
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Blank options:
Blank 1- equal to/greater than/less than
Blank 2- an externality/market power
Blank 3-
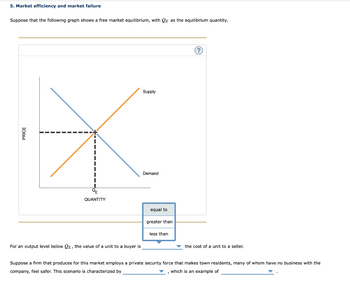
Transcribed Image Text:5. Market efficiency and market failure
Suppose that the following graph shows a free market equilibrium, with QE as the equilibrium quantity.
PRICE
QUANTITY
For an output level below QE, the value of a unit to a buyer is
Supply
Demand
equal to
greater than
less than
(?)
the cost of a unit to a seller.
Suppose a firm that produces for this market employs a private security force that makes town residents, many of whom have no business with the
company, feel safer. This scenario is characterized by
which is an example of
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Part d-garrow_forwardWhen producing a good generates external costs, the producing firm's supply curve will Multiple Choicea. be vertical.b. overstate the total cost of production.c. be above (to the left of) the total-cost supply curve.d. understate the total cost of production.arrow_forward1. An externality exists when agent A’s utility or production function depends on real variables chosen by another agent B, without an offer of compensation or other attention given to the effect of A’s well-being. True or False 2. The "invisible hand" of the market leads to the efficient allocation of goods and services, even in the presence of externalities. True or False 3. If there is a negative production externality, the market price of the good will be higher than the socially-optimal price. True or Falsearrow_forward
- Some economists claim that early child care generates an external benefit to society. a. What is the market equilibrium? What is the socially optimal outcome? How do they differ? b. The government is planning to provide a per-unit subsidy for child care to achieve the socially optimal outcome. How large should this subsidy be? c. How much is the total government subsidy each month to reach a socially optimal outcome?arrow_forwardWhich of the following instruments is government most likely to apply when confronted with a positive externality? (a) Subsidies. (b) Taxation. (c) Coase bargaining. (d) Usage fees.arrow_forwardpart Barrow_forward
- 2. Refer to Graph 10-1. Assume the externality is not internalised. What is the loss to society from the last unit of the good produced by the market? A. P3-P2 B. P2-P1 C. P3-P1 D. ZeroGraph 10-1 Note:- Do not provide handwritten solution. Maintain accuracy and quality in your answer. Take care of plagiarism. Answer completely. You will get up vote for sure.arrow_forwardter 5 i A public good Multiple Choice generally results in substantial negative externalities. can never be provided by a nongovernmental organization. costs essentially nothing to produce and is thus provided by the government at a zero price. can't be provided to one person without making it available to others as well.arrow_forward23arrow_forward
- I Price and cost (thousands of dollars per student) 20 16 12 8 0 200 A) 0 students; 400 students B) 600 students; 600 students C) 400 students; 600 students D) 600 students; 400 students E) 400 students; 400 students S = MC MSB MB 400 600 800 1,000 Quantity (students per year) 35) 35) The figure above shows the market for private elementary school education in Chicago. There is no external cost of private elementary education. If the government does not intervene in this market, the equilibrium number of students being privately educated is and the efficient quantity isarrow_forwardIf the market for a good is producing a negative externality in production (e.g. a polluting firm):(a) In market equilibrium, the marginal cost (MC) to society exceeds the marginal cost (MC) of production.b) In market equilibrium the marginal benefits to society exceed the marginal cost (MC) of production.(c) In market equilibrium the marginal costs (MC) to society exceed the total benefits to societyd) In market equilibrium the private Cmg (MC) of production exceeds the Cmg (MC) for society.For each of the alternatives, explain which is correct and explain which are false or uncertain.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education