Question
Practice
Answer Choices of type of collision = elastic or inelastic
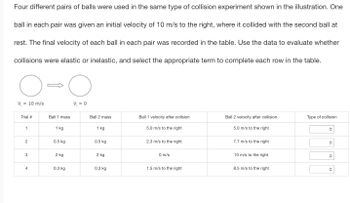
Transcribed Image Text:Four different pairs of balls were used in the same type of collision experiment shown in the illustration. One
ball in each pair was given an initial velocity of 10 m/s to the right, where it collided with the second ball at
rest. The final velocity of each ball in each pair was recorded in the table. Use the data to evaluate whether
collisions were elastic or inelastic, and select the appropriate term to complete each row in the table.
V = 10 m/s
Trial #
1
2
3
4
Ball 1 mass
1 kg
0.5 kg
2 kg
0.3 kg
V₁=0
Ball 2 mass
1 kg
0.5 kg
2 kg
0.3 kg
Ball 1 velocity after collsion
5.0 m/s to the right
2.3 m/s to the right
0 m/s
1.5 m/s to the right
Ball 2 velocity after collision
5.0 m/s to the right
7.7 m/s to the right
10 m/s to the right
8.5 m/s to the right
Type of collision
O
0
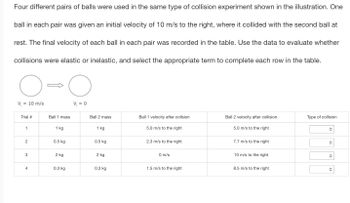
Transcribed Image Text:Four different pairs of balls were used in the same type of collision experiment shown in the illustration. One
ball in each pair was given an initial velocity of 10 m/s to the right, where it collided with the second ball at
rest. The final velocity of each ball in each pair was recorded in the table. Use the data to evaluate whether
collisions were elastic or inelastic, and select the appropriate term to complete each row in the table.
V = 10 m/s
Trial #
1
2
3
4
Ball 1 mass
1 kg
0.5 kg
2 kg
0.3 kg
V₁=0
Ball 2 mass
1 kg
0.5 kg
2 kg
0.3 kg
Ball 1 velocity after collsion
5.0 m/s to the right
2.3 m/s to the right
0 m/s
1.5 m/s to the right
Ball 2 velocity after collision
5.0 m/s to the right
7.7 m/s to the right
10 m/s to the right
8.5 m/s to the right
Type of collision
O
0
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 19 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- I need the answer quicklyarrow_forwardProblem 7.44 Billiard ball A of mass m = 0.123 kg moving with speed vA = 2.80 m/s strikes ball B, initially at rest, of mass mB = 0.135 kg As a result of the collision, ball A is deflected off at an angle of 0, = 30.0° with a speed v', = 2.10 m/s, and ball B moves with a speed v, at an angle of 0, to original direction of motion of ball A.arrow_forwardWhat would be the type of collision of the image below? a.) Elastic b.) Inelastic c.) Completely Inelastic d.) No collision Momentum & Energy: Elastic and Inelastic Collisions Animation Speed Run slower faster Pause Elasticity (enter a number between 0 and 1)08 Reset inelastic Volue VCOM Initial KE red = 250J Initial p red = 50 kgm/s Initial KE blue = 96 J Show Energy & Momentum Values Initial p blue = -24 kgm/s Velocity of red box = 10 mis Velocity of blue box = -8 mis COM Prud Pelue Ep (+) Positive Direction Show Center of Mass Initial velocity of red bax (mis) = 10 Initial velocity of blue box (mis) =-8 Relative velocity initial = 18 (towards) Mass of red box (kg) =5 Show Relative Velocity Mass of blue box (kg) =3arrow_forward
- answer choices in the 2nd screenshotarrow_forwardTutorial Exercise A 2.0-g particle moving at 5.5 m/s makes a perfectly elastic head-on collision with a resting 1.0-g object. (a) Find the speed of each particle after the collision. (b) Find the speed of each particle after the collision if the stationary particle has a mass of 10 g. (c) Find the final kinetic energy of the incident 2.0-g particle in the situations described in parts (a) and (b). In which case does the incident particle lose more kinetic energy? Step 1 The initial velocity of the target object is zero (v2i = 0). Let m, be the mass of the first particle, v,, its initial velocity, and v2r its final velocity. Let m, be the mass of the target object and vr its final velocity. From conservation of momentum before and after the collision, we have the following equation. m V1f + m2v2f = m,V1 + 0 For a perfectly elastic head-on collision, we have the following relationship between the objects' final velocities and initial velocities derived from conservation of momentum and…arrow_forwardThe impulse of the force exerted by wooden target in stopping an arrow with a speed of 400m/s is -2kg-m/s. If it took 0.004 seconds for the arrow to penetrate the wooden block, what is the mass of the arrow? include figure and FBD.arrow_forward
- An air-track cart with mass mi = 0.34 kg and initial speed vo = 0.85 m/s collides with and sticks to a second cart that is at rest initially. Part A If the mass of the second cart is m2 = 0.47 kg, how much kinetic energy is lost as a result of the collision? Express your answer to two significant figures and include appropriate units. ? Value Units Submit Request Answerarrow_forwardCan i get help with these problemsarrow_forwardQuestion 8 pleasearrow_forward
- Current Attempt in Progress Ball B, moving in the positive direction of an x axis at speed v, collides with stationary ball A at the origin. A and B have different masses. After the collision, B moves in the negative direction of the y axis at speed v/2. In what direction does A move, as an angle with respect to the x axis? Number i e Textbook and Media Unitsarrow_forwardAn elastic straight-line collision Follow Example referring to Figure below. YAix = 2.0 m/s Vasx = -2.0 m/s Before Am- mA = 0.50 kg m, = 0.30 kg %3D Yazu =? After w B 5. Calculate the KE , VA and VB after collision.arrow_forwardTwo billiard balls of equal mass undergo a perfectly elastic head-on collision. Part A If one ball's initial speed was 2.40 m/sm/s, and the other's was 3.40 m/sm/s in the opposite direction, what will be their velocities after the collision? Enter your answers numerically separated by a comma. Enter positive value if the direction of the velocity is the same as the direction of the initial velocity of the first ball, and negative value if the direction of the velocity is opposite to the direction of the initial velocity of the first ball.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios