
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
In an ionic compound, the size of the ions affects the internuclear distance (the distance between the centers of adjacent ions), which affects lattice energy (a measure of the attractive force holding those ions together).
Based on ion sizes, arrange these compounds by their expected lattice energy.
Note that many sources define lattice energies as negative values. Please arrange by magnitude and ignore the sign.
||lattice energy||=absolute value of the lattice energy|lattice energy|=absolute value of the lattice energy
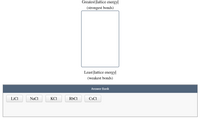
Transcribed Image Text:### Understanding Lattice Energy
In this interactive exercise, you are tasked with arranging compounds based on their lattice energy, which corresponds to the strength of bonds in ionic compounds.
#### Diagram Overview
- **Vertical Arrow Diagram:**
- At the top of the diagram, it states "Greatest |lattice energy| (strongest bonds)".
- At the bottom, it states "Least |lattice energy| (weakest bonds)".
- The objective is to place the given compounds in order from greatest to least lattice energy.
#### Compounds to Arrange
The compounds listed in the answer bank are:
- LiCl (Lithium chloride)
- NaCl (Sodium chloride)
- KCl (Potassium chloride)
- RbCl (Rubidium chloride)
- CsCl (Cesium chloride)
Your task is to place these compounds within the diagram according to the strength of their ionic bonds, which is directly related to their lattice energies. Generally, smaller ions and higher charges result in greater lattice energy.
![In an ionic compound, the size of the ions affects the internuclear distance (the distance between the centers of adjacent ions), which affects lattice energy (a measure of the attractive force holding those ions together).
Based on ion sizes, arrange these compounds by their expected lattice energy.
Note that many sources define lattice energies as negative values. Please arrange by magnitude and ignore the sign.
|lattice energy| = absolute value of the lattice energy
[Diagram: Blank box labeled "Greatest |lattice energy| (strongest bonds)"]](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/b1d14486-aab8-45fa-9185-3d15b7af8b4b/41ac0ad6-30c0-4602-a12e-7e4e5c6c9c9b/85e2lke_thumbnail.png)
Transcribed Image Text:In an ionic compound, the size of the ions affects the internuclear distance (the distance between the centers of adjacent ions), which affects lattice energy (a measure of the attractive force holding those ions together).
Based on ion sizes, arrange these compounds by their expected lattice energy.
Note that many sources define lattice energies as negative values. Please arrange by magnitude and ignore the sign.
|lattice energy| = absolute value of the lattice energy
[Diagram: Blank box labeled "Greatest |lattice energy| (strongest bonds)"]
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The charges and sizes of the ions in an ionic compound affect the strength of the electrostatic interaction between the ions and thus the strength of the lattice energy of the ionic compound. Arrange the compounds according to the magnitudes of their lattice energies based on the relative ion charges and sizes. Highest lattice energy Lowest lattice energy Answer Bank KCI MgO NaF MgF₂arrow_forwardPlease help answer this questionsarrow_forwardPlease don't provide handwritten solutionarrow_forward
- The charges and sizes of the ions in an ionic compound affect the strength of the electrostatic interaction between the ions and thus the strength of the lattice energy of the ionic compound. Arrange the compounds according to the magnitudes of their lattice energies based on the relative ion charges and sizes. (highest to lowest) Mgo,NaF,MgF2, and KCIarrow_forwardPredicting the relative lattice energy of binary ionic compounds In each row, pick the compound with the bigger lattice energy. Note: lattice energy is always greater than zero. Which compound has the bigger lattice energy? BaCh BaS Bel₂ KF O BeBr₂ CsF O 1/5arrow_forwardCalculate the lattice energy of RbH (s) using the following thermodynamic data (all data is in kJ/mol). Note that the data given has been perturbed, so looking up the answer is probably not a good idea. AHsublimation 61 kJ/mol Ionization energy = 383 kJ/mol Rb (s) Rb (g) H - H (g) Bond energy = 416 kJ/mol H (g) Electron affinity = -93 kJ/mol RbH (s) AHOf = -72 kJ/mol kJ/molarrow_forward
- Put the following compounds in order of decreasing expected lattice energy. Na3N, MgCl2, NaCl, Mg3N2arrow_forwardWhich of the following ionic compounds has the largest lattice formation enthalpy (lattice energy); that is, which compound is most favorable to a stable lattice? A) Csl B) Lil C) LiF D) CsF E) MgOarrow_forwardUsing the following data, estimate the overall enthalpy of formation (in kJ/mol) for potassium chloride: K(s) + ½ Cl₂(g) → KCI(s). Process Lattice energy of KCI lonization energy of K Electron affinity of Cl Bond dissociation energy of Cl, Enthalpy of sublimation for K Question 21 of 28 Change in Energy (AHO) -690 kJ/mol 419 kJ/mol -349 kJ/mol 239 kJ/mol 90 kJ/molarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY