
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
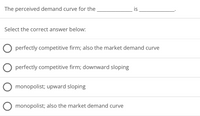
Transcribed Image Text:The perceived demand curve for the
is
Select the correct answer below:
O perfectly competitive firm; also the market demand curve
O perfectly competitive firm; downward sloping
O monopolist; upward sloping
O monopolist; also the market demand curve
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Which of the following statements about monopolies are correct? There is more than one correct answer to this question. You must mark all of the correct answers to receive full credit for this question. OAt the profit maximizing output for a monopoly, P< MR. OMonopolies are always illegal in the U.S. O If a firm enjoys decreasing returns to scale, this may help it to become a monopoly. In a pure monopoly, the firm is the industry. O A patent can help a firm to become a monopoly.arrow_forwardA monopolist is able to maintain into the long run primarily because a. barriers to entry exist b. of collusive behavior c. of mutual interdependence d. of price taking behavior e. of product differentiationarrow_forwardWhich of the following statements is true of a monopoly as compared to a perfectly competitive market with the same costs? * Consumer surplus is smaller. Profit is smaller. Deadweight loss is smaller. Total surplus is larger. O Quantity is larger.arrow_forward
- The graph below shows the demands and marginal revenue in two markets, 1 and 2, for a price discriminating firm along with total marginal revenue, MRT, and marginal cost: Price and cost (dollars) 100 80 60 AS 40 20 0 200 100 300 MR1 400 MR2 MC 500 Quantity How should the firm allocate sales between the two markets? 600 D₁ 700 MRT 800 900 D₂ 1000 Qarrow_forwarda) True or False and Explain: A profit maximizing monopolist has no limit to how high they set the price. b) True of False and explain: When there are economies of scale in production it is possible for a competitive market to sustain the competitive equilibrium. c) When there are economies of scale in production, why is it beneficial to have only one producer?arrow_forwardThe graph shown represents the cost and revenue curves faced by a monopoly. 22 P3 P2 P1 PO MC ATC Q1 Q2 MR Which of the following statements is true? 1. The outcome in a monopoly market would be Q1, P1. II. The outcome in a perfectly competitive market would be Q2, P2. III. The efficient outcome is Q2, P2. Multiple Choice I and II only ○ I only II and Ill only I, II, and III barrow_forward
- Consider a monopoly firm in the short run for which marginal revenue equals rising marginal cost at 150 units of output. At this output, the firm's total cost is $2000, total fixed cost is $800, marginal revenue is $3, and elasticity of demand is 2. Which of the following statements is correct about this firm? The firm should expand production beyond 150 units. O The firm is making a loss greater than total fixed cost and should shut down. The firm is making a profit and should continue to produce 150 units. The firm is making a loss smaller than total fixed cost and should continue to produce 150 units.arrow_forwardQUESTION 2 Quantity 1 2 3 5 456 7 8 9 Price с с с с с с сл сл сл 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 The price and quantity relationship in the table is most likely that faced by a firm in a O monopoly. O concentrated market. O competitive market. O strategic market.arrow_forwardPlease indicated each statement as correct or incorrect..arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education