
Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781305079373
Author: William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
What is the skeletal structure of the product of the following organic reaction?
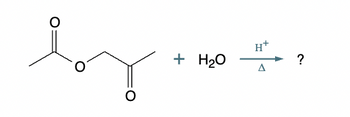
Transcribed Image Text:+ H₂O
H+
Δ
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- When one mole of ethylene gas, C2H4, reacts with fluorine gas, hydrogen fluoride and carbon tetrafluoride gases are formed and 2496.7 kJ of heat are given off. What is Hf for CF4(g)?arrow_forward1/2 O2(g) + H2(g) → H2O(l) ΔHrxn = ?arrow_forwardWrite the equation for the standard enthalpy of formation (ΔHf°) for solid magnesium nitrate.arrow_forward
- Part 1.) 4NH3 (g) +502 (g) - -- > 4 NO (g) 6H2O (g)Write the formation reactions for the compounds shown and their enthalpy of formation values. NO is already provided. rxn 1: -- 1/2 N2 (g) + 1/2 O2 (g) > NO ( g) delta H fNO = ?, rxn 2: N2 (g) + H2 (g) - - > NH3 (g) delta HfNH 3 = ?, rxn 3: H2(g) + O2 (g) - > H 20 (g) delta H fH2O = ? In the delta sheet given I found deltaHf NO +91.3 kJ/mol, deltaHfNH3 = 45.9 kJ/mol, deltaHfH2O -241.8 kJ/mol. Part 2.) Using these three formation reactions (rxn) determine the enthalpy of the rxn. deltaHrxn using Hess's law.arrow_forwardCombustion reactions involve reacting a substance with oxygen. When compounds containing carbon and hydrogen are combusted, carbon dioxide and water are the products. Using the enthalpies of combustion for C₂ H₂ (-1300. kJ/mol), C2H6 (-1560. kJ/mol), and H₂ (-286 kJ/mol), calculate AH for the reaction ΔΗ = C₂H₂(g) + 2H₂(g) → C₂H6 (9) kJarrow_forwardWhat is the enthalpy change when 1.00 mol of carbon dioxide (CO2) is formed? C12H22O11(s) + 12 O2(g) → 12 CO2(g) + 11 H2O(l) ΔH = -5644 kJarrow_forward
- In a coffee-cup calorimeter, 110.0 mL of 1.2 M NaOH and 110.0 mL of 1.2 M HCl are mixed. Both solutions were originally at 22.5°C. After the reaction, the final temperature is 30.5°C. Assuming that all the solutions have a density of 1.0 g/cm³ and a specific heat capacity of 4.18 J/°C.g, calculate the enthalpy change for the neutralization of HCl by NaOH. Assume that no heat is lost to the surroundings or to the calorimeter. AH = 0.182 kJ/molarrow_forwardGiven the following data 2 CIF (g) + O₂(g) → Cl₂ O(g) + F₂O(g) 2 CIF3 (9) +202 (g) → Cl₂ O(g) + 3F₂O(g) 2F2 (g) + O₂(g) → 2F₂O(g) calculate A H for the reaction AH= CIF (g) + F2 (g) → CIF3 (9) Submit Answer kJ Try Another Version ΔΗ = 167.4 kJ Δ Η = 341.4 Κ Δ Η = -43,4 kJ item attempt remainingarrow_forwardd The standard enthalpy change for the following reaction is -602 kJ at 298 K. AH° = -602 kJ Mg(s) + 1/2O₂(g) → MgO(s) ΔΗ — What is the standard enthalpy change for the reaction at 298 K? 2 MgO(s) →→→2 Mg(s) + O₂(g) kj Submit Answer Retry Entire Group 9 more group attempts remainingarrow_forward
- 2CH3OH(g)→2CH4(g)+O2(g),ΔH=+252.8 kJ For a given sample of CH3OH, the enthalpy change during the reaction is 82.9 kJ . What mass of methane gas is produced?arrow_forwardEnthalpy changes for the following reactions can be determined experimentally: N₂ (g) + 3 H₂(g) → 2 NH3(g) ΔΗ° -91.8 kJ/mol-rxn 4 NH3(g) + 5 O2 (g) → 4 NO(g) + 6 H₂O(g) Δ, A, H = -906.2 kJ/mol-rxn H₂(g) + 1/2 O₂(g) → H₂O(g) A, H° = -241.8 kJ/mol-rxn = Use these values to determine the enthalpy change for the formation of NO(g) from the elements (an enthalpy change that cannot be measured directly because the reaction is reactant-favored). 1/2 N₂(g) + 1/2O2(g) → NO(g) kJ/mol-rxn Enthalpy changearrow_forwardWhat is the enthalpy change if 6.00 mol of oxygen (O2) are formed? C12H22O11(s) + 12 O2(g) → 12 CO2(g) + 11 H2O(l) ΔH = -5644 kJarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133949640
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399074
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning