
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
How do I mathematically express this reaction in terms of Qc
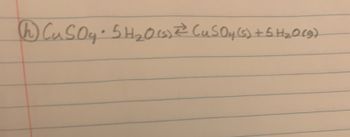
Transcribed Image Text:CuSO4.5H₂0 (1) ²² (u₂SO4(s) + 5 H₂O(g)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Determine the boiling point of CS2, in °C, from the following data: AH, (kJ mol-¹) S° (J mol-¹ K-1) CS₂(g) 115.3 237.8 CS2(1) O-11 811 321 87 43 87.9 151.0 Barrow_forwardGiven that H₂(g) + F₂ (g) →→→ 2 HF(g) 2 H₂(g) + O₂(g) → 2 H₂O(1) calculate the value of AHin for AHixn AHixn 2F₂(g) + 2 H₂O(1) → 4 HF(g) + O₂(g) = = -546.6 kJ AHixn = = -571.6 kJ kJarrow_forwardI am having trouble finding the Kp values here. The free energy of the reaction should be = 2*51.3-2*86.6=-70.6 kJ/mol exponent for Kp should be: (-70.6 kJ/mol * 1000 J/kJ)/(-8.134 J/(mol*K) *298.15K) = 29.1116 so Kp=e29.1116=4.395x1012 but this evidently not correct. Please help?arrow_forward
- Calculate AS° for the reaction 2NO(g) + O2 (9)–→2NO2(9) Express your answer to one decimal place and include the appropriate units.arrow_forwardWhat is the work associated with the decomposition of liquid peroxide forming gaseous oxygen and liquid water at 281.65 K?arrow_forward17. For which of the following highly exothermic processes would you expect AH" and AG* to be about the same? (a) 2 Al(s) + 3/2 02(g) - Al;0:(s) (c) 2 Na(s) + 2 H20(1) → 2 N2OH(aq) + H2(g) (d) 2 NO(g) - N;O(g) (e) 2 Al(s) + Fe2O;(s) - 2 Fe(s) + Al;Oa(s) (b) 2 Ha(g) + Ozl8) - 2 H;0(g)arrow_forward
- 21. Given the following two equations CH5OH(1) + 3 O2(8) 2 СO2(g) + 3 Н20(1) AH = -1370 kJ С-Н(8) + 3 О2(s) → 2 CO2(g) + 2 H2O(1) AH = -1410 kJ Calculate AH for the reaction C2H4(8) + H2O(1) CH5OH(I) ΔΗ- a. -2780 kJ b. 2780 kJ с. 40 kJ d. 40 kJarrow_forward40 kJ Reactants Na Activation Energy H CI 30 kJ Products Na CI 10 kJ Reaction Progress Na and HCl are colliding as shown below with an energy of 5 kJ. Na CI H Potential Energy [kJ]arrow_forwardWhich of the following processes yields a AS = - ? O2 NO(g) + O2(g) ---> 2 NO2(g) NaCIO3(s)---> Na (aq) + CIO3(aq) COCI2(g) -- CO(g) + Cl2(g) CH3OH(1) ---> CO(g) + 2H2(g) None HII>arrow_forward
- Use the following equilibria2CH4(g) C2H6(g) + H2(g) Kc1 = 9.5 × 10-13CH4(g) + H2O(g) CH3OH(g) + H2(g) Kc2 = 2.8 × 10-21to calculate the value of Kc' for the following reaction:2CH3OH(g) + H2(g) C2H6(g) + 2H2O(g)arrow_forward3. For the following reactions, ldentify the unknown, the ?, and circle the change for each of the energy systems. Changes in the Strong Energy Interaction are determined by the net amount of bounds broken or formed and changes in the Electric Energy are determined by the separation of like charges. i. 6429Cu → 6428NI + ? + V a. The unknown "?" is b. PEelectric: increases, decreases, no change c. PEstrong: increases, decreases, no change d. Energy: Exothermic e. Mass: increases, decreases, no change ii. 189F + ? → 1830 + v a. The unknown "?" is b. PEelectric: increases, decreases, no change c. PEstrong: increases, decreases, no change d. Energy: Exothermic e. Mass: increases, decreases, no changearrow_forwardFrom a molecular viewpoint, where does the energy emitted inan exothermic chemical reaction come from? Why does thereaction mixture undergo an increase in temperature eventhough energy is emitted?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY