
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
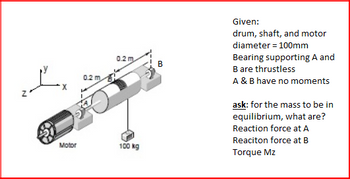
Transcribed Image Text:N
Motor
0.2 m
0.2 m
100 kg
B
Given:
drum, shaft, and motor
diameter = 100mm
Bearing supporting A and
B are thrustless
A & B have no moments
ask: for the mass to be in
equilibrium, what are?
Reaction force at A
Reaciton force at B
Torque Mz
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- View In: English v In the below arrangement, all the string and pulleys are massless and the inclined plane is frictionless. At t 0, spring is unstretched and a constant force F = mg starts to act. Find the maximum extension in the spring. (Assume incline to be sufficiently long). Question 11 F=mg Options 8mg 1. O k 4 mg 2. O 5 k 8 mg 3. O 15 k 8mg 4. O 3karrow_forwardPlease reply as soon as posible, thanks! I don´t have much time:( Static Problem: The spool shown in the figure has a weight of WAB = 27,50 N, and its center of gravity is located at its geometric center O, the spool has a larger radius R=0,17 and an inner radius r=0,13, and it has a coiled rope. Block C has a uniform weight WC= 60 N. Consider the friction between block C and the top of the spool at A, between the spool and the surface at point B and between the rope and pulley D, the friction coefficients are respectively: μs@A=0,30, μs@B =0,45 and μs@D=0,35. The chord is parallel to the plane. Carry out: a) The free-body diagrams of the block and the reel. b) The calculation of the maximum value of P that can be applied without losing the equilibrium of the system.arrow_forward$07-05 DAIL To л Et #D For the above pendulum (no inertia of link) find the equilibrium torque Te at O₂=0, ₂ = 0 and provide a linearized model of dynamics about this equilibrium. Do the saure for the inverted pendulum (0₂= 90°, & = T₂ = 0). Determine if the system is statically stable in both cases. m BUILT bg A Weather alert ^arrow_forward
- Need help on all questions. Please include all units, steps to the problem and information such as its direction or if it is in compression or tension. Thx.arrow_forwardpulley I =10mr? rigid, massless link Horizon tal plone , no gravity, no friction a) Deternine DO F b) obtain the equations of notion. 5m 3marrow_forwardNAME Question 1 (6/20) ANSWER ON THE YELLOW PAGES The nose wheel of the landing gear of an aircraft is extended and retracted by applying a torque M to the rod BC by means of an shaft located at point B. The rod AO, on which the landing wheel is also located, has a combined mass of 100 kg which may be simplified to a point force at point G. The masses of the bars CD and BC may be neglected. If the point D is located underneath point B, the rod CD is at an angle of 30° to the vertical y-axis. At this position the landing gear should be kept stationary, dynamic effects may therefore be neglected. All components are made out of stainless steel with max=200 MPa and Imax = 75 MPa. ALO d. 800 mm 400 mm 200 mm B 300 D M 500 mm OC 500 mm A D Questions, also draw all relevant free-body diagrams: a. Calculate the magnitude of the reaction force at point A. b. Calculate the minimum diameter of the pin in point A. The connection in point A is realized as shown on the right figure. Use a safety…arrow_forward
- Pravinbhaiarrow_forwardProblem 2. A uniform bar of mass m is pivoted at point O and supported at the ends by two springs, as shown in Figure 2. End P of spring PQ is subjected to a sinusoidal displacement, x(t) = x,sinwt. 1=1 m, k=1000 N/m, m=10 kg, xo=1 cm, and w=10 rad/s. a) Drive the equations of motion and find the natural frequency of the bar b) Find the steady-state angular displacement of the bar Simulate the system and plot displacements for the following cases (choose suitable simulation Vont time for each case): 1) With the initial conditions theta0=thetad0=0, an excitation xEsin(wi) Is applied vertically at point P. Choose such w values so that the system is i. in resonance, exPeriencing beating. do D ii. (1) = xo sin wt Uniform bar, mass m 31 Figure 2. Spring-mass systemarrow_forwardPlease reply as soon as posible, thanks! I don´t have much time:( Static Problem: The spool shown in the figure has a weight of WAB = 27,50 N, and its center of gravity is located at its geometric center O, the spool has a larger radius R=0,17 and an inner radius r=0,13, and it has a coiled rope. Block C has a uniform weight WC= 60 N. Consider the friction between block C and the top of the spool at A, between the spool and the surface at point B and between the rope and pulley D, the friction coefficients are respectively: μs@A=0,30, μs@B =0,45 and μs@D=0,35. The chord is parallel to the plane. Carry out: a) The free-body diagrams of the block and the reel. b) The calculation of the maximum value of P that can be applied without losing the equilibrium of the system.arrow_forward
- A turbine rotor is mounted on a stepped shaft that is fixed at both ends as shown in The torsional stiffnesses of the two segments of the shaft are given by ka = 3,000 N-m/rad and k2 = 4,000 N-m/rad. The turbine generates a harmonic torque given by M(t) = Mo cos wt about the shaft axis with M, = 200 N-m and w = 500 rads. The mass moment of inertia of the rotor about the shaft axis is Jo = 0.05 kg-m. Assuming the equivalent torsional damping constant of the system as c, = 2.5 N-m-s/rad, determine the steady-state response of the rotor, 6(1). O(1) ke M(1) = M, cos ot Turbine rotor, Joarrow_forwardspring is to be inserted with an initial compression to produce a force equal to 125 N between the right-hand end of the lever and the stop. When the maximum force at A reaches to a value of 200 N, the end of the lever moves downward by 25 mm. assuming a spring index 8 determine the following parameters: 1. Spring rate 2. Size of the wire 3. Outside diameter of the spring 4. Number of active coils, and 5. Free length, assuming squared and ground ends Note: the allowable shear stress may be taken as 420 MPa, and G = 80 GPa. Hint: Ans. 0.33 N/mm: 3.4 mm; 27.2 mm; 77 mm - 200 mm - 200 mm Lever Stop -Springarrow_forwardneed it correctlyarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY