
Horizontal sequence :RIVL
Vertical sequence:FMK
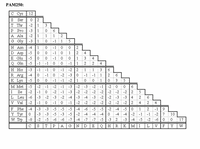
Scoring rules: g/o = -3, g/e = -1, match or mismatch - from PAM250 substitution matrix below.
- NW algorithm.
1. Complete the scoring matrix.
Scoring matrix with PAM250 scores:
| R | I | V | L | |
| F | ||||
| M | ||||
| K |
2. Set up, initialize and complete the NW matrix.
3. Retrace, align and score alignment(s).
Use the arrows and circles for the matrix and path(s).
| R | I | V | L | ||
| F | |||||
| M | |||||
| K |
Align and score all optimal alignments here.
PLZ the arrows and circles for the matrix and path(s) AND SHOW ALL possible Alignment
Here the following points are kept into consideration
1. The opening gap (g/o) is -3 so the first cell is written to be -3.
2. The extending gap (g/e) is -1, so the consecutive cells are increased by -1.
3. The highest from the gaps and the match and mismatch are chosen and then written. It is followed by a arrow from each in order to get the sequencing direction.
4. The scoring value is calculated by using the values from the matrix.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

- I have been stuck for hours on the final 3 genetic problems at the end of this lab. I really need help. I’ve answered the entire blood typing and genetics section but I’m stuck with this. There are 3 questions. The pheno / Geno chart needs to be applied. I have so many variations on my answer but I can’t sit and type them all in to this box. Please help me.arrow_forwardExplain this statement "Major considerations in dosage form design with example" ? Please briefly explain at your own easy words.arrow_forward1arrow_forward
- i found this past paper online and am using it for revision but i cannot find the mark scheme anywhere online. B2 Examples of intra-subject scatter plots between nystagmus intensity and BCVA with best-fit lines are shown in figure 3C for examples of individuals with grades 1 to 4 foveal hypoplasia. Slopes for the best-fit lines for each participant in which the r value were greater than 0.25 are shown in figure 3D. A positive slope predicts that reducing nystagmus improves BCVA. ii. What statistical parameters are generated by this approach and what do they mean?arrow_forwardHELPFUL INFORMATION: When doing automated sequencing, on the other hand, all 4 dideoxynucleotides are added to the same sequencing reaction, and run together in a single capillary gel. 1b What's the difference why can an automated sequencing reaction be done with all 4 dideoxynucleotides mixed together and run together, but not a conventional sequencing reaction?arrow_forwardBriefly explain the major considerations in dosage form design with example? Please answer at your own easy words.arrow_forward
- Ć Chrome File Edit View History Bookmarks Profiles Tab Window Help C Content X Biol 1406 X Content X Begin: Tes X A Tutorial for X acconline.austincc.edu/ultra/courses/_891351_1/cl/outline A Unit 3 Ove X A Unit 3 Ove X 33% mutation: Content X Wed 2:23 PM Q 4 E GTranscript X + ☆ ☐ B Choose ALL of the following that are found in/used in eukaryotic gene expression? Hint: 3 statements are true. mRNA is not modified before translation Requires TATA box for transcription initiation O Transcription terminates at polyadenylation sequence Transcription terminates at terminator sequence Transcription initiation complex Show Allarrow_forwardBriefly Explain what are the Major considerations in dosage form design with example? Please briefly explain at your own easy words.arrow_forwardIs the inhibitor competitive uncompetitive or non competitive? Why?arrow_forward
- 2: Align DNA sequences using dot matrix Horizontal sequence: AGGCTCCC; vertical sequence: GCGCTCCG. Complete the dot matrix. Trace the features. Write the brief description of each feature below the matrix. For the dots, copy/paste this dot: • For noise reduction, use window size 2 x 2, mismatch limit 0, dot position 1, 1. Dot matrix after noise reduction: 3. Use the same sequences. For noise reduction, use window size 3 x 3, mismatch limit 1, dot position 3, 3. Dot matrix after noise reduction:arrow_forwardThe following sequence is palindromic. 5’ ATCGAT Select one: True Falsearrow_forwardAnswer each of the following correctly. Designer Genes Work (This is all about Applications of Recombinant DNA) 1. How does DNA Replicate? 2. What is Genetically Modified Organism (GMO)? 3. Illustrate your own Designer genes based on the following: 1. Identify a special trait. 2. Identify a source organism. 3. Identify a target orgsnism 4. Identify the modified/added trait. Example: Hot Tomato > Chili > Tomato > Spicy Tomato (Look to the picture I provided for this)arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





