model with inverse demand function P(Q) = a Q if Q≤ a 0 if Q > a where Q = 91 +92 and cost functions Ci(qi) = cqi, i = 1,2. The profit function of firm i is given by Ti (91, 92) = qiP(9₁ +92) - cqi. Consider the following grim-trigger strategy. Produce half the monopoly output in the first period and as long as everybody has produced that amount so far. Otherwise produce the Cournot output. Verify that this is a subgame perfect equilibrium.arrow_forwardYou are given the market demand function Q= 3400 – 1000p, and that each duopoly firm's marginal cost is $0.28 per unit, which implies the cost function: C(4:) = 0.28qi, assuming no fixed costs for i = 1, 2. The Cournot equilibrium quantities are q, and 92 (enter your responses as whole numbers).arrow_forward
- Consider a duopoly market with 2 firms. Aggregate demand in this market is given by Q = 500 – P, where P is the price on the market. Q is total market output, i.e., Q = QA + QB, where QA is the output by Firm A and QB is the output by Firm B. For both firms, marginal cost is given by MCi = 20, i=A,B. Assume the firms compete a la Cournot. What are the equilibrium quantities? What is the total quantity supplied on this market? What is the equilibrium price in this market?arrow_forwardConsider a Cournot oligopoly with two firms, where the demand curves are given by P, = 100-Q,-2Q2 P2= 100-2Q,-Q2 and that costs are given by TC(Q,) = Q'1. MC, = 2Q1, TC(Q2) = Q²2, and MC2 = 2Q2. Also, marginal revenues can be written as MR, = 100-2Q,-2Q2. MR2= 100- 2Q, - 2Q2. Solve for each firm's profit. Profit for firm 1= 600, Profit for firm 2= 300 Profit for firm 1= 300, Profit for firm 2= 600 Profit for firm 1= 555.55, Profit for firm 2= 555.55 O Profit for firm 1= 0, Profit for firm 2= 0arrow_forwardQUESTION 13 Consider a market where two firms (1 and 2) produce differentiated goods and compete in prices. The demand for firm 1 is given by D₁(P₁, P2) = 140 - 2p1 + P2 and demand for firm 2's product is D2 (P1, P2) 140 - 2p2 + P1 Both firms have a constant marginal cost of 20. What is the Nash equilibrium price of firm 1? (Only give a full number; if necessary, round to the lower integer; no dollar sign.)arrow_forward
- The firms in a duopoly produce differentiated products. The inverse demand for Firm 1 is The inverse demand for Firm 2 is and P₁ = 52-9₁-0.592. Each firm has a marginal cost of m= $1 per unit. Solve for the Nash-Cournot equilibrium quantities. The Cournot equilibrium quantities are (Enter your responses rounded to two decimal places.) P₂ = 100-92-0.5q1₁. 91 = units 92 units. =arrow_forwardSuppose the iceberg lettuce industry is a Cournot duopoly with two firms: Xtra Leafy (a) and Yummy Farms (y). Xtra Leafy produces q units of output and Yummy Farms produces qy units of output. Aggregate market output is Q = x + y. The (inverse) market demand schedule is: p = 176 - 2Q Both firms have identical cost structures: MC = MC₁ = ATC₂ = ATC₁ = $12 Find Xtra Leafy's Cournot reaction function of the form: 9x = a + bay Where "a" is the reaction function's intercept and "b" is its slope. Note: Please review the formatting instructions above. If any value is negative, be sure to include its negative sign. a. a= b. b = Hint: One of your answers will be negative. Think about why.arrow_forward(4) Firm l's cost function is C1(q1) = q1 and firm 2's cost function is C2(q2) = 2q2. Consider a duopoly selling in a market with inverse demand function p = 12 q. (a) Assume firms choose output simultaneously (Cournot model). Compute the equilibrium quantities and the market price in a Nash equilibrium. (b) Now assume that firm 1 is a leader and chooses its output q1 first. Then, firm 2 chooses its output q2 after observing q1 (Stackelberg model). Find a subgame-perfect Nash equilibrium of this game. Carefully specify the strategies for firm 1 and firm 2. What quantities are produced in equilibrium and what is the market price in equilibrium?arrow_forward
- A homogeneous products duopoly faces a market demand function given by Q = 102P, where Q = Q₁ + Q2. Both Q1 firms have a constant marginal cost MC = 2. 1. Suppose the two firms set their quantities simultaneously by guessing the other firm's quantity choice. Derive the equation of each firm's reaction curve and then graph these curves. 2. What is the Cournot equilibrium quantity and price in this market for each firm? 3. What would the equilibrium price in this market be if it were perfectly competitive? 4. What is the Bertrand equilibrium price in this market?arrow_forward8arrow_forwardConsider a Duopoly model, in which two firms decide a quantity sequentially. For the convenience, let's say Firm 1 is a dominant firm and Firm 2 is a follower. The market demand is given by P=110 - 5Q, where Q is the total output (i.e., Q=Q1+Q2). Each firm has an identical cost function, TCi=7Qi, i=1, 2. Each firm maximizes its profit by choosing the quantity. In this Stackelberg equilibrium, Firm 1 will sell how many units.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education