
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Ll.170.
Transcribed Image Text:پیاز
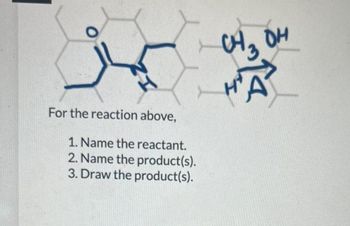
For the reaction above,
1. Name the reactant.
2. Name the product(s).
3. Draw the product(s).
طرح
ان
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A solution of CaCl2CaCl2 in water forms a mixture that is 38.5%38.5% calcium chloride by mass. If the total mass of the mixture is 117.9 g,117.9 g, what masses of CaCl2CaCl2 and water were used?arrow_forwardChemical Bonding -.. V Pennsylvania Acces... Department of Hu.. Bvlgari Man In Blac.. O CHEMICAL REACTIONS Identifying the limiting reactant in a drawing of a mixture The drawing below shows a mixture of molecules: key carbon hydrogen nitrogen sulfur oxygen chlorine Suppose the following chemical reaction can take place in this mixture: 2C,H,(g)+50,(g) → 4 CO,(g)+2H,O(g) Of which reactant are there the most initial moles? Enter its chemical formula: Of which reactant are there the least initial moles? Enter its chemical formula: Which reactant is the limiting reactant? Enter its chemical formula: Explanation Checkarrow_forwardThe great French chemist Antoine Lavoisier discovered the Law of Conservation of Mass in part by doing a famous experiment in 1775. In this experiment Lavoisier found that mercury(II) oxide, when heated, decomposed into liquid mercury and an invisible and previously unknown substance: oxygen gas. 1. Write a balanced chemical equation, including physical state symbols, for the decomposition of solid mercury(II) oxide (HgO) into liquid mercury and gaseous dioxygen. х10 2. Suppose 14.0 mL dioxygen gas are produced by reaction, at a temperature of 110.0 °C and pressure of exactly 1 atm. Calculate the mass of mercury(II) oxide that must have reacted. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits.arrow_forward
- Consider a small bird of mass 30 g. What is the minimum mass of glucose that it must consume (and burn) to fly up to a branch 10 m above the ground?arrow_forward10 Ethylene (CH,CH,) is the starting point for a wide array of industrial chemical syntheses. For example, worldwide about 8.0 × 10º kg of polyethylene are made from ethylene each year, for use in everything from household plumbing to artificial joints. Natural sources of ethylene are entirely inadequate to meet world demand, so ethane (CH,CH,) from natural gas is "cracked" in refineries at high temperature in a kinetically complex reaction that produces ethylene gas and hydrogen gas. Suppose an engineer studying ethane cracking fills a 60.0 L reaction tank with 22.0 atm of ethane gas and raises the temperature to 500. °C. She believes K =0.050 at this temperature. Calculate the percent by mass of ethylene the engineer expects to find in the equilibrium gas mixture. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. Note for advanced students: the engineer may be mistaken about the correct value of K , and the mass percent of ethylene you calculate may not be what she actually observes. %arrow_forwardThe great French chemist Antoine Lavoisier discovered the Law of Conservation of Mass in part by doing a famous experiment in 1775. In this experiment Lavoisier found that mercury(II) oxide, when heated, decomposed into liquid mercury and an invisible and previously unknown substance: oxygen gas. 1. Write a balanced chemical equation, including physical state symbols, for the decomposition of solid mercury(II) oxide (HgO) into liquid mercury and gaseous dioxygen. 2. Suppose 53.0mL of dioxygen gas are produced by this reaction, at a temperature of 50.0°C and pressure of exactly 1atm. Calculate the mass of mercury(II) oxide that must have reacted. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits.arrow_forward
- Request They Both Die at t... ula Enchanted Wa... Question 6 of 20 Balance the following chemical equation (if necessary): Sio,(s) + C(s) → Si(s) + CO(g) 04- 2. 3+ O4+ 1 6. 7 8. 9. Os 6. O9 (s) (1) (g) (aq) C Si Reset • x HO Delete MacBook Air 000 F3 F4 F5 @ %23 2$ % 2 3 5 6. 8 9. W E 5 4- 3. 2. 14arrow_forwardAmmonia gas is obtained by the reaction of nitrogen gas and hydrogen gas. Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction. - X 5 ?arrow_forwardThe great French chemist Antoine Lavoisier discovered the Law of Conservation of Mass in part by doing a famous experiment in 1775. In this experiment Lavoisier found that mercury(II) oxide, when heated, decomposed into liquid mercury and an invisible and previously unknown substance: oxygen gas. 1. Write a balanced chemical equation, including physical state symbols, for the decomposition of solid mercury(II) oxide (HgO) into liquid mercury and gaseous dioxygen. 2. Suppose 71.0 mL of dioxygen gas are produced by this reaction, at a temperature of 50.0 °C and pressure of exactly 1 atm. Calculate the mass of mercury(II) oxide that must have reacted. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits.arrow_forward
- A 14.599 g14.599 g sample of CaCl2CaCl2 was added to 12.147 g12.147 g of K2CO3K2CO3 and mixed in water. A 3.571 g3.571 g yield of CaCO3CaCO3 was obtained. What is the limiting reagent? CaCO3CaCO3 K2CO3K2CO3 CaCl2CaCl2 Calculate the percent yield of CaCO3.CaCO3. yield of CaCO3=CaCO3=arrow_forwardChlorine gas and solid potassium combine to produce solid potassium chloride. Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY