
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
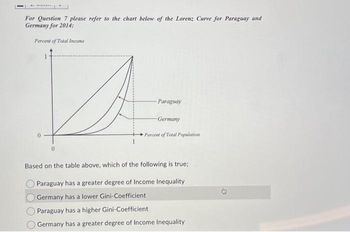
Transcribed Image Text:For Question 7 please refer to the chart below of the Lorenz Curve for Paraguay and
Germany for 2014:
Percent of Total Income
Paraguay
-Germany
Percent of Total Population
Based on the table above, which of the following is true;
Paraguay has a greater degree of Income Inequality
Germany has a lower Gini-Coefficient
Paraguay has a higher Gini-Coefficient
Germany has a greater degree of Income Inequality
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- As income transfer programs accompanying the War on Poverty increased beginning in the latter half of the 1960s, what happened to poverty in the United States? Check all that apply. After the start of the War on Poverty, the downward trend in the poverty rate halted. In 2018, the adjusted poverty rate was only 4 percentage points lower than the official rate in 1970. The poverty rate declined substantially in the period after the War on Poverty, but not in the period before the start of the War on Poverty. The adjusted poverty rate has declined rapidly and is now less than half of the official poverty rate.arrow_forwardPoverty profiles can play an important role in understanding poverty and formulating poverty reduction policies. Provide some specific examples to illustrate how poverty can be constructed and how they can be utilized to design policiesarrow_forwardThe $1.4 billion trick to make us accept income inequality Lotteries take money from the poor and redistribute it unequally. The poor, the uneducated, and minorities play the lottery the most, and it takes a big chunk of their income Source: The Huffington Post, January 12, 2016 If the news clip is correct, how does a lottery change the distribution of income? Draw two Lorenz curves to illustrate your answer. Lotteries result in the distribution of income Draw the Lorenz curve in a country that does not have lotteries. Label it Before Draw the Lorenz curve for the country after the introduction of lotteries. Label it After >>> To reposition the label click on the cross by the label box and dragging it 100 80 60 40- 20 Cumulative percentage of income 100 20 40 60 00 Cumulative percentage of households >>>Draw only the objects specified in the question Garrow_forward
- 3. Comparing Gini coefficients of different countries Aa Aa The following diagram shows the Lorenz curves for three countries. Country X's Lorenz curve is shown in blue, Country Y's Lorenz curve is shown in red, and Country Z's Lorenz curve is shown in green. Region I is the area above Country X's Lorenz curve and below the 45-degree line. Region II is the area below Country X's Lorenz curve and above Country Y's Lorenz curve. Region III is the area below Country Y's Lorenz curve and above Country Z's Lorenz curve. Region IV is the area below Country Z's Lorenz curve. INCOME (Cumulative percent) 100 80 60 40 20 0 The Gini coefficient for Country Z is given by Couny X 20 Country Y Country Z 11 III 60 IV 40 100 HOUSEHOLDS (Cumulative percent) 80 has the highest Gini coefficient.arrow_forwardIncomes in China and India are a small fraction of incomes in the United States. But incomes in China and India are growing more quickly those in the United States. Draw the world Lorenz curve before the growth in income in China and India. Label it Before. >>> Reposition the label by clicking on the edge of the label box and dragging it. Draw the world Lorenz curve after the growth in income in China and India. Label it After. Inequality between the people in China and India and the people in the United States is O A. increasing OB. staying relatively constant C. decreasing OD. increasing in some years and decreasing in other years % 5 6 Selected: none Oll 87 & 7 O * 8 O 100- 80- 60- 40- 20- 0 Cumulative percentage of income ( 9 20 40 80 60 Cumulative percentage of households >>> Draw only the objects specified in the question. Delete Clear * ? ) 0 Next x 10 an rld" it fe dust real- lesto SITI Oriente 1 C++ ( Camp.o NS 1 ye Coding hool Stu Mihailescu NS 2 year. ython - Fu ers [Tutoria…arrow_forwardGDP per capita does not account for distribution; consequently, economic growth may actually reduce inequality equalityarrow_forward
- Use the data from the table below to construct a Lorenz curve. Income Shares in the United States Lowest 20% Second Lowest 20% Third 20% Fourth 20% Highest 20% 5.2 10.3 15.3 22.4 46.9arrow_forwardQ2] Given is the data for Country A and B: Population Fraction Country A's Income Country B's Income bottom 25% 5 million 10 million 2nd 25% 10 million 15 million 3rd 25% 30 million 20 million top 25% 55 million 55 million a) Compute the cumulative income share and neatly plot (using Excel) the Lorenz curve for these two countries with labels. Feel free to use excel template that I have uploaded and copy paste the plot. b) Compute the Gini coefficient assuming the region beneath the two respective Lorenz curve is For country A = 0.2875 For country B = 0.3250arrow_forward2. Constructing a Lorenz curve from income shares data The following table shows the approximate income distribution for Peru, Bulgaria, and Lithuania in 2016. In particular, it shows the income shares of each fifth of the income distribution. Percentage Share, 2016 Percentage of Families Peru Bulgaria Lithuania Lowest fifth 4 9 7 Second-lowest fifth 8 14 12 Middle fifth 12 17 16 Second-highest fifth Highest fifth 20 22 22 56 38 43 has the most total income. On the following graph, plot the Lorenz curves for the three countries. Plot Peru's Lorenz curve using the green points (triangle symbol), Bulgaria's Lorenz curve using the blue points (circle symbol), and Lithuania's Lorenz curve using the purple points (diamond symbol). Be sure to plot the first point of each Lorenz curve at (0,0). Note: Plot your points in the order in which you would like them connected. Line segments will connect the points automatically. CUMULATIVE PERCENTAGE OF MONEY INCOME graph.) 100 20 40 60 80 100…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education