
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
For customers purchasing a refrigerator at a certain appliance store, let A be the
| P(A) = 0.76 | P(B | A) = 0.85 | P(B | A') = 0.75 |
| P(C | A ∩ B) = 0.84 | P(C | A ∩ B') = 0.61 | |
| P(C | A' ∩ B) = 0.69 | P(C | A' ∩ B') = 0.32 |
(a) Construct a tree diagram consisting of first-, second-, and third-generation branches and place an event label and appropriate probability next to each branch.
(b) Compute P(A ∩ B ∩ C). (Round your answer to four decimal places.)
(c) Compute P(B ∩ C). (Round your answer to four decimal places.)
(d) Compute P(C). (Round your answer to four decimal places.)
(e) Compute P(A | B ∩ C), the probability of a U.S. purchase given that an icemaker and extended warranty are also purchased. (Round your answer to four decimal places.)
(c) Compute P(B ∩ C). (Round your answer to four decimal places.)
(d) Compute P(C). (Round your answer to four decimal places.)
(e) Compute P(A | B ∩ C), the probability of a U.S. purchase given that an icemaker and extended warranty are also purchased. (Round your answer to four decimal places.)
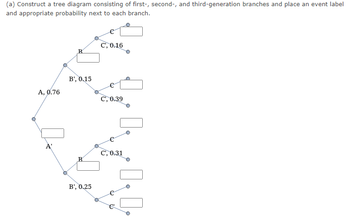
Transcribed Image Text:(a) Construct a tree diagram consisting of first-, second-, and third-generation branches and place an event label
and appropriate probability next to each branch.
A, 0.76
2
B
B', 0.15
B', 0.25
C', 0.16
C', 0.39
C', 0.31
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- During the past 6 months, Rebecca has been late to work 20 out of 125 days. Also, during that time, she encountered a traffic jam on 25 out of the 125 days. On any given day, the probability that she is late to work AND encounters a traffic jam is 0.35. Based on the information, which of following can be concluded? A.O The probabilities of Rebecca being late to work and encountering a traffic jam are NOT independent, because 0.16 x 0.2 + 0.35 B.O The probabilities of Rebecca being late to work and encountering a traffic jam ARE independent, because 0.16 + 0.2 + 0.35 C.O The probabilities of Rebecca being late to work and encountering a traffic jam ARE independent, because 0.16 x 0.2 0.35 D.O The probabilities of Rebecca being late to work and encountering a traffic jam are NOT independent, because 0.16 + 0.2 + 0.35 Copyright © 2021 Illuminate Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Lenovo 11e Home End W E R SO F H. Karrow_forwardAccording to Bayes' Theorem, the probability of event A, given that event B has occurred, is as follows. P(A) • P(B| A) P(A) • P(B| A) + P (A') •P(B| A') P(A| B) = %3D Use Bayes' Theorem to find P(A B) using the probabilities shown below. P(A) =1. P(A') =, P(B| A) =5, 1 and P(B| A') = %3D %3D 10 %3D 4 The probability of event A, given that event B has occurred, is P(A B) =|. (Round to the nearest thousandth as needed.)arrow_forward11. Find the probability of the indicated event if P(E) = 0.20 and P(F)= 0.35. Find P(E and F) if P(E or F)= 0.30 P(E and F) = (Simplify your answer.)arrow_forward
- Find the probability that the car needs work on either the engine, the transmission, or both. Find the probability that the car needs no work on the transmission.arrow_forwardb. Determine P(F or D)= P(F or D). (Type an integer or a decimal.) c. Find the probability that a randomly selected adult is male. P(male) = (Type an integer or a decimal.)arrow_forwardYou purchase a brand new car for $15,000 and insure it. The policy pays 78% of the car's value if there is an issue with the engine or 30% of the car's value if there is an issue with the speaker system. The probability of an issue with the engine is 0.009, and the probability there is an issue with the speaker system is 0.02. The premium for the policy is p. Let X be the insurance company's net gain from this policy. (a) Create a probability distribution for X, using p to represent the premium on the policy. Enter the possible values of X in ascending order from left to right. P(X) (b) Compute the minimum amount the insurance company will charge for this policy. Round your answer to the nearest centarrow_forward
- S P(A/B): A Let event A = Student belongs to at least one club on campus and event B = Student participates in team sports on campus P(B|A) = ANB At AnyTown Polytechnic College, 42% of students belong to a campus club, 38% of students participate in team sports, and 5% belong to at least one campus club and participate in team sports. Compute the probabilities requested below. Round all probabilities to four decimal places, as needed. P(ANB) = P(AnB): Barrow_forwardFor customers purchasing a refrigerator at a certain appliance store, let A be the event that the refrigerator was manufactured in the U.S., B be the event that the refrigerator had an icemaker, and C be the event that the customer purchased an extended warranty. Relevant probabilities are below. P(A) = 0.74 P(B | A) = 0.85 P(B | A') = 0.82 P(C | A ∩ B) = 0.76 P(C | A ∩ B') = 0.55 P(C | A' ∩ B) = 0.75 P(C | A' ∩ B') = 0.25 (a) Construct a tree diagram consisting of first-, second-, and third-generation branches and place an event label and appropriate probability next to each branch. (b) Compute P(A ∩ B ∩ C). (Round your answer to four decimal places.)(c) Compute P(B ∩ C). (Round your answer to four decimal places.)(d) Compute P(C). (Round your answer to four decimal places.)(e) Compute P(A | B ∩ C), the probability of a U.S. purchase given that an icemaker and extended warranty are also purchased. (Round your answer to four decimal places.)arrow_forwarda and barrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman