
Database System Concepts
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780078022159
Author: Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
For the FSM below, assume to start from state S0 and to use the indicated encoding. The following sequence of inputs are going to be selected one after the other at times t0, t1, t2, t3, and t4. Use the FSM to indicate the next state bits and output Y after each time point.
t0 -> AB=00
t1 -> AB=10
t2 -> AB=11
t3 -> AB=11
t4 -> AB=01
Indicate your answer using 3 bits for each time point. For example, if AB=10 at time t0, your answer would be 101, where the first two bits are for the next state (10 -> S2) and the third bit is for the output value Y
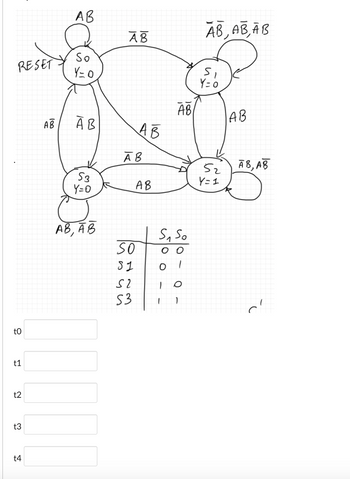
Transcribed Image Text:RESET
to
t1
t2
t3
t4
AB
AB
So
Y= 0
AB
S3
Y=0
ав, ав
AB
Ав
АВ
Ав
SO
81
si
S3
ABI
SA So
оо
O
1 1
АВ, АВ, А В
Si
Y= 0
52
Y= 1
AB
AB, AB
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Problem 1. Byte Stuffing Decode the following "raw" sequence of bits into bytes using HDLC decoding. 111110111001111101arrow_forwardThe symbol £ is magnified and shown in Figure 1 with a grid superimposed. Figure 1 The image in Figure 1 is to be encoded and encrypted using the following steps: 1. Each of the five horizontal rows of the picture is encoded as a 5-bit binary number. White squares are encoded as Os and black squares as 1s. The horizontal rows are therefore encoded as: Row 1: 00110 Row 2: 01001 Row 3: 11100 Row 4: 01000 Row 5: 11110 2. Starting from the left, the first binary digit is multiplied by 16, the second by 8, the third by 4, the fourth by 2, and the fifth by 1. This will convert the 5-bit binary numbers to decimal numbers as shown below: Row 1: (0 x 16) + (0 × 8) + (1 × 4) + (1 × 2) + (0 × 1) = 0 + 0 +4+2+0 = 6. Row 2: (0 x 16) + (1 × 8) + (0 × 4) + (0 × 2) + (1 × 1) = 0 + 8 +0+0+1 = 9. Row 3: (1 x 16) + (1 × 8) + (1 × 4) + (0 × 2) + (0 × 1) = 16+8+4 + 0 + 0 = 28. Row 4: (0 x 16) + (1 × 8) + (0 × 4) + (0 × 2) + (0 × 1) = 0 + 8 +0+0+0= 8. Row 5: (1 x 16) + (1 × 8) + (1 × 4) + (1 × 2) + (0 × 1)…arrow_forwardReset A/0 B/O So S1 B/O AB/1 A/0 A+ BI0 (3) Describe in words what the state machine in figure above does. Using one- hot encodings, complete a state transition table and output table for the FSM above. Write Boolean equations for the next state and output and sketch a schematic of the FSM.arrow_forward
- Convert the following unpacked Binary Coded Decimal (BCD) encodings to their decimal values. Note: Spaces are placed between each 4-bit sequence to make the binary sequence more readable and decrease the likelihood of a mistake. a) 0000 0111 0000 0100 0000 1000 b) 0000 1001 0000 0001 0000 0110arrow_forwardAssume that a system uses 10-bit floating-point representation based on the IEEE floating-point format, in which: . There is 1 sign bit. There are k= 6 exponent bits. The exponent bias is 31. . There are n= 3 fraction bits. ● Convert the decimal number -5.5 into the 10-bit IEEE floating point representation explained above. Write the final result in 10-bit binary format. Show your steps.arrow_forwardAs the error-detection and correction capability of a code increases, we would expect in general the overhead bits to protect a group of data bits to decrease remain the same increasearrow_forward
- 7. Add the following two 8-bit binary numbers, producing an 8-bit result. Indicate the status of the carry and overflow bits at the end of the addition by circling the appropriate choices. The space in between is only for readability. 1101 0110 + 1001 0111 -------------- Overflow? Yes or No Carry? Yes or Noarrow_forwardWhy is Non-Return to Zero encoding is considered the best compared to other encoding methods? Explain ?arrow_forward1 a. If the last operation performed on a computer with an 8-bit word was an addition in which the two operands were 00000010 and 00000011, what would be the value of the following flags? ● Carry • Zero • Overflow Sign • Even Parity ● Half-Carry b. Repeat for the addition of -1 (twos complement) and +1.arrow_forward
- 6. For an 8-bit operand, specify the 8-bit mask and the logical operator to perform the following operations. Bit positions are numbered 7-0, left to right. a. Logical Operator: Logical Mask: b. Set all bits to 1. Logical Operator: C. Clear bits 5, 4, 3, and 2 to 0. All other bits remain unchanged. Logical Mask: d. Complement bits 2, 1, and O. All other bits remain unchanged. Logical Operator: Logical Mask: Set bits 7, 6, and 5 to 1. All other bits remain unchanged. Logical Operator: Logical Mask:arrow_forwardPlease answer ASAParrow_forwardSuppose you have a 4x2 priority encoder whose inputs are shown below in a single row of a truth table. The inputs 13 - 10 are inputs and e1 and e0 are output bits. What value will the data outputs, el and e0, be for this row (assume i3 is the highest priority input and results in the largest encoded value)? i3 12 i1 1 1 O el e0 0 0 el 0 e1 eo 1 e0 e1 e0 1 1 10 1arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Database System Concepts
Computer Science
ISBN:9780078022159
Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780134444321
Author:Tony Gaddis
Publisher:PEARSON

Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780132737968
Author:Thomas L. Floyd
Publisher:PEARSON

C How to Program (8th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780133976892
Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey Deitel
Publisher:PEARSON

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...
Computer Science
ISBN:9781337627900
Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Computer Science
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education