
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
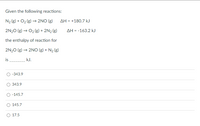
Transcribed Image Text:Given the following reactions:
N2 (g) + O2 (g) → 2NO (g)
AH = +180.7 kJ
2N20 (g) → O2 (g) + 2N2 (g)
AH = -163.2 kJ
the enthalpy of reaction for
2N20 (g) → 2NOo (g) + N2 (g)
is
kJ.
-343.9
343.9
-145.7
145.7
O 17.5
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 26arrow_forwardThe thermochemical equation for the combustion of propane is shown below: C3H8(g) + 5 O2(g) → 3 CO2(g) + 4 H2O(liq) ΔrH° = -2220 kJ/mol-rxn What is the enthalpy change for the following reaction? 9 CO2(g) + 12 H2O(liq) → 3 C3H8(g) + 15 O2(g) a) -6600 kJ b) -8880 kJ c) +6660 kJ d) +8880 kJ e) +4440 kJarrow_forwardCalculate the standard enthalpy of formation of carbon disulfide (liquid) from its elements, given C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g) S(s) + O2(g) → SO2(g) AH = -296.8 kJ CS2(1) + 3 O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2 SO2(g) AH = -393.5 kJ AH = -1076.8 kJ 89.7 kJ -386.5 kJ -1767.1 kJ 386.5 kJ None of the abovearrow_forward
- Given the standard enthalpy changes for the following two reactions: (1) 2Hg(1) + O2(g) 2HgO(s) AH° = -181.6 kJ (2) Hg(1) + Cl2(g)→HgCl2(s) AH° = -224.3 kJ what is the standard enthalpy change for the reaction: (3) 2HgCl2(s) +02(g) )→2HgO(s) + 2Cl½(g) AH° = ? kJ Try Another Version 3 item attempts remaining Submit Answerarrow_forwardCalculate the enthalpy change for the reaction: 3NO2(g) + H2O(ℓ) ---> 2HNO3(aq) + NO(g) Given: 2NO(g) + O2(g) ---> 2NO2(g) ΔH = −116 kJ 2N2(g) + 5O2(g) + 2H2O(ℓ) ---> 4HNO3(aq) ΔH = −256 kJ N2(g) + O2(g) ---> 2NO(g) ΔH = +183 kJarrow_forwardThe following reaction is endothermic. 2 ZnO(s) 2 Zn(s) + O2(g) AH(1) = 697 kJ Calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction of the elements to form one mole of ZnO(s). Zn(s) + 1/2 O2(g) ZnO(s) AH(2) = kJarrow_forward
- Use the following information to determine the enthalpy for the reaction shown below. CS2() + 302(g) → CO2(g) + 2SO2(g) C(graphite) + O2(g) CO2(g) S(s) + O2(g) SO2(g) C(graphite) + 2S(s) CS2() AH = -393.5 kJ AH =-296.8 kJ AH = 87.9 kJ Select one: a. -899.2 kJ b. +1075.0 kJ C. -778.2 kJ d. -1075.0 kJ e. +778.2 kJarrow_forwardFind the enthalpy of reaction A,H° for the following reaction : 2 S(s) + 3 02(g) → 2 SO3(g) 1. S(s) + O2(g) → SO2(g) A;H°;(SO2,g) = -297KJ/mol 2. 2 SO3(g) → 2 SO2(g) + O2(g) AH°2 = 198kJ/mol %D a. -792 kJ/mol b. +792 kJ/mol c. +396 kJ/mol d. -396 kJ/molarrow_forwardA scientist measures the standard enthalpy change for the following reaction to be 6.7 kJ : CO(g) + H,O(1)–CO;{g) + H2(g) Based on this value and the standard enthalpies of formation for the other substances, the standard enthalpy of formation of CO(g) is kJ/mol.arrow_forward
- Find the standard enthalpy of formation of ethyne gas, C2H2(g), given the following data: C2H2(g) + 5/2 O2(g) → 2 CO2(g) + H20(1) C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g) AH°; = -393.5 kJ H2(g) + 1/2 O2(g) – H20(1) AH°F = -285.8 kJ AH° = -1300 kJ 227 kJ -17 kJ 52 kJ 73 kJ O 177 kJarrow_forwardEnthalpy aarrow_forwardthe thermochemical equation: 2H2S(g) + 3O2(g) --> 2H2O(I) + 2SO2(g) has a standard enthalpy of reaction equal to -1,124.06 KiloJoules. What is the enthalpy change for the combustion of 0.5 gram of H2S?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY