
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
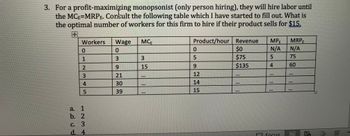
Transcribed Image Text:3. For a profit-maximizing monopsonist (only person hiring), they will hire labor until
the MCE=MRPE. Consult the following table which I have started to fill out. What is
the optimal number of workers for this firm to hire if their product sells for $15.
+
Workers
0
12345
1
a.
b. 2
C. 3
d. 4
Wage
0
3
9
21
30
39
MCE
3
15
111
Product/hour Revenue MPE
N/A
5
0
SIIHE
5
9
12
14
15
$0
$75
$135
LER
4
T
110
F FOCUS
MRPE
N/A
75
60
40
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Complete the following labor supply table for a firm hiring labor competitively: Marginal Resource Wage Rate Marginal Revenue Product Units of Labor Total Labor Cost (Labor) Cost $14 - - 1 14 $38 14 28 3 14 24 4 14 20 14 14 14 10 2.arrow_forwardYou are a labor economist trying to evaluate whether the labor market for computer scientists is competitive or monopsonistic. Based on previous research, you know that the production function for computers depends only on labor input: Y = -0.5L^2 + 10L; where Y is the output of computers and L is the quantity of labor used. The price of a computer is p = 2. You also know that the labor supply, as a function of the wage, for computer scientists is the following, where w is the wage per unit of labor: L = -10 + w. a. Find the equilibrium wages and employment (wc; Lc) that would prevail if the market for computer scientists were competitive. [Remember that a competitive firm takes the wage as given : that is, it assumes that the quantity of workers that it hires has no effect on the price of the next worker. (Of course, the equilibrium wage must equate demand and supply)].arrow_forwardIf there is inelastic demand for your labor, how does that influence individual (or union) "bargaining power"?arrow_forward
- The inverse labour demand curve of a monopsonist employer is W = 38,500 – 112L, where W is the annual salary and L is the number of workers hired. The labor supply is given by W = 10,700 + 100L. (a) The marginal expenditure equation is ME= . Do not include a comma in your answer. Please use capital letters (e.g. L not l) (b) To the nearest integer, the monopsonist would hire workers and, given that number of workers, the salary they would pay is, rounded to 2 decimal places (e.g. 4.12) . Do not include a comma in your answer.arrow_forwardSolve for and fill in the missing portions of the following table to derive the monopsonist's derived demand curve for labor and answer the following question: Number of Total Physical Marginal Physical Product Marginal Revenue Workers Product Price Product 246 9,557.10 32.70 1 32.70 247 9,589.75 32.65 1 32.65 248 9,622.35 32.60 1 32.60 249 9,654.90 32.55 1 32.55 250 9,687.40 32.50 1 32.50 251 9,719.85 32.45 1 32.45 252 9,752.25 32.40 1 32.40 253 9,784.60 1 32.35 254 9,816.90 32.30 1 32.30 Question: What is the marginal revenue from hiring the 253rd worker? $32.40 $32.30 $32.35arrow_forwardWhat is a monopsony? What distinguishes a monopsony from a competitive employer of inputsarrow_forward
- 23. Question 23 is based on the below-mentioned diagram illustrates a monopsony outcome. The monopsony firm MRP = marginal revenue product, MFC = marginal factor cost and the wage is determined by the labour supply curve at this level of output. In the absence of a union the monopsony firm hires Lm workers and pays them Wm. MFC wage Wu Wm Lm S O a. hire less than Lm workers. Ob. hire a maximum of Lm workers. Ochire greater than Lm workers. Od. None of the above. MRP Quantity of labor Suppose the union and firm negotiates a wage above Wu, the firm will Aarrow_forwardLabor (workers per day) Total Product (per day) 10 4000 11 4389 12 4752 13 5083 14 5376 15 5625 The firm can hire as many workers as they want at the prevailing market wage of $150 a day per worker. In addition, the firm pays $200 a day for equipment. Enter ONLY numbers. No comma, units, or decimals. 1. What is the marginal product of the 12th worker? 2. What is the average product of hiring 12 workers? 3. What is the total variable cost per day if 12 workers are hired ? 4. What is the total fixed cost per day if 12 workers are hired?arrow_forwardFill in the blanks: Workers Employed 0 1 2 3 4 Quantity Produced 0 15 25 33 39 Output Price ($) 10 10 10 10 10 Refer to the above table for a profit-maximizing, competitive firm. If the prevailing wage is $100, then the firm will hire worker(s).arrow_forward
- Use the data in the tables to answer the question that follows. Market Price of Output Quantity Supplied of Output Quantity Demanded of Output $5 25,000 60,000 $10 50,000 50,000 $15 75,000 40,000 $20 100,000 30,000 $25 125,000 20,000 Firm Quantity of Labor Total Product 0 0 15 105 30 190 45 265 60 325 What is the marginal revenue product of the 45th unit of labor, assuming this market is perfectly competitive in both the factor and output markets? A-$30. B-$50. C-$63. D-$100. E-$2,650 (2) The marginal benefit to suppliers will be less than the marginal cost to the single buyer. This describes A-perfect competition. B-monopolistic competition. C-an oligopoly. D-a monopoly E-a monopsonyarrow_forwardRead the "Clear it Up: Do Profit Maximizing Employers Exploit Labor" Do Profit Maximizing Employers Exploit Labor? (Source: OER) If you look back at the labor dynamics of supply and demand, you will see that only the firm pays the last worker it hires what they’re worth to the firm. Every other worker brings in more revenue than the firm pays him or her. This has sometimes led to the claim that employers exploit workers because they do not pay workers what they are worth. Let’s think about this claim. The first worker is worth $x to the firm, and the second worker is worth $y, but why are they worth that much? It is because of the capital and technology with which they work. The difference between workers’ worth and their compensation goes to pay for the capital, technology, without which the workers wouldn’t have a job. The difference also goes to the employer’s profit, without which the firm would close and workers wouldn’t have a job. The firm may be earning excessive profits,…arrow_forwardSuppose the market supply is given by L=2.8w. Assume the product market is competitive and the product price is p=$12. Also suppose MPL=8.6-0.8L and that the firm has monopsony power. A.Graph the marginal revenue product of labour. The slope of this curve is equal to The vertical intercept of this curve is equal to .Write the formula for the inverse supply of labour and graph the supply curve. The slope of this supply curve is B. For this firm, the fully simplified formula for marginal cost is MC₁ = __ L (Enter the value which completes the formula. Do not enter the variable, it has been given) Illustrate this market graphically, including accurate numbers for slopes and intercepts. Write the condition which the monopsonist's optimal choice of labour must satisfy. This monopsonist will choose employment level . At this employment level, the firm will offer the wage $ , and the value marginal product of labour is $ The average cost of labour for this monopsonist is $ and the firm's…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education