
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
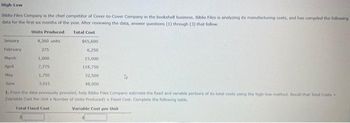
Transcribed Image Text:High-Low
Biblio Files Company is the chief competitor of Cover-to-Cover Company in the bookshelf business. Biblio Files is analyzing its manufacturing costs, and has compiled the following
data for the first six months of the year. After reviewing the data, answer questions (1) through (3) that follow.
Units Produced
4,360 units
275
1,000
7,775
1,750
3,015
Total Cost
January
February
March
April
May
June
1. From the data previously provided, help Biblio Files Company estimate the fixed and variable portions of its total costs using the high-low method. Recall that Tutal Costs -
(Variable Cost Per Unit x Number of Units Produced) Fixed Cost, Complete the following table.
Total Fixed Cost
Variable Cost per Unit
$65,600
6,250
15,000
118,750
32,500
48,000
4
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1: Introducing High Low Method
VARIABLE COST
Variable Cost is a cost that varies with the level of output.
Variable costs include costs of goods sold (COGS), raw materials and inputs to production, packaging, wages, etc.
FIXED COST
Fixed costs are costs that constant at any level of activity.
fixed costs are rent and lease costs, salaries, utility bills, insurance, loan repayments, Depreciation, Advertisement etc
HIGH LOW METHOD
Under High Low Method Variable Cost Per Unit is Computed :—
= (Total cost at highest level - Total cost at lowest level) ÷ (Highest level - Lowest level)
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- tps://ezto.mheducation.com/ext/map/index.h Saved Required information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Scavenger Company, a manufacturer of recycling bins, began operations on January 1 of the current year. During this time the company produced 60,000 units and sold 55,000 units at a sales price of $15 per unit. Cost information for this year is shown in the following table: Production costs $ 2.50 per unit Direct materials Direct labor $ 3.00 per unit $ Variable overhead Fixed overhead 0.75 per unit $240,000 in total Non-production costs Variable selling and administrative Fixed selling and administrative $ 10,000 in total $50,000 in total Given the Scavenger Company data, what is net income using absorption costing? Multiple Choice < Prev 5 of 7 #arrow_forwardPLEASE TO PERFORM IN EXCEL AND SHOW FORMULAS Comercial El Suspiro, S.A., purchases 2'100,000 units per year of a component. The cost of each order is $25.00. The annual unit maintenance cost is 27% of its cost of $2.00. On a 360-day basis, calculate the reorder point, knowing that it takes 10.5 days for the supplier to put in the LAB company the goods, and the company sorts and stores them in 1.5 days, calculate the reorder point.arrow_forwardharshalarrow_forward
- Ponderosa, Inc., produces wiring harness assemblies used in the production of semi-trailer trucks. The wiring harness assemblies are sold to various truck manufacturers around the world. Projected sales in units for the coming five months are given below. January 10,000 February 10,500 March 13,900 April 16,000 May 18,500 The following data pertain to production policies and manufacturing specifications followed by Ponderosa: Finished goods inventory on January 1 is 900 units. The desired ending inventory for each month is 20 percent of the next month’s sales. The data on materials used are as follows: Direct Material Per-Unit Usage Unit Cost Part #K298 2 $4 Part #C30 3 7 Inventory policy dictates that sufficient materials be on hand at the beginning of the month to satisfy 30 percent of the next month’s production needs. This is exactly the amount of material on hand on January 1. The direct labor used per unit of…arrow_forwardHigh Country, Incorporated, produces and sells many recreational products. The company has just opened a new plant to produce a folding camp cot that will be marketed throughout the United States. The following cost and revenue data relate to May, the first month of the plant's operation: Beginning inventory 0 Units produced 43, 000 Units sold 38,000 Selling price per unit $ 80 Selling and administrative expenses: Variable per unit $ 3 Fixed (per month) $ 564,000 Manufacturing costs: Direct materials cost per unit $ 15 Direct labor cost per unit $ 7 Variable manufacturing overhead cost per unit $ 3 Fixed manufacturing overhead cost (per month) $ 817,000 Management is anxious to assess the profitability of the new camp cot during the month of May. Required: 1. Assume that the company uses absorption costing. a. Calculate the unit product cost. b. Prepare an income statement for May. 2. Assume that the company uses variable costing. a. Calculate the unit product cost. b. Prepare a…arrow_forwardPlease avoid solutions in an image format thanksarrow_forward
