
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
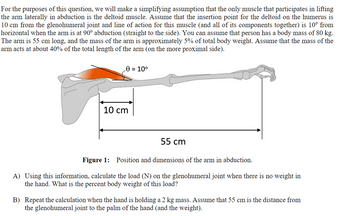
Transcribed Image Text:For the purposes of this question, we will make a simplifying assumption that the only muscle that participates in lifting
the arm laterally in abduction is the deltoid muscle. Assume that the insertion point for the deltoid on the humerus is
10 cm from the glenohumeral joint and line of action for this muscle (and all of its components together) is 10° from
horizontal when the arm is at 90° abduction (straight to the side). You can assume that person has a body mass of 80 kg.
The arm is 55 cm long, and the mass of the arm is approximately 5% of total body weight. Assume that the mass of the
arm acts at about 40% of the total length of the arm (on the more proximal side).
0 = 10°
10 cm
55 cm
Figure 1: Position and dimensions of the arm in abduction.
A) Using this information, calculate the load (N) on the glenohumeral joint when there is no weight in
the hand. What is the percent body weight of this load?
B) Repeat the calculation when the hand is holding a 2 kg mass. Assume that 55 cm is the distance from
the glenohumeral joint to the palm of the hand (and the weight).
SAVE
AI-Generated Solution
info
AI-generated content may present inaccurate or offensive content that does not represent bartleby’s views.
Unlock instant AI solutions
Tap the button
to generate a solution
to generate a solution
Click the button to generate
a solution
a solution
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Below is a diagram of a human arm. 5.0 cm F M -15 cm- Ꮃ . A -35 cm- W B The forearm is lifted by the biceps muscle, which is attached approximately 5.0 cm from the joint. Champion athletes are often found to have muscle attachments farther from the joint than the average person (5.5 cm). (a) Why does this small change in the muscle attachment position give an advantage when lifting or throwing? Explain clearly, referring to the above diagram.10 108arrow_forwardts During the push-off phase of walking, the GRF measured by a force plate at the foot is 1,671 N applied under the toes at an angle of 75 with respect to the right horizontal. The muscle force supplied by the soleus and gastrocnemius muscles is 5,002 N, which is applied parallel to the tibia. The leg segment is oriented at 52 with respect to the right horizontal. Fm Vertical jof force Horizontal joint force GRFarrow_forwardWhat is the compression force on S1 if lumbosacral angle is 50 degrees? What is the pressure if the contact area is 15 cm^2?arrow_forward
- You are trying to evaluate the amount of force a worker must exert and see if implementing an assistive device would help reduce injury for the work. Pictured below, the worker and the job you are assessing. You are interested in the shoulder joint for this problem. ● The drill weighs 3.1 kg and is 80 cm away (horizontal distance) from the shoulder joint ● The worker's arm weighs 17 lbs from the shoulder to the fingers. The center of mass of this weight is 40cm from the shoulder joint. Show the units. 1. Draw a FBD for the right arm only. a. Assume the drill is not touching the wall. b. Assume the worker is not supporting themselves on anything c. Assume the deltoid muscle is holding up the drill. The deltoid muscle is pointing towards the shoulder joint and runs parallel to the arm but 2 cm above the shoulder joint Also, calculate the deltoid muscle force. Is the muscle for pointing towards the shoulder or away from the shoulder?arrow_forwardThe tune-up specifications of a car call for the spark plugs to be tightened to a torque of 38 N ⋅ m. You plan to tighten the plugs by pulling on the end of a 25-cmlong wrench. Because of the cramped space under the hood, you’ll need to pull at an angle of 120° with respect to the wrench shaft. With what force must you pull?arrow_forwardWhile cutting in a sport, an individual generates the following forces surrounding their ankle joint. The Achilles tendon is creating an eccentric force that is equal to 900 N directed down and to the right at an angle of 80 degrees below the right horizontal. They also have a GRF that is directed up and to the left at a magnitude of 3100 Newtons that is directed up and to the left at an angle of 82 degrees above the left horizontal. The lateral malleolus of the ankle joint helps to create a stable base for the ankle joint in the frontal (horizontal plane) and can produce up to a maximum horizontal reaction force of 200 N. After that it must rely on the ankle ligaments to help in stabilizing the joint. Part A) How much force, if any, do the ankle ligaments need to produce during this movement if the goal is to create a static horizontal situation? Part B) What is the resultant force and direction of this movement without the addition of the ankle ligaments, if the Force of gravity is…arrow_forward
- You are sitting in a chair and you are ready to kick a soccer ball from a sitting position using only your quadriceps muscles to rotate your knee. Be sure you will not pivot your hips, as you are sitting in the chair; we want to simplify this problem to include only rotating your lower leg at the knee joint and keeping your thigh firmly fixed to the seat. For our purposes, your quadriceps muscles can be treated as a single string that exerts a tension on the knee at a right angle from a lever arm of 2.00 cm. The knee is connected to a plausible 50.0 cm lower leg as measured from the pivot point of the knee to the contact point where we will kick the ball.Before we kick it, we would like to balance the ball on our contact point (at our ankle, say) 50.0 cm away from the pivot point of the knee by extending the lower leg straight out (upper leg aligned with the lower leg). The soccer ball has a mass of 400 grams. We will neglect all mass of all parts of the leg here for brevity c) We now…arrow_forwardYou are sitting in a chair and you are ready to kick a soccer ball from a sitting position using only your quadriceps muscles to rotate your knee. Be sure you will not pivot your hips, as you are sitting in the chair; we want to simplify this problem to include only rotating your lower leg at the knee joint and keeping your thigh firmly fixed to the seat. For our purposes, your quadriceps muscles can be treated as a single string that exerts a tension on the knee at a right angle from a lever arm of 2.00 cm. The knee is connected to a plausible 50.0 cm lower leg as measured from the pivot point of the knee to the contact point where we will kick the ball.Before we kick it, we would like to balance the ball on our contact point (at our ankle, say) 50.0 cm away from the pivot point of the knee by extending the lower leg straight out (upper leg aligned with the lower leg). The soccer ball has a mass of 400 grams. We will neglect all mass of all parts of the leg here for brevity.a) Draw an…arrow_forwardYou are sitting in a chair and you are ready to kick a soccer ball from a sitting position using only your quadriceps muscles to rotate your knee. Be sure you will not pivot your hips, as you are sitting in the chair; we want to simplify this problem to include only rotating your lower leg at the knee joint and keeping your thigh firmly fixed to the seat. For our purposes, your quadriceps muscles can be treated as a single string that exerts a tension on the knee at a right angle from a lever arm of 2.00 cm. The knee is connected to a plausible 50.0 cm lower leg as measured from the pivot point of the knee to the contact point where we will kick the ball. Before we kick it, we would like to balance the ball on our contact point (at our ankle, say) 50.0 cm away from the pivot point of the knee by extending the lower leg straight out (upper leg aligned with the lower leg). The soccer ball has a mass of 400 grams. We will neglect all mass of all parts of the leg here for brevity. Draw an…arrow_forward
- A football (soccer) player can kick the ball with about 4 kN of force. Suppose an athlete accidentally kicks their competitor's tibia instead of the ball. This injury may be modeled by the diagram below, where the kick is represented by force F. Assume that the load is applied directly in the middle of the tibia. For the sake of simplicity, model the bone as a solid beam with 2 cm x 2 cm square cross-sectional area. Note that the pin and roller in the model do not induce reaction moments. Use E = 16 GPa. F = 500 N/cm 20 cm (a) Draw a free body diagram (FBD) including all external forces.arrow_forwardA father lifts his child as shown in the figure below. How much torque does the child exert, taking the knee as the pivot? How much torque does the weight of the leg itself exert? What force () should the upper leg muscle exert to lift the child at a constant speed?arrow_forwardIn the parallel jaw pliers shown, the clamping jaws remain parallel as objects of various sizes are held. If 60 N is applied to the handles what is the force applied between the jaws. Assume that pins B and E slide freely in the slots in the jaws.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY