
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
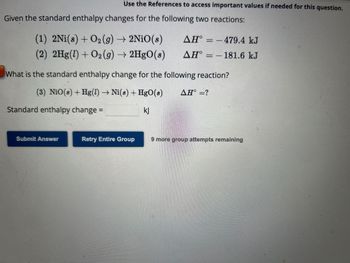
Transcribed Image Text:Given the standard enthalpy changes for the following two reactions:
Use the References to access important values if needed for this question.
(1) 2Ni(s) + O₂(g) → 2NiO(s)
(2) 2Hg(1) + O2(g) → 2HgO(s)
Standard enthalpy change =
Submit Answer
What is the standard enthalpy change for the following reaction?
(3) NiO(s) + Hg(1)→ Ni(s) + HgO(8) AH° =?
kj
AH°
AH°
Retry Entire Group
-479.4 kJ
-181.6 kJ
9 more group attempts remaining
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- When methanol, CH, OH, is burned in the presence of oxygen gas, O₂, a large amount of heat energy is released. For this reason, it is often used as a fuel in high performance racing cars. The combustion of methanol has the balanced, thermochemical equation CH₂OH(g) + O₂(g) → CO₂(g) + 2 H₂O(1) AH = -764 kJ How much methanol, in grams, must be burned to produce 983 kJ of heat? mass: garrow_forwardImportant values if needed for this question. A scientist measures the standard enthalpy change for the following reaction to be -901.8 kJ : Fe203(s) + 2 AI(s): Al203(s) + 2 Fe(s) Based on this value and the standard enthalpies of formation for the other substances, the standard enthalpy of formation of Al203(s) is kJ/mol.arrow_forward2. A small immersion heater was used to heat water in an insulated cup. The heater was placed in 100.0 g of distilled water initially at 21.0°C, and turned on for 60.0 seconds while the water was stirred with a thermometer. The final temperature of the water was measured to be 37.5°C. Assume the specific heat capacity of the water is 4.18 J/g °C. (a) Calculate the total heat energy in joules absorbed by the water and the average power in watts (1 watt = 1 joule/s) delivered by the heater. The heater was used to deliver 3000 joules of energy to 100.0 g of methanol (CH,OH(E)) in the same manner. The temperature of the methanol increased by 11.8 Celsius degrees. (b) Calculate the specific heat capacity of the methanol liquid. (c) (i) Calculate the mass of water (H,O, Co= 4.181 Jgl °C-) at 20.0°C that would be requireć %3D to cool a 30.0-g block of copper (Cu, co0.385 J gl °C-l) from 50.0°C to 25.0°C in an insulated cup. %3D (ii) Which liquid, water or methanol, would be more effective as…arrow_forward
- A 350.0 g iron pot is heated on a stove for a period of time until it is hot. The stove is turned off and 516 g of cold water (10.0 °C) is added to the pot. When thermal equilibrium is reached, the temperature of the water is 28.4 ° C. What was the initial temperature of the iron pot, assuming heat was exchanged between these two objects and none was lost to the surroundings? (The specific heat capacity of iron is 0.450 J/g °C. The specific heat capacity of water is 4.184 J/g °C) Give only the numerical answer in the box and not units. Give 4 sig figs in your answer. Show the calculations for the problem by writing it on a paper, upload the image file/pdf file in the question for file upload.arrow_forwardWhat is the enthalpy change when 2.00 mol of oxygen (O2) react? C12H22O11(s) + 12 O2(g) → 12 CO2(g) + 11 H2O(l) ΔH = -5644 kJarrow_forwardConsider these reactions, where M represents a generic metal. 2 M(s) + 6HCl(aq) →→→ 2 MC1₂(aq) + 3H₂(g) HCI(g) HCl(aq) H₂(g) + Cl₂(g) → 2 HCI(g) MCI, (s) → MCI, (aq) Use the given information to determine the enthalpy of the reaction 2 M(s) + 3 Cl₂(g) → 2 MC1₂ (s) 1. 2. 3. 4. ΔΗ = AH₁ = -694.0 kJ AH₂ = -74.8 kJ AH3= -1845.0 kJ AH4 = -375.0 kJ kJarrow_forward
- 2. Slaked lime (Ca(OH)2(s)) is produced when lime (calcium oxide, Cao (s)) reacts with liquid water. 65.2 kJ of heat is released for each mol of Ca(OH)2 that is produced. (a) Write a thermochemical equation for the reaction. (b) What is the enthalpy change when 523.3 kg of lime reacts with excess water?arrow_forwardConsider these reactions, where M represents a generic metal. 2 M(s) + 6HCl(aq) 2 MC13(aq) + 3H₂(g) HCl(g) HCl(aq) H₂(g) + Cl₂ (g) - MC13 (s) →→→ MC1₂ (aq) Use the given information to determine the enthalpy of the reaction 2 M(s) + 3 Cl₂(g) → 2 MC1₂ (s) 1. 2. 3. 4. AH = 2 HCl(g) AH₁ = -553.0 kJ ΔΗ, = −74.8 kJ AH3 = -1845.0 kJ AH4 = -337.0 kJ kJarrow_forwardA gas expands and does work on the surroundings equal to 4.92 Latm. At the same time, it releases 98.6 J of heat to the surroundings. What is the change in energy in J of the gas? (write the solution without decimals)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY