
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
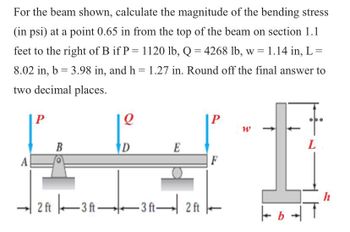
Transcribed Image Text:For the beam shown, calculate the magnitude of the bending stress
(in psi) at a point 0.65 in from the top of the beam on section 1.1
feet to the right of B if P = 1120 lb, Q = 4268 lb, w = 1.14 in, L =
8.02 in, b = 3.98 in, and h = 1.27 in. Round off the final answer to
two decimal places.
P
Q
W
D
E
L
2 ft |、▬▬3 ft ▬▬▬3 ft▬| 2 ft
F
| b
h
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1arrow_forward1.Hollow circular section 2) the composite circular section where G of the inner core is greater than G of the outer shell 3. the composite circular section where G of the inner core is less than G of the outer shell 4. For any beam in bending the flexural stress is zero at the centroule of the cross section 5. For any beam is bending the shear stress is the maximum at the centroid of the cross sectionarrow_forwardPlease help me understand how to get the internal loadings acting at point C. The value of W is derived from the 400 lb/ft written to the top left of the picture.arrow_forward
- The rim of an iron flywheel's cross section (S+3) ft. A 12" by 3" triangle has a diameter of 12". What is the weight of the rim? Iron weights 450 pounds per cubic foot. S=10arrow_forwardDetermine the largest permissible value of P for the beam and loading shown, knowing that the allowable normal stress is +8 ksi in tension and –18 ksi in compression. (Round the final answer to two decimal places.)arrow_forwardw1 B w2 Determine the shear force and bending moment at the one-third, middle, and two-thirds of the length of the beam (from point A), respectively. Use wl = 7 kN/m, w2 = 4 kN/m, and a =4 m. The shear force at the one-third of the length of the beam (from point A) in kN is (round to the nearest integer): kN The shear force at the middle of the length of the beam (from point A) in kN is (round to the nearest integer): KN The shear force at the two-thirds of the length of the beam (from point A) in kN is (round to the nearest integer): |kN The bending moment at the one-third of the length of the beam (from point A) in KN.m is (round to the nearest integer): kN.m The bending moment at the middle of the length of the beam (from point A) in kN.m is (round to the nearest integer): kN.m The bending moment at the two-thirds of the length of the beam (from point A) in kN.m is (round to the nearest integer): kN.marrow_forward
- 2. A 150 kip-ft (negative 150 kip-feet) moment is acting at the centroid of the cross section shown on the next page. Determine the bending stress-in psi - at a point that is located (a) at the top surface of the cross section. (b) 3 inches down from the top surface of the cross section. (c) 12 inches up from the bottom surface of the cross section. (d) 3 inches up from the bottom surface of the cross section. (e) at the bottom surface of the cross section. Marrow_forwardDetermine the bending stress at point A of the beam, and the orientation of the neutral axis. Using the method in Appendix A, the principal moments of inertia of the crosssection are Iz = 8.828 in4 and Iy = 2.295 in4, where z and y' are the principal axes. Solve the problem using Eq.arrow_forwardA simply supported beam of hollow rectangular cross section is 100mm deep and 60mm wide with a wall thickness of 10mm. The beam has a span of 6m and carries a load as shown . Neglecting the weight of the beam draw a bending moment diagram and calculate the maximum bending moment. And determine the maximum bending stress in the material.arrow_forward
- The cantilever beam AB will be installed so that the 60-mm side forms an angle β between 0 and 90° with the vertical. The 660-N vertical force P is applied at the center of the free end of the beam. Determine the value of β for which the normal stress at point a is a maximum and the corresponding value of that stress. (Round the final answer to two decimal places.)arrow_forwardFor the beam shown below, assume that E/= 6 × 104 kN-m² is constant through the length of the beam. If a = 3 m, b=5 m and c= 3 m and the distributed load w = 5.2 kN/m: a) determine beam slope at C. Enter your answer in rad to 5 decimal places. a B W b с с H Xarrow_forwardA cross-section of a beam is shown in Figure Q2. If the shear force in this section is V determine the value and the location of the maximum shear stress in the section. In Figure Q2, a = 68 mm and the origin of the coordinate system is at centroid of the cross section. y= A Z= a I₂ = S = AY mm; Figure Q2 Answer The vertical coordinate (y-coordinate; the y-axis serves as the axis of symmetry of the cross- section.) and horizontal coordinate (z-coordinate) of the location where the maximum shear stress occurs in the section are mm; O 4a Tmax= The vertical distance from the location where the maximum shear stress occurs in the section to the bottom side (AB) of the cross section can be calculated as Distance = mm B Second moment of area The second moment of area employed in the equation to calculate maximum shear stress can be calculated as Shear stress a (units : mm¹ ) First moment of area The first moment of area employed in the equation to calculate maximum shear stress can be…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY