
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
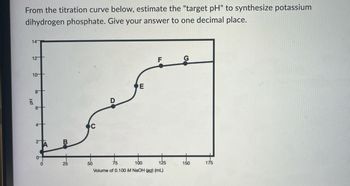
Transcribed Image Text:From the titration curve below, estimate the "target pH" to synthesize potassium
dihydrogen phosphate. Give your answer to one decimal place.
14
12
10
PH
8
L
T
L
b
14
B
25
50
E
F
75
100
125
Volume of 0.100 M NaOH (ag) (ml)
G
150
175
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- You collected the following data from a titration experiment using a 0.118M standardized NaOH solution to titrate a 26.65 mL solution with an unknown Molarity concentration (M) of sulfuric acid (H2SO4). Find molarity Initial Burette Reading (mL) Final Burette Reading (mL) Vol Delivered (mL) Molarity Trail #1 0.15 19.47 19.32 ?arrow_forwardCalculate the concentration of an HCl solution if 100.0 mL of the HCI required 33.00 mL of 0.2000 M Mg(OH)₂ to reach the titration endpoint. Mg(OH)2 + 2 HCl → 2 H₂O + MgCl₂ There is enough information to calculate the moles of base but not the moles of acid. mol b. 0.1320 i. OH-1 p. CO3² W. PO4³ a. 0.1000 h. CaCO3(s) o. H₂PO4-¹ v. H₂CO3 bb. 3.300 x 10-² hh. 2.16 x 10-6 L)(- mol Mg(OH)3)(- mol HCI c. HX j. H30+1 q. HCO3-¹ x. HCzH3Oz dd. 2 jj. 0.2000 d. Al+3 k. SO4² r. H₂S CC. 3 ii. 1.60 x 10-5 e. CO₂ 1. Mg+2 S. HS-1 y. C₂H30₂-1 ee. 1 = mol HCI mol Mg(OH)₂ M HCI f. CaF2(aq) m. C-1 t. S-2 z. 1 x 10-14 ff. 0.099536 kk. 6.600 x 10-³ g. HF(aq) n. HPO 2 u. H₂O(lig) mol Mg(OH)3 aa. 1.32 x 102 gg. 3.95 x 10-3 mol HCIarrow_forwardWhat is the function of indicator in a titration? Edit View Insert Format Tools Table 12pt ✓ Paragraph BIU IU AT²V 2 T² : Carrow_forward
- Help pleasearrow_forward1.00 x 10-² A student was titrating a solution of HC4H7O₂ with a Sr(OH)2 solution. Determine the pH at a particular point in the titration. Do this by constructing a BCA table and determining the pH. Complete Parts 1-2 before submitting your answer. Before (mol) Change (mol) After (mol) NEXT > 40.0 mL of a 0.200 M HC4H7O2 solution was titrated with 100 mL of 0.100 M Sr(OH)2 (a strong base). Fill in the ICE table with the appropriate value for each involved species to determine the moles of reactant and product after the reaction of the acid and base. You can ignore the amount of water in the reaction. 0 -1.00 x 10-² 1 HC4H-O₂(aq) + 0.100 1.20 x 10-² 0.200 OH-(aq) -1.20 x 10-² 2.00 x 10-³ 2 2.00 x 10-² H₂O(l) + -2.00 × 10-³ -2.00 x 10-² C4H7O₂ (aq) 8.00 x 10-³ RESET -8.00 x 10-³arrow_forwardDo not give answer in image and hand writingarrow_forward
- Fill out the tables and find pHarrow_forwardHello! If you could please help me with this questionarrow_forwardYou collected the following data from a titration experiment using a 0.118M standardized NaOH solution to titrate a 26.65 mL solution with an unknown Molarity concentration (M) of sulfuric acid (H2SO4). Find molarity Initial Burette Reading (mL) Final Burette Reading (mL) Vol Delivered (mL) Molarity Trail #1 0.15 19.47 19.32 ?arrow_forward
- Consider the titration of a 40.0 mL sample of 0.150 M CH3NH2 (Kb=4.4×10−4) with 0.200 M HBr. Determine each quantity:Part A:What is the volume of acid required to reach the equivalence point?Express your answer using one decimal place.V = mL Part B:What is the pH at the equivalence point? Express your answer using two decimal places.pH = Part C:Select an appropriate indicator for this titration. - picarrow_forwardCalculate the molarity of an NaOH solution from the following titration data. Be sure the answer has the correct amount of significant figures. The chemical equation for this titration is as follows: NaOH + KHP ⟶ NaKP + H2O NaOH buret reading, inital: 15.27 mL NaOH buret reading, final: 8.32 mL Mass of KHP (204.22 g/mol): 1.1592 g Calculate the molarity of an NaOH solution from the following titration data. Be sure the answer has the correct amount of significant figures. The chemical equation for this titration is as follows: NaOH + KHP ⟶ NaKP + H2O NaOH buret reading, inital: 15.27 mL NaOH buret reading, final: 8.32 mL Mass of KHP (204.22 g/mol): 1.1592 garrow_forwardA chemist titrates 140.0 mL of a 0.4430 M hydrochloric acid (HCI) solution with 0.4963 M NaOH solution at 25 °C. Calculate the pH at equivalence. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. Note for advanced students: you may assume the total volume of the solution equals the initial volume plus the volume of NaOH solution added. PH =0 × 9arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY