
Principles of Economics 2e
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9781947172364
Author: Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher: OpenStax
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
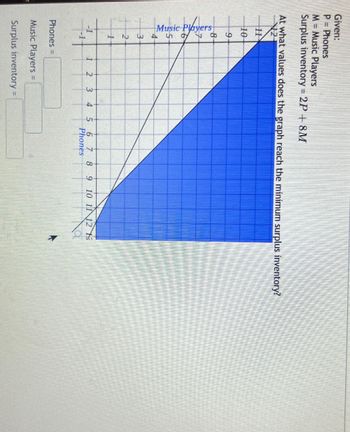
Transcribed Image Text:Given:
P = Phones
M = Music Players
Surplus inventory = 2P + 8M
At what values does the graph reach the minimum surplus inventory?
12
11
10
9-
Music
54
Players
8
3
2
1
-1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9 10 11 12 13
-1
Phones
Phones =
Music Players =
Surplus inventory =
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Continuing from Exercise 7.1, the films factory sits on land owned by the firm that it could rent for 30,000 per year. What was the films economic profit last year?arrow_forwardCan you think of an industry (or product) with near infinite elasticity of supply in the short term? That is, what is an industry that could increase Qs almost without limit in response to an increase in the price?arrow_forwardHighFlyer Airlines wants to build new airplanes with greatly increased cabin space. This will allow HighFlyer Airlines to give passengers more comfort and sell more tickets at a higher price. However, redesigning the cabin means rethinking many other elements of the airplane as well, like engine and luggage placement, and the most efficient shape of the plane for moving through the air. HighFlyer Airlines has developed a list of possible methods to increase cabin space, along with estimates of how these approaches would affect the planes operating costs and ticket sales. Based on these estimates, Table 13.5 shows the value of R, how much should the firm invest in R on top of the private return; that is, an R private return to HighFlyer Airlines would have a 9 social return. How much investment is socially optimal at the 6 interest rate?arrow_forward
- What would the gasoline price elasticity of supply mean to UPS or FedEx?arrow_forward(Determinants of Price Elasticity) Would the price elasticity of demand for electricity be more elastic over a shorter or a longer period of time?arrow_forwardThink back to a purchase that you made recently. How would you describe your thinking before you made that purchase?arrow_forward
- Name some farm that can cause a shift in the supply curve in markets for goods and services.arrow_forwardFour films called Elm, Maple, Oak, and (Shelly, produce wooden chairs. However, they also produce a great deal of garbage (a mixture of glue, varnish, sandpaper, and wood scraps). The first row of Table 12.6 shows the total amount of garbage (in tons) that each film currently produces. The other rows of the table show the cost of reducing garbage produced by the first five tons, the second five tons, and so on. First, calculate the cost of requiring each firm to reduce the weight of its garbage by one-fourth. Now, imagine that the government issues marketable permits for the current level of garbage, but the permits will shrink the weight of allowable garbage for each film by one-fourth. What will be the result of this alternative approach to reducing pollution?arrow_forwardA firms marginal cost curve above the average variable cost curve is equal to the films individual supply curve. This means that every time a firm receives a price from the market it will be willing to supply the amount of output where the price equals marginal cost. What happens to the films individual supply curve if marginal costs increase?arrow_forward
- Table 3.8 shows information on the demand and supply for bicycles, where the quantities of bicycles are measured in thousands. What is the quantity demanded and the quantity supplied at a price of 210? At what price is the quantity supplied equal to 48,000? Graph the demand and supply curve for bicycles. How can you determine the equilibrium price and quantity from the graph? How can you determine the equilibrium price and quantity from line table? What HIE die equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity? If the price was 120, what would the quantities demanded and supplied he? Would a shortage or surplus exist? If so, how large would the shortage or surplus he?arrow_forwardThe Stopdecay Company sells an electric toothbrush for $25. Its sales have averaged 8,000 units per month over the past year. Recently, its closest competitor, Decayfigh ter, reduced the price of its electric toothbrush from $35 to $30. As a result, Stopde cays sales declined by 1,500 units per month. What is the arc cross elasticity of demand between Stopdecays toothbrush and Decayfighters toothbrush? What does this indicate about the relationship between the two products? If Stopdecay knows that the arc price elasticity of demand for its toothbrush is 1.5, what price would Stopdecay have to charge to sell the same number of units as it did before the Decayfighter price cut? Assume that Decayfighter holds the price of its toothbrush constant at $30. What is Stopdecays average monthly total revenue from the sale of electric toothbrushes before and after the price change determined in part (b)? Is the result in part (c) necessarily desirable? What other factors would have to be taken into consideration?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Economics 2eEconomicsISBN:9781947172364Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David ShapiroPublisher:OpenStax
Principles of Economics 2eEconomicsISBN:9781947172364Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David ShapiroPublisher:OpenStax Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506893Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506893Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781305506725Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781305506725Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an...EconomicsISBN:9781305506381Author:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. HarrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an...EconomicsISBN:9781305506381Author:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. HarrisPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:9781947172364
Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:OpenStax

Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781337617383
Author:Roger A. Arnold
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...
Economics
ISBN:9781305506893
Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou...
Economics
ISBN:9781305506725
Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an...
Economics
ISBN:9781305506381
Author:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:Cengage Learning