
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
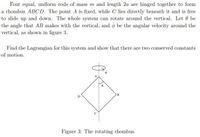
Transcribed Image Text:Four equal, uniform rods of mass m and length 2a are hinged together to form
a rhombus ABCD. The point A is fixed, while C lies directly beneath it and is free
to slide up and down. The whole system can rotate around the vertical. Let 0 be
the angle that AB makes with the vertical, and o be the angular velocity around the
vertical, as shown in figure 3.
Find the Lagrangian for this system and show that there are two conserved constants
of motion.
B
Figure 3: The rotating rhombus.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Derive the equation of motion of the following system and express them in matrix form. m, ↑ 9, Ct) ki m2 Y2(t) kz Share your results here.arrow_forwardConsider a satellite moving in a torque-free environment. The inertial frame and satellite body-fixed frame are represented by N-frame and B-frame, where {^₁, ñ2, ñ3} and {b₁, 62, 63} are right-handed vector bases fixed in N-frame and B-frame, respectively. {b} is aligned with the principal axis of inertia, where 6₁ and 63 are associated with the minimum and maximum moments of inertia, respectively. Denote the satellite angular velocity by w = wibį and the inertia tensor about the CoM by Ie. Suppose that I at time t = 0 is given by: Ic(t = 0) = 2ñ₁ñ₁ +2.25 ñ₂n₂ +2.25 ñ3ñ3 -0.75 n₂n3 -0.75 n3n2 (dimensionless) (a): First, let us characterize the inertia property of the satellite from the given information. (a.1): Express the satellite inertia tensor about the CoM in B-frame. Sketch the inertia ellipsoid of this body with B-frame.arrow_forwardThe turning moment diagram for a petrol engine is drawn to the following scales : Turning moment, 1 mm = 5 Nm; crank angle, 1 mm = 1°. The turning moment diagram repeats itself at every half revolution of the engine and the areas above and below the mean turning moment line taken in order are 295, 685, 40, 340, 960, 270 mm. The rotating parts are equivalent to a mass of 36 kg at a radius of gyration of 150 mm. Determine the coefficient of fluctuation of speed when the engine runs at 1800 r.p.m.arrow_forward
- ms mp mL A small frog of mass me clings to the left end of a uniform pole of mass mp and length L, and a large frog of mass my clings to the right end of the pole as shown in this top-down view. The system is rotating about its center of mass. The large frog is moving with tangential speed UL. Treat the frogs as point masses. Show all work and solve in terms of given variables. A. Find the center of mass of the system measured from the right end of the pole. B. What is the magnitude of the angular velocity of the system?arrow_forward4. Find the velocities of points B, C, and D of the double-slider mechanism illustrated in the figure below if crank 2 rotates at 42 rad/s cw. Use the graphical method.... y -3". 5 160 D 120° 3 Figure P3.22 RAO₂ = 2 in, RBA = 10 in, RCA=4 in, RCB = 7 in, and RDC = 8 in.arrow_forwardNeed asaparrow_forward
- Please i need her solvearrow_forwardA solid cylinder (mass 1.2kg, radius 5.0cm) on a horizontal table is connected to a block (mass 200 g) via a pulley (mass 0.80kg, radius 10.0cm) via a light, rigid string. Draw free body diagram for each of the object 1) list the dynamic and kinematic equations that related to all three objects. 2) find the acceleration of the falling block 3) fnd the angular acceleration of the cylinder and the friction force on itarrow_forwardA mechanical system consists of a ("long") rigid rod of length d and mass M, and another ("short") rigid rod of length I and mass m. The rods are attached at a fixed 90° angle such that the endpoint of the long rod touches the middle of the short rod; see the figure below. The mass per unit length of the rods is constant. The system can move in a vertical plane (x, y) with the endpoint O of the long rod fixed, so that the system is free to oscillate in the vertical plane about the point O. Gravity acts along the vertical y direction. 0 d a) How many degrees of freedom does the system have? [Expect to use a line to answer this question.] â b) Calculate the moment of inertia of the system constituted by the rods about an axis orthog- onal to the plane (x, y) and passing through O. Assume that the widths of the rods are negligible, so that you can effectively treat them as one-dimensional objects. [Expect to use about half a page to answer this question.] c) Determine the distance of the…arrow_forward
- A rod assembly rotates around the z-axis. The mass C is 10 kg and its initial velocity is 7 m/s. A moment and force both acts as shown in the figure where M = 8t2+5 N.m and F = 60 N. Find the velocity of mass C after 2 seconds.arrow_forwardSolve accordingly to given 3 parts belowarrow_forwardConsider a satellite moving in a torque-free environment. The inertial frame and satellite body-fixed frame are represented by N-frame and B-frame, where {^₁, ŵ2, ñ3} and {b₁, 62, 63} are right-handed vector bases fixed in N-frame and B-frame, respectively. {1;} is aligned with the principal axis of inertia, where ☎₁ and 3 are associated with the minimum and maximum moments of inertia, respectively. Denote the satellite angular velocity by w = wib; and the inertia tensor about the CoM by Ic. Suppose that I at time t = 0 is given by: Ic(t = 0) = 2ñ₁ñ₁ +2.25 ñ¿Ñ₂ +2.25 ñ³Ñ3 – 0.75 ñ¿ñ3 −0.75 3₂ (dimensionless) Express the satellite inertia tensor about the CoM in B-frame. Determine [BN] at time t = 0, i.c., the direction cosine matrix (DCM) that represents the orientation of B-frame relative to N-frame.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY