
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%

Transcribed Image Text:For the following reaction, 13.0 grams of sodium are allowed to react with 6.45 grams of water.
sodium(s) + water(1) → sodium hydroxide(aq) + hydrogen (g)
What is the maximum amount of sodium hydroxide that can be formed?
Mass =
g
What is the FORMULA for the limiting reactant?
What amount of the excess reactant remains after the reaction is complete?
Mass =
g
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
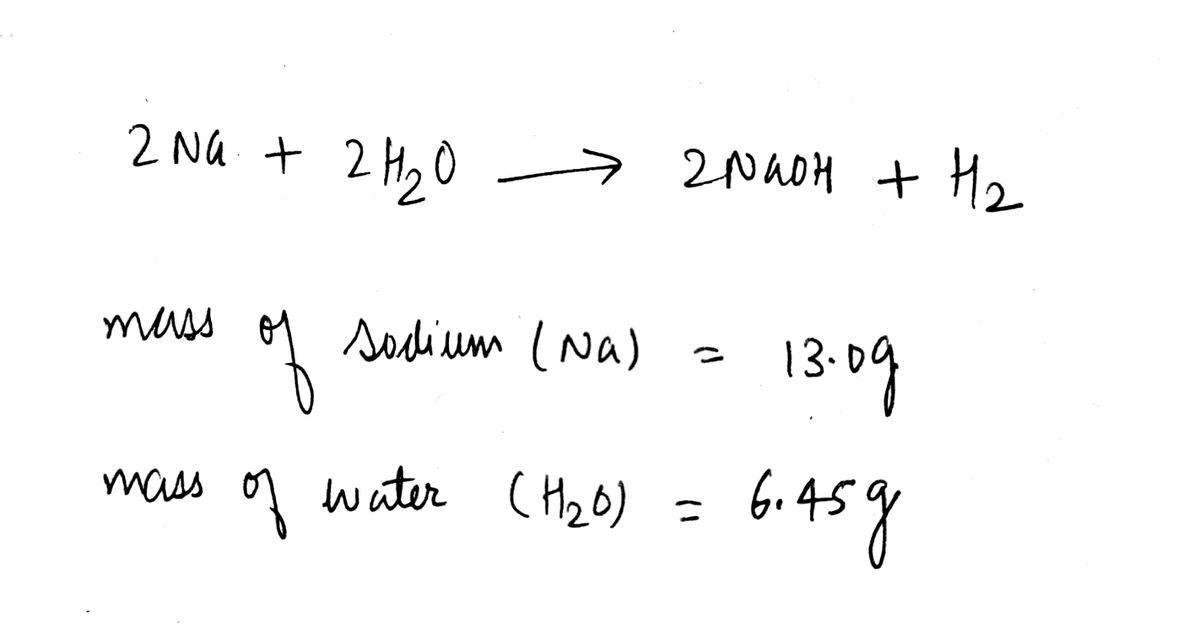
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Elemental phosphorus reacts with chlorine gas according to the equationP4(s)+6Cl2(g)→4PCl3(l)A reaction mixture initially contains 45.53 g P4 and 130.9 g Cl2. Once the reaction has reached completion, what mass (in g) of the excess reactant is left? Express the mass in grams to three significant figures.arrow_forwardFor the following reaction, 22.6 grams of sodium chloride are allowed to react with 52.2 grams of silver nitrate. sodium chloride ( aq ) + silver nitrate ( aq ) → silver chloride (s) + sodium nitrate ( aq ) What is the maximum amount of silver chloride that can be formed? grams What is the FORMULA for the limiting reagent? What amount of the excess reagent remains after the reaction is complete? gramsarrow_forwardA mixture of potassium chloride and potassium bromide weighing 3.562 g is heated with chlorine, which converts the KBr completely to potassium chloride. The total mass of potassium chloride after the reaction of 3.199 g. What percentage of the original mixture was potassium bromide?arrow_forward
- For the following reaction, 11.1 grams of sulfur are allowed to react with 22.6 grams of carbon monoxide. sulfur(s) + carbon monoxide(g) → sulfur dioxide(g) + carbon(s) What is the maximum amount of sulfur dioxide that can be formed? Mass= g What is the FORMULA for the limiting reactant? What amount of the excess reactant remains after the reaction is complete? Mass = garrow_forwardFor the following reaction, 55.4 grams of potassium hydrogen sulfate are allowed to react with 21.5 grams of potassium hydroxide. potassium hydrogen sulfate (aq) + potassium hydroxide (aq) sulfate (aq) + water (1) →potassium What is the maximum amount of potassium sulfate that can be formed? grams What is the FORMULA for the limiang reagent? What amount of the excess reagent remains after the reaction is complete? gramsarrow_forwardA mixture consisting of only copper(II) chloride (CuCl₂) and calcium chloride (CaCl₂) weighs 1.0052 g. When the mixture is dissolved in water and an excess of silver nitrate is added, all the chloride ions associated with the original mixture are precipitated as insoluble silver chloride (AgCl). The mass of the silver chloride is found to be 2.3492 g. Calculate the mass percentages of copper(II) chloride and calcium chloride in the original mixture. Mass percent CuCl₂ Mass percent CaCl₂ = % %arrow_forward
- For the following reaction, 11.8 grams of magnesium nitride are allowed to react with 15.9 grams of water. magnesium nitride(s) + water(1) → magnesium hydroxide(aq) + ammonia(aq) What is the maximum amount of magnesium hydroxide that can be formed? Mass= g What is the FORMULA for the limiting reactant? What amount of the excess reactant remains after the reaction is complete? Mass= garrow_forwardFor the following reaction, 20.9 grams of iron are allowed to react with 43.3 grams of chlorine gas. Iron + chlorine ---> iron(III)chloride What is the maximum mass of iron(III) chloride that can be formed? Mass = ____g What is the FORMULA for the limiting reactant? What mass of the excess reagent remains after the reaction is complete? Mass = ____garrow_forwardFor each of the following reactions, translate formulas and symbols into words. Be sure to account for coefficients and physical states. THEN, write the equation and illustrate it on poster paper. Use different colors to represent each element. Check your illustrations for conservation of mass. 3 2KI(aq) + Br2(1)→2KBr(aq) + 12(s) 4 3Zn(s) + 2FeCl3(aq) → 2Fe(s) + 3ZnCl₂(aq) Chemical Equations & Symbolsarrow_forward
- For the following reaction, 46.0 grams of iron(II) chloride are allowed to react with 152 grams of silver nitrate. iron (II) chloride (aq) + silver nitrate(aq) → iron(II) nitrate(aq) + silver chloride(s) What is the maximum amount of iron(II) nitrate that can be formed? Mass= 9 What is the FORMULA for the limiting reactant? What amount of the excess reactant remains after the reaction is complete? Mass= 9arrow_forwardFor the following reaction, 45.5 grams of iron(II) chloride are allowed to react with 110 grams of silver nitrate. iron (II) chloride (aq) + silver nitrate(aq) → iron(II) nitrate (aq) + silver chloride (s) What is the maximum amount of iron(II) nitrate that can be formed? Mass= What is the FORMULA for the limiting reactant? What amount of the excess reactant remains after the reaction is complete? g Mass=arrow_forwardA mixture consisting of only chromium(III) bromide (CrBr3) and aluminum bromide (AlBr3) weighs 1.1218 g. When the mixture is dissolved in water and an excess of silver nitrate is added, all the bromide ions associated with the original mixture are precipitated as insoluble silver bromide (AgBr). The mass of the silver bromide is found to be 2.2708 g. Calculate the mass percentages of chromium(III) bromide and aluminum bromide in the original mixture. Mass percent CrBr3 Mass percent AlBr3 = % %arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY