
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
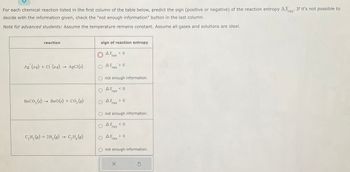
Transcribed Image Text:**Chemical Reaction Entropy Prediction Worksheet**
For each chemical reaction listed in the table below, predict the sign (positive or negative) of the reaction entropy (ΔS_rxn). If it's not possible to decide with the information given, select "not enough information".
**Note for Advanced Students:** Assume the temperature remains constant. All gases and solutions are ideal.
| Reaction | Sign of Reaction Entropy |
|---------------------------------------|-----------------------------------|
| Ag⁺(aq) + Cl⁻(aq) → AgCl(s) | ⦿ ΔS_rxn < 0 |
| | ○ ΔS_rxn > 0 |
| | ○ Not enough information |
| | |
| BaCO3(s) → BaO(s) + CO2(g) | ○ ΔS_rxn < 0 |
| | ○ ΔS_rxn > 0 |
| | ○ Not enough information |
| | |
| C2H2(g) + 2H2(g) → C2H6(g) | ○ ΔS_rxn < 0 |
| | ○ ΔS_rxn > 0 |
| | ○ Not enough information |
**Legend:**
- \( \Delta S_{\text{rxn}} < 0 \): The reaction decreases entropy.
- \( \Delta S_{\text{rxn}} > 0 \): The reaction increases entropy.
- Not enough information: Inadequate data to determine the sign of entropy change.
The table has options for each reaction, with the first reaction (Ag⁺(aq) + Cl⁻(aq) → AgCl(s)) selected for \( \Delta S_{\text{rxn}} < 0 \), indicating a decrease in entropy.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The standard reaction free energy AG=-1482. kJ for this reaction: 4 Fe(s) + 30₂(g) 2 Fe₂O3(s) Use this information to complete the table below. Round each of your answers to the nearest kJ. reaction 2Fe₂O₂ (s) 4Fe(s) + 30, (g) - Fe(s) + O₂(g) → Fe₂03 (s) Fe₂O₂ (s) → Fe(s) + 0₂ (8) AG kJ kJ X 5arrow_forward16. Answer question in pic :)arrow_forwardCalculate the standard entropy, ASixn, of the reaction at 25.0 °C using the table of thermodynamic properties. C₂H₂(g) + H₂O(1) C₂H₂OH(1) ASixn -1.3 ×10² = Calculate the standard Gibbs free energy of the reaction, AGixn. The standard enthalpy of the reaction, AHin, is -44.2 kJ.mol-¹. AGixn = -5.5 Incorrect J.K¯¹·mol¯¹ kJ.molarrow_forward
- https://www.webassign.net/blb12/a-table-c.pdf ^ | Just copy and paste this in the search bar into googlearrow_forwardFor each of the following reactions determine if the change in entropy was positive or negative:A) Water at 40°C → Water at 25°CB) 2NO2(g) → N2O4(g)C) CH3OH (l) → CH3OH (g)D) PbCl2(s) → PbCl2(aq)arrow_forwardFor a gaseous reaction, standard conditions are 298 K and a partial pressure of 1 atm for all species. For the reaction N₂(g) + 3 H₂(g) ⇒ 2NH₂(g) the standard change in Gibbs free energy is AG° = −32.8 kJ/mol. What is AG for this reaction at 298 K when the partial pressures are PN₂ = 0.100 atm, PH₂ = 0.100 atm, and PNH₂ = 0.750 atm? AG = 737 kJ/molarrow_forward
- The standard reaction free energy AG° = 29. kJ for this reaction: Fe2O3(g) + 2H2 (g) --> 2 Fe(s) + 3H2O(l) Use this information to complete the table below. Round each of your answers to the nearest kJ.arrow_forwarddetermine whether each reaction is spontaneous under standard conditions. If a reaction is not spontaneous, write the corresponding spontaneous reaction. K2O2 (s) → 2K (s) + O2(g) PbCO3 (s) → PbO (s) + CO2 (g) P4 (s) + 6H2(g) → 4PH3 (g) 2AgCl (s) + H2S (g) → Ag2S (s) + 2HCl (g)arrow_forwardFor each chemical reaction listed in the first column of the table below, predict the sign (positive or negative) of the reaction entropy ASxn. If it's not possible to decide with the information given, check the "not enough information" button in the last column. Note for advanced students: Assume the temperature remains constant. Assume all gases and solutions are ideal. reaction + Ag (aq) + Cl (aq) Ag Cl (s) C₂H₂(g) + 2H₂(g) → C₂H₂(g) 6 MgCl₂ (s) + H₂O(1) MgO (s) + 2H C1 (g) sign of reaction entropy AS 0 rxn not enough information. AS 0 rxn not enough information. AS 0 not enough information. Xarrow_forward
- The standard reaction free energy AG° = - 190. kJ for this reaction: CH3OH(g) + CO(g) -»HCH3CO2(l) Use this information to complete the table below. Round each of your answers to the nearest kJ.arrow_forwardWhich pure substance under standard conditions would have the highest entropy? O2 HCl CH3OH Sarrow_forwardExplain pleaseeeeeeeeeeearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY