
Database System Concepts
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780078022159
Author: Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Given an IntNode struct and the operating functions for a linked list, complete the following functions to extend the functionality of the linked list(this is not graded).
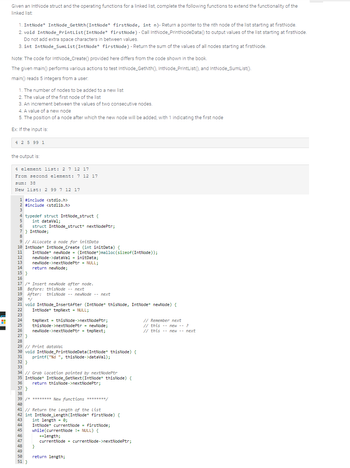
Transcribed Image Text:H
Given an IntNode struct and the operating functions for a linked list, complete the following functions to extend the functionality of the
linked list:
1. IntNode* IntNode_GetNth (IntNode* firstNode, int n)- Return a pointer to the nth node of the list starting at firstNode.
2. void IntNode_PrintList (IntNode* firstNode) - Call IntNode_PrintNodeData() to output values of the list starting at firstNode.
Do not add extra space characters in between values.
3. int IntNode_SumList (IntNode* firstNode) - Return the sum of the values of all nodes starting at firstNode.
Note: The code for IntNode_Create() provided here differs from the code shown in the book.
The given main() performs various actions to test IntNode_GetNth(), IntNode_PrintList(), and IntNode_SumList().
main() reads 5 integers from a user:
1. The number of nodes to be added to a new list
2. The value of the first node of the list
3. An increment between the values of two consecutive nodes.
4. A value of a new node
5. The position of a node after which the new node will be added, with 1 indicating the first node
Ex: If the input is:
4 2 5 99 1
the output is:
4 element list: 2 7 12 17
From second element: 7 12 17
sum: 38
New list: 2 99 7 12 17
1 #include <stdio.h>
2 #include <stdlib.h>
3
4 typedef struct IntNode_struct {
5
int dataVal;
6
7 } IntNode;
8
9 // Allocate a node for initData
10 IntNode* IntNode_Create (int initData) {
11
12
13
14
15 }
16
17 /* Insert newNode after node.
18 Before: thisNode -- next
19 After: thisNode-newNode --next
20 */
21 void IntNode_InsertAfter (IntNode* thisNode, IntNode* newNode) {
22 IntNode* tmpNext = NULL;
23
24 tmpNext = thisNode->nextNodePtr;
25
26
27 }
28
37 }
struct IntNode_struct* nextNodePtr;
38
IntNode* newNode = (IntNode*) malloc(sizeof(IntNode));
newNode->dataVal = initData;
29 // Print dataVal
30 void IntNode_PrintNodeData (IntNode* thisNode) {
printf("%d ", thisNode->dataVal);
31
newNode->nextNodePtr = NULL;
return newNode;
32}
33
34 // Grab Location pointed by nextNodePtr
35 IntNode* IntNode_GetNext (IntNode* thisNode) {
36
40
thisNode->nextNodePtr = newNode;
newNode->nextNodePtr = tmpNext;
46
47
39 /* ******** New functions ********/
48
49
50
51 }
return thisNode->nextNodePtr;
41 // Return the Length of the list
42 int IntNode_Length (IntNode* firstNode) {
43
44
45
int length = 0;
IntNode* currentNode = firstNode;
while (currentNode != NULL) {
}
++length;
currentNode = currentNode->nextNodePtr;
return length;
// Remember next
// this
// this
--
new -- ?
new -- next
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- please fill in the blanks and complate the codearrow_forwardC++ program for the following please: Create a generic function print(ls, n) that prints to standardoutput the first n elements of list ls. The elements are printed on separatelines. If ls has less than n elements, then the entire list is printedarrow_forwardCreate a ToArray function for the LinkedList class that returns an array from a linked list instance.arrow_forward
- struct insert_at_back_of_sll { // Function takes a constant Book as a parameter, inserts that book at the // back of a singly linked list, and returns nothing. void operator()(const Book& book) { /// TO-DO (3) /// // Write the lines of code to insert "book" at the back of "my_sll". Since // the SLL has no size() function and no tail pointer, you must walk the // list looking for the last node. // // HINT: Do not attempt to insert after "my_sll.end()". // ///// END-T0-DO (3) ||||// } std::forward_list& my_sll; };arrow_forwardPlease written by computer source 16 In this lab, you need to implement a simple linked list using dynamic memory allocation. The structure of node in the linked list has been declared in “lab3.h”. Also, the functions of linked list have been declared in “lab3.h” as well. In “main.c”, these functions are called. Your work is to finish these function implementations in a separate C source file, and create a makefile which can compile your separate C source file along with “main.c” and “lab3.h”. You can follow the comments in “main.c” and “lab3.h” to finish this lab. Please do not change “main.c” and “lab3.h”, because your separate C source file will be compiled with these two files posted on BlackBoard. When you test your program, please put “main.c”, “lab3.h”, your separate C source file and your makefile in the same directory and compile. Code provided: lab3.h #include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #ifndef LAB3_H #define LAB3_H struct node { int data; struct…arrow_forwardEvery time you write a non-const member function for a linked list, you should always think about if that function is preserving your class invariants. Group of answer choices A. True B. Falsearrow_forward
- } (1 of 3 parts) Consider the function below that is given the head and tail pointers to a double linked list. bool patronum (Node ✶h, Node * t) { bool c = true; if (t nullptr) return true; Node* p = t; while (p != h) { Node* j = p; Node* r = p->prev; EXAM for (Node* r = p->prev; r != nullptr; r = r->prev) { if (j->value > r->value) { c = false; j = r; } swap(p->value, j->value); p = p->prev; return c;arrow_forwardIn this task you will work with the linked list of digits we have created in the lessons up to this point. As before you are provided with some code that you should not modify: A structure definition for the storage of each digit's information. A main() function to test your code. The functions createDigit(), append(), printNumber(), freeNumber(), readNumber() and divisibleByThree() (although you may not need to use all of these). Your task is to write a new function changeThrees() which takes as input a pointer that holds the address of the start of a linked list of digits. Your function should change all of those digits in this linked list that equal 3 to the digit 9, and count how many replacements were made. The function should return this number of replacements. Provided codearrow_forwardC++ Create a generic function add_bookends(ls, e) that adds a copy of element e to the front and back of list ls.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Database System Concepts
Computer Science
ISBN:9780078022159
Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780134444321
Author:Tony Gaddis
Publisher:PEARSON

Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780132737968
Author:Thomas L. Floyd
Publisher:PEARSON

C How to Program (8th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780133976892
Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey Deitel
Publisher:PEARSON

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...
Computer Science
ISBN:9781337627900
Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Computer Science
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education