
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Transcribed Image Text:0: (34 || 4 10:14
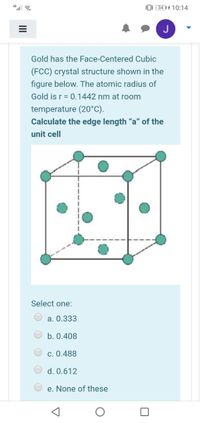
Gold has the Face-Centered Cubic
(FCC) crystal structure shown in the
figure below. The atomic radius of
Gold is r = 0.1442 nm at room
temperature (20°C).
Calculate the edge length “a" of the
unit cell
Select one:
a. 0.333
b. 0.408
c. 0.488
d. 0.612
e. None of these
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Answer the following question with drawing the atom configurations of the plane or direction.What is the planar density for the (110) plane in a FCC structure?arrow_forward1. Many substances crystallize in a cubic structure. The unit cell for such crystals is a cube having an edge with a length equal to do. -Face diagonal a. What is the length, in terms of do, of the face diagonal, which runs diagonally across one face of the cube? (Hint: Use the Pythagorean theorem.) b. What is the length, again in terms of do. of the cube diagonal, which runs from one corner, through the center of the cube, to the opposite corner? (Hint: Make a right triangle having a face diagonal and an edge of the cube as its sides, with the hypotenuse equal to the cube diagonal, then use the Pythagorean theorem again.) 2. In an FCC structure, the centers of the atoms are found on the corners of the cubic unit cell and at the center of each face. The unit cell has an edge whose length is the distance from the center of one corner atom to the center of another corner atom on the same edge. The atoms on the diagonal of any face are touching. One of the faces of the unit cell is shown…arrow_forward3. Under what conditions, will the body centered tetragonal lattice become (a) a bcc structure? (b) an fcc structure?arrow_forward
- Copper has a cubic structure with a = 0.36151 nm. The atomic radius is 0.1278 nm. The densityis 8.93 g/cm3, and the atomic mass is 63.55 g/mol. Determine(a) the number of atoms in each unit cell; and(b) the packing factor in the unit cell.arrow_forwardSketch the planar cross section for the following planes in the FCC structure (label the edge lengths in terms of a and R) and calculate the planar densities for the three planes (do so in terms of both atoms/nm2 AND the dimensionless quantity): a. (001)b. (011)c. (111)arrow_forward1. It is often convenient to represent a fcc lattice as simple cubic, with a cubic primitive cell of side a and a four-point basis. (a) Show that the structural factor is then either 4 or 0 at all points of the simple cubic reciprocal lattice. (b) Show that when points with zero structural factor are removed, the remaining points of the reciprocal lattice makes up a bcc cubic lattice with conventional cell of side 4л/a. Why is this expected?arrow_forward
- Need help on thisarrow_forwardCopper is a typical face-centered-cubic metal. In its pure state, it has extremely high electrical conductivity. Oxygen in copper causes a major reduction of conductivity. To investigate this issue further, I want to you to tell me whether oxygen atoms substitute for copper atoms, or if they enter interstitial sites.arrow_forwardAnswer only 1arrow_forward
- Consider an fcc lattice with cube side length 1.2 Å. What are the planar densities of the (110) and (100) planes respectively (in units of 1020 atoms/m?): (This question has only one correct answer) O a. (100) = 2.08, (110) = 0.98 O b. (100) = 1.39, (110) = 0.98 O c. (100) = 1.39, (110) = 1.20 O d. (100) = 0.98, (110) = 1.39arrow_forward4. Figure out the indexes of the following lattice planes. (The arrows are the basic vectors of the lattice.) (a) (b) (c)arrow_forwardConsider a unit cell with lattice dimensions a, b, and c in the x-, y and z directions. Which of the following sets of Miller indices can represent a crystallographic plane with intercepts of b and (c/4) along the y- and z-axes respectively? (more than one answer is possible for this question. marks will only be awarded for the question if all the correct options are selected (i.e. 'all or nothing' marking scheme). a. b. C. d. (214) (421) (114) e. (412)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY