
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
A square footing supporting a column applies a uniform pressure of 100 kPa on top of a deep clay deposit. Based on the bulbs of pressure developed below the footing shown in the following figure, which of the following statements are correct (select all that apply)?
A.Immediately after construction, the effective vertical stress developed at Points B and C is the same.
B.Immediately after construction, the excess pore water pressure (∆u) developed at Point B is lower than ∆u developed at Point A.
C.After construction, the excess pore water pressure at Point C dissipates faster than that dissipated at Point B.
D.
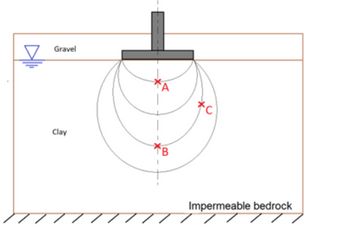
Transcribed Image Text:Gravel
Clay
C
Impermeable bedrock
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 1 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- For most practical problems, how does the effective stress in cohesionless soil calculated/arrow_forwardA rectangular footing with dimensions of 8ft x 12ft is constructed at the surface of the ground and supports a column with a load of 192,000 lbs. The load applied to the footing results in a uniform stress distribution at the base of the footing. What is the change in vertical stress 12 feet below the ground, underneath Point A, at the corner, on the diagram?arrow_forwardShear Stress 5. Please provide proper discussion and illustration. Clear and complete solution please thank you. A clay soil has an undrained shear strength (cohesion, Cu) of 800 psf. How could the strength of this soil be increased?arrow_forward
- Q 1) A concrete foundation rests on the surface of a soil mass. Determine the vertical stress increase at point A. 4 m 1 m 1.5 m PLAN 1.5 m Fondation Load 3000 KN 2 m SECTION A Soilarrow_forwardindicate the final answer in 3 decimal places.arrow_forwardQ1: Choose the correct answer 1. Lateral earth pressure (passive or active) is a dependent of A. the angle of internal friction the cohesion of soil b. c. the unite weight of the soil d. all of the above 2. Tension cracks occur a. b. within the active zone of a cohesive soil within the active zone of a cohesionless soil within the passive zone of a cohesive soil c. 3. d. within the passive zone of a cohesionless soil resist the applied earth loads only by their weight. a. Gravity walls b. Cantilever walls c. MSE walls d. Counterfort walls 4. The main disadvantage of using cohesive soils to backfill retaining structures a. decrease passive pressure b. cause tension cracks c. groundwater accumulation behind the wall d. increase active pressure 5. of clay is required when designing shallow foundations. a. Elastic settlement b. Settlement during construction c. Final consolidation settlement d. Secondary settlementarrow_forward
- For the following statements: P: The lateral stress in the soil while being tested in an oedometer is always at-rest. Q: For a perfectly rigid strip footing at deeper depths in a sand deposit, the vertical normal contact stress at the footing edge is greater than that at its centre. R: The corrections for overburden pressure and dilatancy are not applied to measured SPT-N values in case of clay deposits. The correct combination of the statements is P Q R (a) True True False (b) False (c) False False True False False (d) True True Truearrow_forwardSolve itarrow_forwardCalculate: a.) The unit weight of soil at a depth of 3m below the ground surface. b.) The normal stress of soil at a depth of 3m below the ground surface. c.) The potential shear strength of the soil at a depth of 3m below the ground surface when the water table is at a depth of 3.5m and the soil is cohesionless. d.) The modified value of the shear strength if the water table reaches the ground surface. e.) The modified value of the shear strength if the water table reaches the ground surface but the soil has a cohesion of 12 kPa.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning