
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
For many materials, the stress-strain curve can be written by the Ramberg-Osgood equation presented below, where the parameters E, k and n are obtained from the stress-strain diagram of a given material. Considering the s-e diagram shown in the figure for a certain material, determine E, k and n and obtain the formula for the curve.
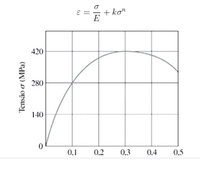
Transcribed Image Text:+ ko"
420
280
140
0,1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
Tensão o (MPa)
||
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Determine the elastic modulus and the yield strength for the material having the stress-strain curve shown. Use the 0.2% offset method. 1600 1400 1200 E 1000 800 600 400 200 0.5 1 1.5 2 Strain, percent Elastic modulus: (Express your answer in whole numbers.) E = ksi Yield strength: (Express your answer using three significant figures.) Sy = ksi Stress, psiarrow_forwardAn aluminum alloy [E = 70 GPa; v = 0.33; a = 23.0x10-6/°C] pipe is subjected to a tensile load P. The pipe has an outside diameter of D = 280 mm, a cross-sectional area of A = 7550 mm², and a length of L = 9.5 m. The initial longitudinal normal strain in the pipe is zero. After load P is applied and the temperature of the pipe has been increased by AT = 40°C, the longitudinal normal strain in the pipe is found to be 2260 με. Calculate the magnitude of load P. Answer: P = M. L kN D Parrow_forwardPlease show the step by step cancellation on how the bulk modulus formula became V2 formula (volume)arrow_forward
- The following stress condition is applied to a cubic material. Normal stress in the x direction is 15 Mpa, normal stress in the z direction is -7 Mpa and the shear stress in the x-z plane is 59 Mpa (a) Write the stress tensor (b) Find the maximum normal stress (c) Find the angle with respect to the x-axis at which the maximum normal stress is applied (d) Find the maximum shear stress (e) Determine the angle with respect to the x-axis at which the maximum shear stress is experiencedarrow_forwardA particular body is in plane stress where the normal and shear stresses vary with position according to the following continuous functions: 2x – y², 0yy = 10z,0xy 5x + 10y (values in N/m2) Oxx What body forces per unit volume (N/m³) are needed to keep the body in static equilibrium? O fx = 12, fy = 5 %D fx = 5, fy = 2 O fx = 10, fy = 0 O none neededarrow_forwardConsider a material with the stress-strain diagram shown where the yield point is 400 MPa (similar to a generic metal, but approximated to make the calculations easier). The material is stressed to 900 MPa. What is the change in the modulus of resilience? 1200- 800 σ (MPa) 400 a more realistic curve 0.10 0.20 0.30 0.40 εarrow_forward
- Given the stress tensor: Find: 3 36 27 0 σ = 27-36 00 0 18 (a) The components of the traction (force per unit area) acting on a plane with unit normal n= 2 21 3 3'3 T (b) The component of the traction in the direction of the normal (c) The angle between the traction and the normal vector (d) The magnitude of the traction vector (e) The net force acting on a cube with corners at (x,y,z)=(±1,±1,±1)arrow_forwardLast 2arrow_forward5 mm 40mm 20மm r 10 mm 20mm P.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY