
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
14th Edition
ISBN: 9781337514835
Author: MOYER
Publisher: CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
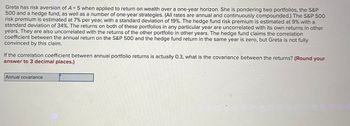
Transcribed Image Text:Greta has risk aversion of A = 5 when applied to return on wealth over a one-year horizon. She is pondering two portfolios, the S&P
500 and a hedge fund, as well as a number of one-year strategies. (All rates are annual and continuously compounded.) The S&P 500
risk premium is estimated at 7% per year, with a standard deviation of 19%. The hedge fund risk premium is estimated at 9% with a
standard deviation of 34%. The returns on both of these portfolios in any particular year are uncorrelated with its own returns in other
years. They are also uncorrelated with the returns of the other portfolio in other years. The hedge fund claims the correlation
coefficient between the annual return on the S&P 500 and the hedge fund return in the same year is zero, but Greta is not fully
convinced by this claim.
If the correlation coefficient between annual portfolio returns is actually 0.3, what is the covariance between the returns? (Round your
answer to 3 decimal places.)
Annual covariance
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, finance and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Greta has risk aversion of A = 3 when applied to return on wealth over a one-year horizon. She is pondering two portfolios, the S&P 500 and a hedge fund, as well as a number of one-year strategies. (All rates are annual and continuously compounded.) The S&P 500 risk premium is estimated at 7% per year, with a standard deviation of 20%. The hedge fund risk premium is estimated at 10% with a standard deviation of 35%. The returns on both of these portfolios in any particular year are uncorrelated with its own returns in other years. They are also uncorrelated with the returns of the other portfolio in other years. The hedge fund claims the correlation coefficient between the annual return on the S&P 500 and the hedge fund return in the same year is zero, but Greta is not fully convinced by this claim. What should be Greta's capital allocation? (Do not round your intermediate calculations. Round your answers to 2 decimal places.) S&P Hedge % % Risk-free asset %arrow_forwardGreta has risk aversion of A = 4 when applied to return on wealth over a one-year horizon. She is pondering two portfolios, the S&P 500 and a hedge fund, as well as a number of one-year strategies. (All rates are annual and continuously compounded.) The S&P 500 risk premium is estimated at 5% per year, with a standard deviation of 17%. The hedge fund risk premium is estimated at 10% with a standard deviation of 32%. The returns on both of these portfolios in any particular year are uncorrelated with its own returns in other years. They are also uncorrelated with the returns of the other portfolio in other years. The hedge fund claims the correlation coefficient between the annual return on the S&P 500 and the hedge fund return in the same year is zero, but Greta is not fully convinced by this claim. If the correlation coefficient between annual portfolio returns is actually 0.3, what is the covariance between the returns?arrow_forwardGreta has risk aversion of A = 3 when applied to return on wealth over a one-year horizon. She is pondering two portfolios, the S&P 500 and a hedge fund, as well as a number of one-year strategies. (All rates are annual and continuously compounded.) The S&P 500 risk premium is estimated at 6% per year, with a standard deviation of 18%. The hedge fund risk premium is estimated at 8% with a standard deviation of 33%. The returns on both of these portfolios in any particular year are uncorrelated with its own returns in other years. They are also uncorrelated with the returns of the other portfolio in other years. The hedge fund claims the correlation coefficient between the annual return on the S&P 500 and the hedge fund return in the same year is zero, but Greta is not fully convinced by this claim. a-1. Assuming the correlation between the annual returns on the two portfolios is 0.3, what would be the optimal asset allocation? (Do not round intermediate calculations. Enter your answers…arrow_forward
- Greta has risk aversion of A = 5 when applied to return on wealth over a one-year horizon. She is pondering two portfolios, the S&P 500 and a hedge fund, as well as a number of one-year strategies. (All rates are annual and continuously compounded.) The S&P 500 risk premium is estimated at 5% per year, with a standard deviation of 20%. The hedge fund risk premium is estimated at 12% with a standard deviation of 35%. The returns on both of these portfolios in any particular year are-uncorrelated with its own returns in other years. They are also uncorrelated with the returns of the other portfolio in other years. The hedge fund claims the correlation coefficient between the annual return on the S&P 500 and the hedge fund return in the same year is zero, but Greta is not fully convinced by this claim. What should be Greta's capital allocation? (Do not round your intermediate calculations. Round your answers to 2 decimal places.) S&P Hedge Risk-free asset % % %arrow_forwardGreta has risk aversion of A= 5 when applied to return on wealth over a one-year horizon. She is pondering two portfolios, the S&P 500 and a hedge fund, as well as a number of 1-year strategies. (All rates are annual and continuously compounded.) The S&P 500 risk premium is estimated at 9% per year, with a standard deviation of 17%. The hedge fund risk premium is estimated at 11% with a standard deviation of 32%. The returns on both of these portfolios in any particular year are uncorrelated with its own returns in other years. They are also uncorrelated with the returns of the other portfolio in other years. The hedge fund claims the correlation coefficient between the annual return on the S&P 500 and the hedge fund return in the same year is zero, but Greta is not fully convinced by this claim. a-1. Assuming the correlation between the annual returns on the two portfolios is indeed zero, what would be the optimal asset allocation? (Do not round intermediate calculations. Enter your…arrow_forwardManshukharrow_forward
- Greta has risk aversion of A = 3 when applied to return on wealth over a one-year horizon. She is pondering two portfolios, the S&P 500 and a hedge fund, as well as a number of 3-year strategies. (All rates are annual and continuously compounded.) The S&P 500 risk premium is estimated at 8% per year, with a standard deviation of 22%. The hedge fund risk premium is estimated at 10% with a standard deviation of 37%. The returns on both of these portfolios in any particular year are uncorrelated with its own returns in other years. They are also uncorrelated with the returns of the other portfolio in other years. The hedge fund claims the correlation coefficient between the annual return on the S&P 500 and the hedge fund return in the same year is zero, but Greta is not fully convinced by this claim. Compute the estimated 1-year risk premiums, standard deviations, and Sharpe ratios for the two portfolios. (Do not round your intermediate calculations. Round "Sharpe ratios" to 4 decimal…arrow_forwardGreta has risk aversion of A = 3 when applied to return on wealth over a one-year horizon. She is pondering two portfolios, the TSX/S&P Composite Index and a hedge fund, as well as a number of one-year strategies. (All rates are annual and continuously compounded.) The TSX/S&P Composite Index risk premium is estimated at 5% per year, with a standard deviation of 20 %. The hedge fund risk premium is estimated at 10% with a standard deviation of 35%. The returns on both of these portfolios in any particular year are uncorrelated with its own returns in other years. They are also uncorrelated with the returns of the other portfolio in other years. The hedge fund claims the correlation coefficient between the annual return on the TSX/S&P Composite Index and the hedge fund return in the same year is zero, but Greta is not fully convinced by this claim. If the correlation coefficient between annual portfolio returns is actually 0.3, what is the covariance between the returns? (Round your…arrow_forwardGreta has risk aversion of A = 3 when applied to return on wealth over a one-year horizon. She is pondering two portfolios, the TSX/S&P Composite Index and a hedge fund, as well as a number of one-year strategies. (All rates are annual and continuously compounded.) The TSX/S&P Composite Index risk premium is estimated at 5% per year, with a standard deviation of 20%. The hedge fund risk premium is estimated at 10% with a standard deviation of 35%. The returns on both of these portfolios in any particular year are uncorrelated with its own returns in other years. They are also uncorrelated with the returns of the other portfolio in other years. The hedge fund claims the correlation coefficient between the annual return on the TSX/S&P Composite Index and the hedge fund return in the same year is zero, but Greta is not fully convinced by this claim. a-1. Assuming the correlation between the annual returns on the two portfolios is indeed zero, what would be the optimal…arrow_forward
- Greta has risk aversion of A = 3 when applied to return on wealth over a 1-year horizon. She is pondering two portfolios, the S&P 500 and a hedge fund, as well as a number of 1-year strategies. (All rates are annual and continuously compounded.) The S&P 500 risk premium is estimated at 9% per year, with a standard deviation of 17%. The hedge fund risk premium is estimated at 11% with a standard deviation of 32%. The returns on both of these portfolios in any particular year are uncorrelated with its own returns in other years. They are also uncorrelated with the returns of the other portfolio in other years. The hedge fund claims the correlation coefficient between the annual return on the S&P 500 and the hedge fund return in the same year is zero, but Greta is not fully convinced by this claim. Required: a-1. Assuming the correlation between the annual returns on the two portfolios is 0.3, what would be the optimal asset allocation? a-2. What is the expected risk premium on the…arrow_forwardNikularrow_forwardGreta has risk aversion of A = 5 when applied to return on wealth over a one-year horizon. She is pondering two portfolios, the TSX/S&P Composite Index and a hedge fund, as well as a number of one-year strategies. (All rates are annual and continuously compounded.) The TSX/S&P Composite Index risk premium is estimated at 10% per year, with a standard deviation of 16%. The hedge fund risk premium is estimated at 8% with a standard deviation of 26%. The returns on both of these portfolios in any particular year are uncorrelated with its own returns in other years. They are also uncorrelated with the returns of the other portfolio in other years. The hedge fund claims the correlation coefficient between the annual return on the TSX/S&P Composite Index and the hedge fund return in the same year is zero, but Greta is not fully convinced by this claim. a-1. Assuming the correlation between the annual returns on the two portfolios is 0.3, what would be the optimal asset allocation? (Do not…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT

EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
Finance
ISBN:9781337514835
Author:MOYER
Publisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT