
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
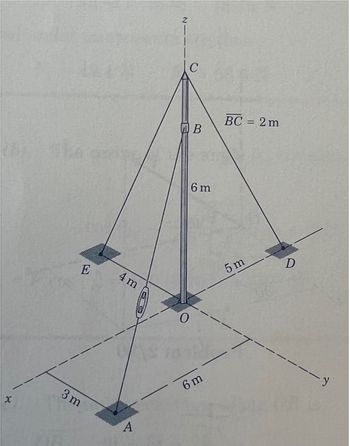
The tension in cable AB is 900 N. What is the component of force from this tension in the positive x direction? List in Newtons to three significant figures.
Transcribed Image Text:Sure!
---
**Figure Description and Analysis**
**Title: Guy Wire System for Tower Stabilization**
In the provided diagram, we observe a three-dimensional representation of a tower with multiple supporting guy wires. The system is designed to stabilize the tower using several key locations and dimensions.
**Diagram Breakdown:**
1. **Axis:**
- The diagram operates in a three-dimensional coordinate system with \(x\), \(y\), and \(z\) axes. The origin \(O\) is at ground level, where the tower appears to be anchored.
2. **Tower:**
- The vertical tower is denoted by coordinates \(O\) and \(B\) with a length of 6 meters.
- Point \(B\) is at the top of the vertical tower (at x = y = 0, z = 6 meters).
3. **Guy Wires:**
- Several guy wires are used to stabilize the tower by attaching it to the ground at various points.
- Wire BC is connected from point \(B\) of the tower to point \(C\) at the top (coordinates of C are unknown but it appears vertically aligned with \(O\)) and has a length of 2 meters.
4. **Anchoring Points:**
- The anchoring points for the guy wires on the ground are represented by points \(A\), \(D\), and \(E\).
- Point \(A\) is positioned at (x = 3 meters, y = -6 meters).
- Point \(D\) is located at (x = 5 meters, y = 6 meters).
- Point \(E\) is positioned at (x = -4 meters, y = -4 meters).
**Interpretations:**
- **Stability Mechanism:**
- The guy wires (lines connecting the top of the tower with points \(A\), \(D\), and \(E\)) are crucial for providing stability against lateral forces like wind pressure.
- By attaching the wires at strategically distant positions on the ground and connecting them to the tower, it ensures the stability and balance of the structure.
- **Geometric and Mechanical Considerations:**
- For engineering and mechanical design, understanding the lengths and angles of these wires, as well as the tensions they carry, is fundamental. This ensures the tower remains erect and safe under various force conditions.
This diagram serves as
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- WHAT ARE THE PROPERTIES OF THE PSEUDO-FORCES [CHORIOL, TRANSVERSE, AND PULSATINC], THEN ILLUSTRATE WITH A DRAWINGarrow_forwardQuestion 1(a) The bracket shown in Figure 1(a) is subjected to two forces F1 and F2. Resultant of these two forces is R which is directed as shown in the figure. Find the magnitudes of F, and F2 in Newtons and write these forces in Cartesian form. Take R = 420 N, a = 23.9 degrees and B = 40 degrees. y 35° a R B F2 Figure 1(a)arrow_forwardConsider the following force system 250 N XN 30° देख am YN where X = 350 N and Y = 600 N. Calculate the magnitude and direction of the resultant force. Enter your answer for the magnitude in N and the direction in degrees with respect to the positive x-axis, both correct to three significant figures in the appropriate boxes below. Magnitude: R= Direction: 0= N degreesarrow_forward
- You need the shear modulus for a particular material in order to calculate shear strain for a known applied shear shear stress. You can't find shear modulus for the material, but you can find elastic modulus (200 GPa) and Poisson's ratio (0.3). Which of the following could you use as the shear modulus for your calculations? 200 GPa O 60 GPa O 77 GPa O 154 GPaarrow_forwardTwo cables support an unknown weight. If the tension in cable BC is 100 lbs, thenwhat is the unknown weight? Don’t forget to draw a FBD. (Im new to this and need some help)arrow_forwardDetermine the stress resultants N(x), V(x), M(x) and draw the diagrams of the stress resultants and calculate the extremal values. At first, consider all parameters (F, a, L, ...) as variables and fill in their actual values at the end of your calculation.arrow_forward
- The figure shows a bicycle wheel resting against a small step whose height is h = 0.100 m. The weight and radius of the wheel are W = 20.0 N and r = 0.390 m. A horizontal force is applied to the axle of the wheel. As the magnitude of increases, there comes a time when the wheel just begins to rise up and loses contact with the ground. What is the magnitude of the force when this happens? Number Units ✪ Farrow_forwardAn object is subjected to four forces as shown in figure Q1(a). Determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant force. F2= 600 N F = 800 N 45°- 60 F4= 300 N 13 12 F = 650 Narrow_forwardThe force shown in the figure (Eigure 1) moves an object from -010 -0.75 1. Figure Force, F (N) 0.8/ 0.6 0.4- 0.2 0 0.25 0.50 Position, x (m) 0.75 1 of 1 ▼ How much work is done by the force? Express your answer using two significant figures. View Available Hint(s) ΠΡΕΙ ΑΣΦΑ + W Submit Part B ? W How much work is done by the force if the object moves from 0.15 m 10-0.60 m 7 Express your answer using two significant figures. View Available Hint(s) VG] ΑΣΦ J ? Jarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY