
Biochemistry
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781319114671
Author: Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher: W. H. Freeman
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
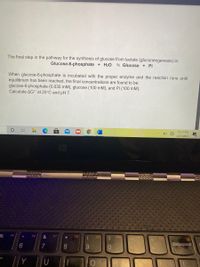
Transcribed Image Text:The final step in the pathway for the synthesis of glucose from lactate (gluconeogenesis) is:
Glucose-6-phosphate + H20
5 Glucose + Pi
When glucose-6-phosphate is incubated with the proper enzyme and the reaction runs until
equilibrium has been reached, the final concentrations are found to be:
glucose-6-phosphate (0.035 mM), glucose (100 mM), and Pi (100 mM).
Calculate AG" at 25°C and pH 7.
10:21 PM
4/21/2021
F5
F6
F7
F8
F10
F9
7
8.
Backspace
ー の
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
how did you get 0.03x10^-4? Also, what is the final answer?
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
how did you get 0.03x10^-4? Also, what is the final answer?
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biochemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The glycolytic enzyme aldolase catalyzes the following cleavage reaction: Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate ↔ glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate + dihydroxyacetone phosphate Here is information on the concentrations of these compounds in hepatocytes (liver cells). Reactant Concentration (M) Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate 1.4 x 10-5 glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate 3 x 10-6 dihydroxyacetone phosphate 1.6 x 10-5 The standard transformed free energy change (ΔG'°) of the reaction is +23.8 kJ/mol. At body temperature (37oC), is the reaction exergonic or endergonic in the hepatocyte? What is the value of the actual free energy change (ΔG) in the cell?arrow_forward5arrow_forwardat what substrate concentration is v= 5.0 mM s^-1 for the enzyme catalyzed hydrolysis of trehalose?arrow_forward
- The M and H subunits of lactate dehydrogenase have very similar sizes and shapes but differ in amino acidcomposition. If the only difference between the two were that theH subunit had a glutamic acid in a position where the M subunithad a serine, how would the five isozymes of LDH separate on electrophoresis using a gel at pH 8.6?arrow_forward. The optimal conditions for salivary lysozyme (hydrolyzing glycoproteins of bacterial wall) are 37 C - temperature and pH is 5.2. Explain the decrease in this enzyme activity if the temperature will rise up to 60 °C and pH will be changed to 8.0. To answer the question: a) draw the graph of the velocity dependency on temperature and pH; b) calculate the relative enzyme activity if 10 mg of lysozyme catalyzes the formation of 5 uM of the product per 2 minutes. Concidor NH3: 5.arrow_forward(b) You are investigating the effects of several agents on the activity of alcohol dehydrogenase. The enzyme activity data are shown in the table below. Construct a [substrate] vs. activity plot and a double-reciprocal plot for this enzyme. Be sure to label all axes. Determine the Vmax and KM for AD from the graphs in each type of plot. AD activity (nM/min) AD activity + agent A (nM/min) AD activity + agent B (nM/min) [Alcohol] (nM) 0.1 14 2 0.5 50 7 8. 1.0 65 10 30 2.0 72 12 45 4.0 80 14 62 8.0 85 15 75 32.0 90 16 90arrow_forward
- 1. Hydrolysis of 1 M glucose 6-phosphate catalyzed by glucose 6-phosphatase is 99% complete at equilibrium (i.e., 1% of the substrate remains). Which of the following statements is most nearly correct? (R= 8.315 J/mol-K; T = 298 K) A AG" is-11 kl/mol. B) AG" is +5 kJ/mol. C) AG" is 0 kJ/mol. DAG" is +11 kJ/mol. E) AG" cannot be determined from the information given. Explain your choice in one line: -2.16x298 (2) - 11386.15 -> 11.4 КТ 5 The high state conculto alle My negative and st" positive (either for D) then onditions, onearrow_forwardA solution of [U 14C] glucose-1-phosphate (specific activity = 16,000 cpm/mmole) was incubated with glycogen and glycogen phosphorylase, an enzyme which adds glucose units on to glycogen. Radioactivity was incorporated into the glycogen primer at a rate = 2550 cpm/min. The rate of the enzymatic reaction in units of mmole glucose incorporated per minute is: (a) 0.016 mmol/min (b) 0.57 mmol/min (c) 0.16 mmol/min (d) 5.7 mmol/minarrow_forwardCalculcate Kcat for PNP substrate for both enzyme concentrations. enzyme volume: 20 ul Bovine Intensince Alkaline phosphatase molecular weight: 140,000 Bovine intenstine Alkaline phosphatase activity: 300 units/ml and 14 units/mg extinction coefficient PNP: 18.5 abs (mM-1 cm-1) Vmax: 0.332 moles/sec a) enzyme 1 concentration: undiluted b) enzyme 2 concentration: 1:1 dilutionarrow_forward
- 8L.3.4arrow_forwardPyruvate carboxylase catalyzes the first step of gluconeogenesis. ATP + HCO3─ + pyruvate → oxaloacetate + ADP + Pi ∆G0’ = ─2.1 kJ mol-1 a) Calculate ΔG for this reaction under the following physiological conditions: 370C, pH 7 [pyruvate] = [HCO3─] = 4.0 mM [oxaloacetate]= 2.0 mM [ATP] = 3.5 mM [Pi] = 5.0 mM [ADP] = 1.8 mMarrow_forwardWe want to measure the activity of alanine aminotransferase (ALAT) present in a serum. The reaction catalyzed by the enzyme is: Reaction 1: I- *H₂N- glutamate H - C-COO CH₂ CH₂ COO 0.1 M phosphate buffer pH 7.4 : 550 μL 1.2 M alanine: 100 μL CH3 pyruvate CH3 C time (min) A340 CIO O COO The enzyme reaction is alized in the following conditions: In a 1 cm-cuvette are added: COO™ pyruvate lactate dehydrogenase* (LDH, 300 µμg.mL-¹): 50 μL 1.5 mM NADH : 200 μL 0.04 M a-ketoglutarate: 500 µL serum containing ALAT: 600 μµL ALAT NADH + H+ 0 0.915 a-cétoglutarate COO LDH * Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) reduces pyruvate into lactate, with the concomitant oxydation of NADH. This allows to indirectly measure the amount of product formed. с=0 CH₂ 1 0.741 Reaction 2: NAD+ CH₂ COO™ H-C CH3 OH COO™ lactate alanine H + *H3N-C The reaction is performed at 25 °C and the absorbance at 340 nm is monitored every minute, for 5 min. The absorbance values are given in the table below: Data: ENADH at 340 nm =…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781319114671
Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781464126116
Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781118918401
Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305961135
Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9780134015187
Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. Peterson
Publisher:PEARSON