
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
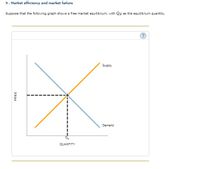
Transcribed Image Text:5. Market efficiency and market failure
Suppose that the following graph shows a free market equilibrium, with Qg as the equilibrium quantity.
Supply
Demand
QUANTITY
PRICE

Transcribed Image Text:For an output level exactly at QE, the value of a unit to a buyer is
the cost of a unit to a seller.
Suppose a firm that produces for this market employs a private security force that makes town residents, many of whom have no business with the
company, feel safer. This scenario is characterized by
which is an example of
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Continuing from the previous questions where you are a manager of a firm is the exclusive manufacturer of a unique pair of rainbow shorts with demand and cost functions that are Q=100−2P; C=40+2Q2. Now assume that the firm incurs a one-time cost of $10 for a zoning violation. What is the price that the manager should now charge to maximize profits? (Just give the number, no need to include "$")arrow_forwardPlease answer all parts...arrow_forwardRecall a sharecropping agreement is where a farmer provides a percentage of their yield to a landowner in exchange for renting the land. Consider the graph below and answer the following questions (include calculations in work): 11 VMPL 10 8 a*VMPL 5 4 3 2 1 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 Labor (Hour) "andınoarrow_forward
- There are two firms in a market, where quantities are the strategic variable within two periods. In each of the two periods t = 1; 2 the inverse demand function Ptis given by P: (y') = 5-y'. The cost function of firm i is given by C=3+2y, where i=1,2. In the first period firm1 is a protected monopolist. Profits of a firm can be interpreted as the sum of its profits in each period. In order to maximize their profits, firms set quantities. Define the monopoly solution. (i) (ii) Firm1 must choose the same quantity in each period y = yf due to the technological restrictions. Considering ył firm2 thinking to enter in period 2. Define the profit maximizing yi if y is given. (iii) Suppose that firm 2 will enter in the second period. What quantity will firm 1 have? What is the equilibrium P, Q and profit?arrow_forwardSuppose that the following graph shows a free market equilibrium, with QE as the equilibrium quantity. PRICE QE QUANTITY Supply Demand For an output level exactly at Q, the value of a unit to a buyer is ? the cost of a unit to a seller.arrow_forwardam. 128.arrow_forward
- Suppose that a factory that enjoys a monopoly in their market has one of their senior engineers retire. Losing this engineer caused the marginal and average total costs to increase by $20. As a result of this rise in costs, the factory changes its price to continue to maximize profit. We should expect production to: Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer. a increase. b decrease. not change.arrow_forwardSuppose the inverse demand curve in a market is D(p) =a-bp, where D(p) is the quantity demanded and p is the market price. Firm 1 is the leader and has a cost function c1(y1)=cy1 while firm 2 is the follower with a cost function c2(y2 )= y^22/2 (picture attached). Firm 1 sets its price to maximise its profit. Firm 1 correctly forecasts that the follower takes the price leader’s chosen price as given (price taker) and chooses output so as to maximise its own profit. Write down the profit function of the follower. Calculate the profit maximising quantity that the follower selects given the leader’s chosen price p (i.e., calculate the follower’s supply curve S(p)). Interpret the solution to the profit maximising problem. The leader is facing the residual demand curve R(p)=D(p)-S(p) with D(p) and S(p) as defined in (c) above. Calculate the leader’s residual demand curve using the result in (c). Solve for p as a function of the leader’s output y1, i.e. the inverse demand function facing…arrow_forwardProblem 6 Casper consumes cocoa and cheese. Cocoa is sold in an unusual way. There is only one supplier, and the more cocoa you buy from him, the higher the price you have to pay per unit. In fact y units of cocoa will cost Casper y² dollars (i.e. the price of y units is y dollars, hence the quadratic cost). Cheese is sold in the usual way at a price of 2 dollars per unit. Casper's income is 20 dollars and his utility function is U(x, y) = x+2y, where z is his consumption of cheese and y is his consumption of cocoa. a. Sketch Casper's budget set and shade it in. b. Sketch some of his indifference curves and label the optimal bundle that he chooses. c. Calculate the amount of cheese and the amount of cocoa that Casper demands at these prices and this income, i.e. calculate the optimal bundle. (Recall that you can find the slope of any curve using the Total Differential, i.e. the MRS formula works in general)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education