- 1arrow_forwardPonderosa, Inc., produces wiring harness assemblies used in the production of semi-trailer trucks. The wiring harness assemblies are sold to various truck manufacturers around the world. Projected sales in units for the coming five months are given below. January 10,000 February 10,500 March 13,900 April 16,000 May 18,500 The following data pertain to production policies and manufacturing specifications followed by Ponderosa: Finished goods inventory on January 1 is 900 units. The desired ending inventory for each month is 20 percent of the next month’s sales. The data on materials used are as follows: Direct Material Per-Unit Usage Unit Cost Part #K298 2 $4 Part #C30 3 7 Inventory policy dictates that sufficient materials be on hand at the beginning of the month to satisfy 30 percent of the next month’s production needs. This is exactly the amount of material on hand on January 1. The direct labor used per unit of…arrow_forwardHello Company makes three different products. Due to the constraints of their manufacturing equipment and warehouse facility, the company is only able to produce, store, and sell a total of 50,000 units each month. The production of Products A and B varies each month; however, Product C is a special order for one customer who purchases the same number of units every month. Pete Davila, the CEO, has |provided the following data from last month for each product. Income Statement Product A Product B Product C Мax Cарacity 5,000 8.00 $ 2.00 $ Units 43,000 10.00 $ 3.00 $ 20,000 $ 2,000 50,000 Price per unit Variable expense per unit $ $ $ 50.00 15.00 $ 20.00 Total Fixed Costs 40,000 $ 10,000 Product Sales $ 430,000 $ 40,000 $ 100,000 $ 570,000 (169,000) 401,000 (70,000) 331,000 Variable Costs (129,000) (10,000) 30,000 $ (30,000) 70,000 $ Contribution Margin $ 301,000 $ Fixed Costs (20,000) 281,000 (40,000) (10,000) (10,000) 60,000 $ Operating income (loss) Required Using the Data Table…arrow_forward
- Required information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Iguana, Inc., manufactures bamboo picture frames that sell for $20 each. Each frame requires 4 linear feet of bamboo, which costs $1.50 per foot. Each frame takes approximately 30 minutes to build, and the labor rate averages $12 per hour. Iguana has the following inventory policies: • Ending finished goods inventory should be 40 percent of next month's sales. • Ending direct materials inventory should be 30 percent of next month's production. Expected unit sales (frames) for the upcoming months follow: March April May June July August 360 420 470 570 545 595 Variable manufacturing overhead is incurred at a rate of $0.20 per unit produced. Annual fixed manufacturing overhead is estimated to be $7,200 ($600 per month) for expected production of 4,000 units for the year. Selling and administrative expenses are estimated at $650 per month plus $0.50 per unit sold. Iguana, Inc., had $10,800 cash on…arrow_forwardHigh Country, Incorporated, produces and sells many recreational products. The company has just opened a new plant to produce a folding camp cot that will be marketed throughout the United States. The following cost and revenue data relate to May, the first month of the plant’s operation: Beginning inventory 0 Units produced 45,000 Units sold 40,000 Selling price per unit $ 79 Selling and administrative expenses: Variable per unit $ 3 Fixed (per month) $ 555,000 Manufacturing costs: Direct materials cost per unit $ 16 Direct labor cost per unit $ 7 Variable manufacturing overhead cost per unit $ 4 Fixed manufacturing overhead cost (per month) $ 720,000 Management is anxious to assess the profitability of the new camp cot during the month of May. Required: 1. Assume that the company uses absorption costing. a. Calculate the unit product cost. b. Prepare an income statement for May. 2. Assume that the company uses variable costing. a. Calculate the…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education