
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Given the reaction mechanism and the quantities listed below, find the limiting reagent and the theoretical yield of the given reaction:
0.5 grams 2-naphthol (weight: 114.17 g/mol)
0.2 grams KOH (weight: 56.11 g/mol)
30 mL iodoethane (weight: 155.97 g/mol, density: 1.94 g/mL)
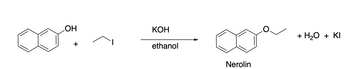
Transcribed Image Text:The image depicts a chemical reaction process.
**Reactants:**
1. **1-Naphthol (C₁₀H₇OH):** Illustrated on the left with a naphthalene ring structure and a hydroxyl group (OH) attached.
2. **Ethyl iodide (C₂H₅I):** Shown as a simple ethyl group (C₂H₅) attached to an iodine (I) atom.
**Reagents and Conditions:**
- **Potassium hydroxide (KOH):** Used in this reaction as a base.
- **Ethanol:** Serves as the solvent.
**Reaction Process:**
- The 1-naphthol reacts with ethyl iodide in the presence of potassium hydroxide in ethanol.
**Products:**
1. **Nerolin (Ethyl naphthyl ether):** The main product, shown on the right. It's characterized by an ethyl group (C₂H₅) connected to the oxygen that links to the naphthalene ring.
2. **Water (H₂O):** A byproduct formed during the reaction.
3. **Potassium iodide (KI):** Another byproduct formed in the process.
This reaction showcases the formation of an ether from an alcohol and an alkyl halide, commonly referred to as the Williamson ether synthesis.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider the reaction below and answer the question below the reaction. A student performed a synthesis of ethyl 4-aminobenzoate (C) as shown in the reaction above. The student added 1.20 g of 4-aminobenzoic acid and 12.0 mL of ethanol together in the presence of sulfuric acid. The reaction mixture was heated to reflux for a period of 45 minutes. H₂N OH 4-aminobenzoic acid MM 137.14 g/m ol A 77.7% 56.1 % 128 % 72.2 % + CH3CH₂OH ethanol MM 46.10 g/mol H+ H₂N OCH₂CH3 + H₂O ethyl 4-aminobenzoate MM 165.19 g/mol C B Let's assume the theoretical yield of the reaction is 7.22 g and the student produced 5.61 g of ethyl 4-aminobenzoate. What is the percent yield of the reaction?arrow_forward11:11 AM Sun Oct 22 < Question 16 of 34 13% % Submit If 10.0 moles of O₂ are reacted with excess NO in the reaction below, and only 5.0 mol of NO₂ were collected, then what is the percent yield for the reaction? 2 NO (g) + O₂(g) → 2 NO2 (g)arrow_forwardab and Mastering 7 > 2 F2 W S You may want to reference (Pages 245-246) Section 7.8 while completing this problem. # Calcium cyanamide reacts with water to form calcium carbonate and ammonia via the following reaction: CaCN₂ (s) + 3H₂O(1)→ CaCO3(s) + 2NH3(g) 3 E O 80 F3 D h My Questions | bartleby $ 4 2008 F4 R F % 5 F5 T openvellum.ecollege.com G ^ 6 How many grams of water are needed to react with 71.0 g CaCN₂? 195] ΑΣΦ 5 → mass H₂O = F6 Submit Part B Y How many grams of NH3 are produced from 5.22 g CaCN₂? 4 IVE ΑΣΦ mass NH3 = Submit Part C Request Answer mass CaCO3 = MacBook Air Request Answer H E Course Home How many grams of CaCO3 form if 156 g water react? Copyright © 2022 Pearson Education Inc. All rights reserved. | Terms of Use | Privacy Policy | Permissions | Contact Us | & 7 44 F7 U IVE ΑΣΦ 5 Pearson *00 8 J DII F8 I 1 C → C ( 9 K Ċ DD F9 0 ? -0 ? ? L g g P 7.8: Mass Calculations for Chemical Reactions Review | Constants I Periodic Table g F10 P : (1 F11 { + 11 Ⓒ+ [ 11 1 F12…arrow_forward
- please number the solutions like they are presented in the problem ( asap plz with explanation)arrow_forwardFor the following chemical reaction, CO (g) + H₂O (g) → CO2 (g) + H₂ (g) Kc = 0.0257 What is the Kc expression for this reaction? O a. Kc = [CO]/[CO2][H2] O b. Kc = [CO2][H2]/[CO] O c. Kc = [CO2][H2]/[CO][H2O] O d. Kc = [CO][H2O]/[CO2][H2]arrow_forwardConsider the reaction below and answer the question below the reaction. A student performed a synthesis of ethyl 4-aminobenzoate (C) as shown in the reaction above. The student added 1.20 g of 4-aminobenzoic acid and 12.0 mL of ethanol together in the presence of sulfuric acid. The reaction mixture was heated to reflux for a period of 45 minutes. H₂N OH 4-aminobenzoic acid MM 137.14 g/m ol 2.44 g 1.21 g 3.24 g 1.45 g + CH3CH₂OH ethanol MM 46.10 g/mol B H+ H₂N OCH₂CH3 + H₂O ethyl 4-aminobenzoate MM 165.19 g/mol A с What is the theoretical yield for the reaction?arrow_forward
- Aktiv Chemistry - с tab : lock esc control + X https://app.101edu.co 1 12 22 Sucrose (C₁₂H₂₂O₁) is combusted in air according to the following reaction: C₁₂H₂₂O₁(s) + O₂(g) → CO₂(g) + H₂O(1) 12 22 11 How many moles of carbon dioxide would be produced by the complete combustion of 21.7 grams of sucrose in the presence of excess oxygen? A Aktiv Chemistry L option Z 2 W S X command #3 20 F3 X E D $ 4 C 888 F4 R F 17 dº % 5 V F5 T G Question 11 of 17 MacBook Airarrow_forwardPlease helparrow_forwardGiven the following exothermic combustion reaction, calculate An and list two or more stresses that would improve product yield. CH12O6(5) + 602) 6 CO) + 6 H,Oarrow_forwardIn the laboratory, hydrogen gas of good purity can most easily be obtained by the reaction of a strong acid, like sulfuric acid, on a reactive metal, such as zinc: Zn(s)+H,SO,(aq) ZnSO,(aq)+H, (g) Suppose an engineer decides to study the rate of this reaction. He prepares four reaction vessels by adding 160.9 g of solid zinc and 83. mL of 5.0 M sulfuric acid solution to each, and then filling the remainder of the vessel with distilled water. The volume and temperature of each vessel is shown in the table below. Arrange the reaction vessels in decreasing order of initial rate of reaction. In other words, select a "1" next to the vessel in which the engineer can reasonably expect the initial rate of reaction to be highest, a "2" next to the vessel in which the initial rate of reaction would be next highest, and so on. alo Ar initial rate of vessel volume temperature reaction A 1.0 L 14.0 °C В 4.0 L 14.0 °C ? 2.0 L 14.0 °C 8.0 L 14.0 °C v ? 1 (highest) 2 4 (lowest) >arrow_forwardWhich statement about the reaction below is correct? 2A(g) + 5B(g) → 8C(g) + 6D(g) Group of answer choices A is consumed at a slower rate than B is consumed. C is produced at a slower rate than A is consumed. C is produced at a slower rate than D is produced. D is produced at a faster rate than A is consumed.arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosarrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY