
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
A uniform plank is 5.00 m long and weighs 100 N. The cord that attaches to the plank 1.00 m from the bottom end holds it from sliding. There is no friction between the floor and beam and the wall and beam. Find the tension in the cord. Hint: Find theta and alpha. Think about where you will put the axis of rotation.
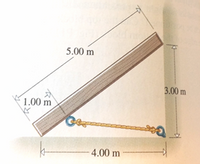
Transcribed Image Text:5.00 m
3.00 m
1.00 m
4.00 m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The cable spool shown at the right has a weight of 50 lbs and has a moment of inertia of .28 slug-ft^2. Assume the spool rolls without slipping when we apply a 50-lb tension in the cable. Find: friction force between the spool and the ground.arrow_forwardAlso find the normal force between the crate and the wedgearrow_forwardA 10-m uniform beam of weight 100 N is supported by two ropes at its ends. If a 400-N person sits at the center of the beam, what is the tension in the right rope?arrow_forward
- Answers typed in are incorrect. Tried them many times and they are not right. Please dont give me the same wrong answers marked with a red X.arrow_forward1.0m 3.0m 0.5m mi m2 PA N, 5. The drawing above shows two objects on a board supported at two locations. The m; = 40 kg (centered over P), m;=20 kg and m3=10 kg. c. Determine the force exerted by N2. (Take torques around P.) d. m2 rolls to the right. Just before the board starts to tip everything is balanced on N2 with no force on N1. Determine how far to the right of N2 m2 could roll without the board tipping. You might find it easier to take torques around a point rather than P.arrow_forwardA beam with a length of 2 m and a mass of 10 kg supports a 50 kg box. The beam is connected to a wall by a hinge at its base and a horizontal wire. The wire is connected to the beam 1.5 m from the hinge and makes an angle θ of 35o to the beam. The goal is to find the tension in the wire and the horizontal and vertical components of the force exerted by the hinge on the board Calculate the tension in the string. write down Newton’s 2nd law for both x and y directions. find the horizontal and vertical components of the force that the hinge exerts on the beam. Suppose the maximum tension that the wire can withstand is 1500 N. What is the maximum load that the hinge can support before the wire breaks?arrow_forward
- A. Draw a different configuration, and make it a diagram similar to Fig. 3. Specifyeach mass and angle you’d be using.B. Determine the tensions T1 and T2 which would be created by each hangingmassC. find the unknown components of T3D.calculate the magnitude and direction of T3arrow_forwardThe 60 kg two-wheeled cart is described in the figure and parameter table below, with G indicating the location of the center of gravity. It is to be pulled so that it goes up the small step. Find the normal force on each wheel, and the magnitude and direction of the force applied at handle. HINT: remember that there are two wheels sharing the load @080 BY NO SA 2021 Cathy Zupke 4₁1 G L₁ L₂ parameter value 0.6 0.5 0.8 0.7 0.2 A L3 LA d L3 units m m m m m B L₂ F For the answers, take to the right and up to be the positive directions. The normal force at each wheel at A in the x direction is Ax= 150 XN The magnitude of the force at B is F Measured from the positive horizontal axis, the angle of F= 45 X° = 212 XNarrow_forwardWrite down equations for static equilibrium. Calculate the moment about C, and leave the answer in terms of the unknow force of magnitude |FB| After that Caclulate |FB|arrow_forward
- Please asaparrow_forwardIf the mass of cylinder is 100 kg, find the tension developed in wires AB and AC and find the support reactions in point O.. 3 m 1.5 m to 1.5 m 3 m B 1 marrow_forwardThe pulley system shown in Figure Q1c lifts a mass,m,of 550 kg.Calculate the force FA necessary to maintain the suspended mass in static equilibrium; and determine the forces at the ceiling anchor points A and B. Assume frictionless and weightless pulleys and use g = 9.81 m/s2.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY