
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
For a certain chemical reaction , the standard Gibbs free energy of reaction is 83.7 kJ. Calculate the
temperature at which the equilibrium constant
K = 1.9x 10-16
Round your answer to the nearest degree.
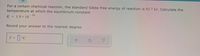
Transcribed Image Text:For a certain chemical reaction, the standard Gibbs free energy of reaction is 83.7 kJ. Calculate the
temperature at which the equilibrium constant
K = 1.9x 101.
Round your answer to the nearest degree.
T =
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A 65.0 g piece of gold at 650 K is dropped into 162 g of H2O(l) at 298 K in an insulated container at 1 bar pressure. CP,m for Au and H2O at 298 K are 25.4 and 75.3 J⋅K−1⋅mol−1, respectively. Calculate the temperature of the system once equilibrium has been reached. Assume that CP,m for Au and H2O are constant at their values for 298 K throughout the temperature range of interest.arrow_forwardFor the reaction: 1A(g) + 4B(g) 5 2C(g) + 2D(g) where Kp = 9.483 · 103 %3D the gaseous components are added, each at a partial pressure of 1.238 atm, to a 4.101L vessel at 32.19 °C. Calculate the AG (in kJ) for this reaction under these conditions. 0°C = 273.15 K Ř = 8.314 J/K (molar Universal Gas Constant) %D The answer is given with three numbers after the decimal (do not apply significant figure rules). Example: 25.123arrow_forwardFor a certain chemical reaction, the standard Gibbs free energy of reaction is -107. kJ. Calculate the temperature at which the equilibrium constant K = 1.2 × 1020 Round your answer to the nearest degree. T = 0 °Carrow_forward
- For a certain chemical reaction, the standard Gibbs free energy of reaction at 15.0 °C is 147. kJ . Calculate the equilibrium constant K for this reaction.Round your answer to 2 significant digits.arrow_forwardFor a certain chemical reaction, the standard Gibbs free energy of reaction at 30.0°C is 73.3 kJ. Calculate the equilibrium constant K for this reaction. Round your answer to 2 significant digits.arrow_forwardConsider the oxidation of a generic metal M into a metal oxide as shown in the reaction. 2 M(s) +20₂(g) → M₂O4(s) For this reaction, AH = -4.961 kJ/mol and AS ixn = 12.12 J/(mol-K) at 298 K. What is the standard change in Gibbs free energy for the reaction in the forward direction? AGixn= What is the equilibrium constant of this reaction at 298 K? Kp = What is the equilibrium pressure of O₂(g) over M(s) at 298 K? MacBook Pro tyne URI + kJ/mol Oarrow_forward
- The equilibrium constant for a system at chemical equilibrium at 318 oC is 3.4 x 10-3. Calculate the Gibbs free-energy change, deltaGo, for the system at 318 oC.Enter your answer here: kJ/molarrow_forwardFor a gaseous reaction, standard conditions are 298 K and a partial pressure of 1 atm for all species. For the reaction N, (g) + 3 H, (g) = 2 NH,(g) the standard change in Gibbs free energy is AG° = –72.6 kJ/mol. What is AG for this reaction at 298 K when the partial pressures are PN, = 0.500 atm, PH, = 0.500 atm, and PNH, = 0.600 atm? AG = kJ/molarrow_forwardEnter your answer in the provided box. Kf for the complex ion Ag(NH3)2+ is 1.5 × 107 at 25 ° C. Using this information, calculate the value of Δ G o f for Ag(NH3)2+(aq).arrow_forward
- Determine the molar ΔH°solution for a soluble ionic compound when the dissolution of 0.171 moles of that compound leads to a 12.9 °C temperature increase in a constant pressure calorimeter. The heat capacity of the calorimeter is 1.120 kJ/℃.arrow_forwardFor a certain chemical reaction, the standard Gibbs free energy of reaction is -133. kJ. Calculate the temperature at which the equilibrium constant K = 8.2 x 10- 22 Round your answer to the nearest degree. T= \| °Carrow_forwardFor a certain chemical reaction, the standard Gibbs free energy of reaction is - 149. kJ. Calculate the temperature at which the equilibrium constant K = 1.3 × 1026. Round your answer to the nearest degree. T=arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY