
Concept explainers

Given molecule:
HCN
Hydrogen is an element having 1 valence electrons, Carbon is having 4 valence electrons, and nitrogen is having 5 valence electrons.
Thus, the total valence electrons will be 1+4+5 = 10 valence electrons.
Thus, the Lewis structure of HCN molecule is represented as follows:
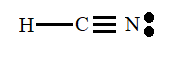
According to the Lewis structure of HCN molecules there are 4 bonding electron pairs and one non-bonding electron pairs.
Therefore, HCN has 4 bonding groups.
Number of lone pairs = 1
As carbon is forming triple bond with nitrogen and single bond with hydrogen thus, the number of electron groups around carbon is 4.
Thus, the molecular geometry and electron geometry at carbon atom will be linear as it has 2 bonding pairs.
Step by stepSolved in 7 steps with 2 images

- ng pH and the Hydronium lon Concentration oncentration of hydronium ions in ithmic scale: -log[H3O+] ] = 10-PH eases. As pH increases, acidity 17 7 7 6.761 2 WUG 9 F2 W S # 3 80 F3 E D $ 4 hallu Rank the following from most to least acidic. Rank from most to least acidic. To rank Items as equivalent, overlap them. ▶View Available Hint(s) F4 R F pH = 14 pH = 5 Most acidic MATE % 5 F5 T G ^ [H3O+] 10² [H3O+] 10-0 MacBook Air 6 ostv SA F6 Y & 7 H F7 U LE O * ► 11 8 Reset Help F8 pH = 3 Least acidic 1 4 9 W 11 K F9 O L F10 P Review F11 L {arrow_forwardWrite the reaction that happens with Nile Blue A and NaOH. Given is the compound, Nile Blue A. Thank youarrow_forward3. Answer the following questions regarding the neutralization of HCl using NaOH: a. If the volume of both HCl and NaOH were doubled, how would this change the value of gran? Explain. b. If the volume of both HCl and NaOH were doubled, how would this change the value of AHran? Explain. c. If only the volume of NaOH was doubled, how would this change the value of qran? Explain. d. If only the volume of NaOH was doubled, how would this change the value of AT? Explain. 8/16/2023arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





