Question
Suppose that an external force of 10 N directed toward the top of the page is applied to the bar as shown in Figure P15.23. In steady state, is the machine acting as a motor or as a generator? Find the power supplied by or absorbed by: a. the electrical voltage source VT. b. RA. c. the external force.
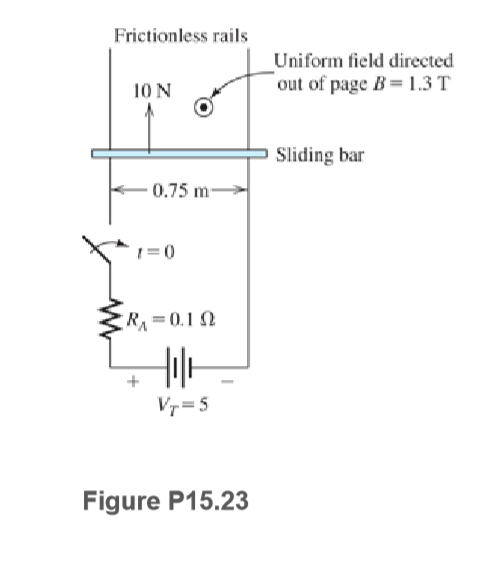
Transcribed Image Text:Frictionless rails
Uniform field directed
out of page B= 1.3 T
10 N
Sliding bar
0.75 m-
1=0
R=0.12
Vr = 5
Figure P15.23
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- You use an electrical generator with a hand crank to power a small radio. While cranking, you note the voltage reading measured across a capacitor that is used to store all the energy you're cranking out using your muscles. After an hour, you see the voltage reading is 2.2V. The capacitor has a capacitance of 3.5 x10-6F. You averaged 3.4 rotations on the crank every second. How much energy did your muscles donate to the radio's capacitor? (Give your answer in x10-6J)arrow_forward6. The parallel plates of a 10 μF vacuum filled capacitor are separated by 0.142 mm. A potential difference of 35 V is placed across the capacitor with a battery. a. What is the energy stored in the capacitor? b. If Teflon with a dielectric constant of 2.1 is inserted between the plates, while it is still connected to the battery, what is the new energy stored in the capacitor?arrow_forwardProblem Eight. The dielectric constants shown are ₁ 1.0, K₂ = 2.0, 0.20 m², and the distance = 3.0. The area of each plate is A between the plates is entire capacitor is 4.0 MV/m. K3 = d = 1.0 mm. The dielectric strength of the 30. Find the maximum energy (in mJ) that can be stored on the capacitor. (A) 8.0 (C) 6.0 (D) 24 (B) 1.0 (E) 36 K₁ K₂ K3arrow_forward
- A student reaches to open a door and gets a small electric shock. She knows that the shock is caused by static electricity, but it seems like in the winter she gets shocked more than in the summer. The student asks her science teacher if there are times of the year when there is more static electricity that builds up than other times of the year. The teacher replies that there is, and it depends on the humidity, or moisture in the air. The more humid the air is, the less static will build up and, therefore, the less you get shocked. Explain why static electricity does not build up as much when the air is humid. In your response, be sure to include: an explanation of static electricity is formed. an explanation of why the student felt a shock when reaching for the door handle. an explanation of how moisture in the air allows static electricity to dissipate. Be sure to consider the completeness of your response, supporting details, and accurate use of terms.arrow_forwardConsider what happens when a person moves around in dry conditions. The rubbing of motion leads to static electric charge building up on the body. Assume the capacitance of the human body to be about 155 pF. a) How much charge would have to build up on a body to generate a potential difference of 10 kV? b) A particular cell phone can have its circuits destroyed if exposed to an electric shock containing 300 u.J of energy. What voltage does that correspond to if the shock is coming from a human body?arrow_forwardHybrid vehicles are powered by a gasoline engine paired with an electric motor and batteries. Hybrids get much better mileage in the stop and go of city driving than conventional vehicles do. When you brake to a stop in a conventional car, friction converts the kinetic energy of the car’s motion into thermal energy in the brakes. In a typical hybrid car, depressing the brake pedal will connect a generator that converts much of the car’s kinetic energyinto chemical energy in a battery. Explain how this makes a hybrid vehicle more efficient.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios