
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
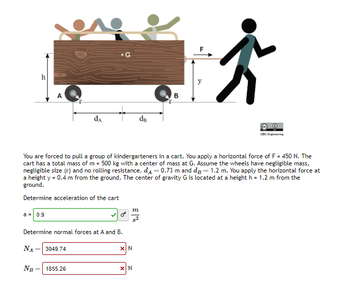
Transcribed Image Text:### Physics Problem: Pulling a Cart of Kindergarteners
**Problem Statement:**
You are forced to pull a group of kindergarteners in a cart. You apply a horizontal force of \( F = 450 \, \text{N} \). The cart has a total mass of \( m = 500 \, \text{kg} \) with a center of mass at \( G \). Assume the wheels have negligible mass, negligible size (\( r \)) and no rolling resistance. The distances are given by \( d_A = 0.73 \, \text{m} \) and \( d_B = 1.2 \, \text{m} \). You apply the horizontal force at a height \( y = 0.4 \, \text{m} \) from the ground. The center of gravity \( G \) is located at a height \( h = 1.2 \, \text{m} \) from the ground.
**Given Data:**
- Horizontal force: \( F = 450 \, \text{N} \)
- Mass of the cart: \( m = 500 \, \text{kg} \)
- Distance from A to center of mass \( G \): \( d_A = 0.73 \, \text{m} \)
- Distance from B to center of mass \( G \): \( d_B = 1.2 \, \text{m} \)
- Height from application of force \( F \) to the ground: \( y = 0.4 \, \text{m} \)
- Height of center of gravity \( G \) from the ground: \( h = 1.2 \, \text{m} \)
**Determine:**
1. **Acceleration of the Cart (a):**
- \( a = 0.9 \, \frac{\text{m}}{\text{s}^2} \)
2. **Normal Forces at A and B ( \( N_A \) and \( N_B \)):**
- \( N_A = 3049.74 \, \text{N} \)
- \( N_B = 1855.26 \, \text{N} \)
**Visual Explanation:**
The diagram shows a cart being pulled by a person. The cart contains kindergarteners and has two wheels denoted as points A and B.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Physics 121 Spring 2021 - Document #11: Homework #04 & Reading Assignment page 4 of 8 Problem 1: Gnome Ride - This from a Previous Exam I. A Gnome of given mass M goes on the Gnome Ride as follows: He stands on a horizontal platform that is connected to a large piston so that the platform is driven vertically with a position as a function of time according to the following equation: y(t) = C cos(wt) Here w is a constant given angular frequency, C is a given constant (with appropriate physical units) and y represents the vertical position, positive upward as indicated. Part (a) - What is the velocity of the Gnome at time t = 0? Explain your work. Present your answer in terms of the given parameters Part (b) – What is the net force on the Gnome at time t = 0? Explain your work. Present your answer in terms of the given parameters Part (c) – What is the Normal Force on the Gnome at time t = 0? Explain your work. Present your answer in terms of the given parameters Some Possibly Useful…arrow_forward2. (Inspired by a walk in Baker Student Center.) An escalator handles a steady load of 30 people per minute taking them from the first to the second floor through a vertical rise of 24 feet. Let us say the average person riding the elevator weighs 160 lb. a. What output power on a motor do you require to drive the unit? Take literally one minute to find an electric motor online that could do this job. You can search “_ hp electric motor" and state the motor name, power, cost, and vendor. Of course, round up your hp, not down to meet your specs. (In practice, this is an area where you can spec the motor in equivalent Watts, if you choose.) b. What is the electric power that is input to the motor considering losses within the escalator system due to friction, vibration, etc.? Your chosen motors surely have a different efficiencies and sources may even present efficiency as a function of power/rpm, so let's all use the value of e= 0.85 for consistency.arrow_forwardIntro to Transport Processes TRUE or FALSE. Please provide a quick explanation thanks! 1. Each molecule of a system has a certain quantity of mass, thermal energy, or momentum associated with it. 2. Momentum transport in a fluid depends bulk movement of molecules and not on individual molecule of the system. 3. At same mass, the momentum of a molecule is greater than the other molecules if it has less velocity?arrow_forward
- Helparrow_forwardGiven: The plane accelerates in its current trajectory with a= 100 m/s^2 Farag Angle theta= 5° W=105 kips F_drag= 80 kips m= 1000 lbs Find: F_thrust, F_lift Please include the KD. Fthrust Futel t Fueight 000 BY NC SA 2013 Michael Swanbomarrow_forwardRecall the discussion on spacecraft from the chapter opener. The following problems consider a rocket launch from Earth’s surface. The force of gravity on the rocket is given by F(d)=−mk/d2, where m is the mass of the rocket, d is the distance of the rocket from the center of Earth, and k is a constant. 172. As the rocket travels away from Earth’s surface, there is a distance D where the rocket sheds some of its mass, since it no longer needs the excess fuel storage. We can write this function as F(d)=⎨(−m↓1 k / d^2) if d < D (−m↓2 k / d^2) if d ≥ D Is there a D value such that this function is continuous, assuming m1≠m2?arrow_forward
- From the image below, identify the values of the position coordinates SA and SB. SA is for block A and B is for pulley B. Datum 2 4m 2m $A Number $B = Number m m B с ▬▬ Datum 1 5m 3m A @ 09 Engineeringarrow_forwardYou are watching a live concert. You can also find the concert streaming live on Spotify. About how far must you stand from the stage in order for the live concert and the live stream to be perfectly in sync? HINT: Assume the radio signal (Spotify) has to travel all the way around the Earth. circumference of the Earth (average): 40,041,000 m Speed of sound: 345 m/s Speed of light: 300,000,000 m/sarrow_forwardI could really use some assistance on part b,c,d,e,farrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY