
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
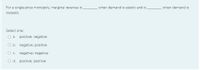
Transcribed Image Text:For a single-price monopoly, marginal revenue is
when demand is elastic and is
when demand is
inelastic.
Select one:
O a. positive; negative
O b. negative; positive
O c. negative; negative
O d. positive; positive
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- QUESTION 8 Which of the following is true for monopoly and perfect competition? O A. The demand for the individual firm's product is perfectly elastic. O B. Economic profits can be sustained indefinitely over time. OC. Marginal revenue is horizontal at the industry equilibrium price. O D. Profits are maximized by producing at the level of output where marginal revenue is equal to marginal costarrow_forwardThe accompanying graph depicts the Marginal Cost (MC), Average Total Cost (ATC), and Marginal Revenue (MR) curves for a perfectly (or purely) competitive firm. Move point A to identify the profit maximizing price and quantity for this firm. Price and Cost 20 19 18 17 16 DEHBEFOON OSION-O 15 14 13- 12 11 10 8 6 4 MR=D A Perfectly Competitive Firm A MC ATC 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Quantityarrow_forward✓ Question Completion Status: A non- competitive firm's demand curve is P = 10-4Q. So its MR is O 5-2Q O 10-40 10-8Q 05-Q QUESTION 3 For a non-competitive firm with a demand curve P = 1800-2Q and marginal costs of MC = $200, how much is the equilibrium quantity (Q)? 360 400 560 620 QUESTION 4 For a non-competitive firm with a demand curve P = 1800-2Q and marginal costs of MC = $200, how much is the equilibrium price (P*)? O $500 (4750 Click Save and Submit to save and submit. Click Save All Answers to save all answers. Save All Ararrow_forward
- Refer to the diagram to the right. Suppose the firm is currently producing Q, units. What happens if it expands output to Q, units? TC TR O A. It incurs a loss. O B. It will be moving toward its profit maximizing output. Oc. It makes less profit. O D. Its profit increases by the size of the vertical distance df. a 1,000 Qo Q, Q2 Q3 Quantity d...... . ....... Costs and revenuearrow_forwardplease fast 31.arrow_forwardThe perceived demand curve for the is Select the correct answer below: O perfectly competitive firm; also the market demand curve O perfectly competitive firm; downward sloping O monopolist; upward sloping O monopolist; also the market demand curvearrow_forward
- In the Cournot model the final level of output is the output that would be produced if the industry was a monopoly, and is the output that would be produced if the industry was perfectly competitive. O a. greater than; less than O b. greater than; equal to Oc. equal to; less than O d. less than; greater than In the Cournot model, when a new firm begins production it assumes its demand curve is O a. the market demand less the amount the other firm is selling. O b. the market demand plus the amount the other firm is selling. Oc. the same as the competing firm's demand curve. O d. one-half of the competing firm's demand curve.arrow_forward#2arrow_forwardFigure A Competitive Firm1.2 MC ATC AVC Given Pl =$7.00 P2 $8.50 P3 =$9.20 QI=100.00 A P3 B P2 P1 MR Quantity Q1 Refer to Figure A Competitive Firm1.2. At an output level of Q1, the average fixed cost is about O $0.70 O No answer text provided. O No answer text provided. O S0.80 %24arrow_forward
- Market power is what allows firms to make profit and it comes from all of the following except O Patents High consumer demand Government licenses Product innovationarrow_forwardQuestion 3 The demand curve facing a monopoly firm is: O A. equivalent to the market demand curve. B. horizontal at the market equilibrium price. C. non-existent D. equivalent to the firm's marginal cost curve.arrow_forwardSuppose a perfectly competitive industry can produce a product with total cost TC = 30 and the market demand for the product is given by Q = 120- Suppose that the same market can be served by a monopolist operates with the same cost and demand functions. How does the consumer surplus change due to monopoly relative to perfect competition? O It falls by 3600 It does not change OIt falls by 6000 It falls by 4800arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education