
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
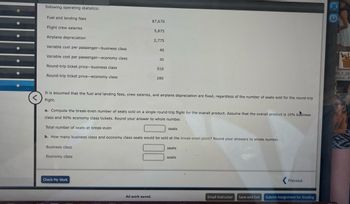
Transcribed Image Text:following operating statistics:
Fuel and landing fees
Flight crew salaries
Airplane depreciation
Variable cost per passenger-business class
Variable cost per passenger-economy class
Round-trip ticket price-business class
Round-trip ticket price-economy class
Business class
Economy class
$7,670
Check My Work
5,875
All work saved.
2,775
40
<
It is assumed that the fuel and landing fees, crew salaries, and airplane depreciation are fixed, regardless of the number of seats sold for the round-trip
flight.
30
a. Compute the break-even number of seats sold on a single round-trip flight for the overall product. Assume that the overall product is 10% business
class and 90% economy class tickets. Round your answer to whole number.
Total number of seats at break-even
b. How many business class and economy class seats would be sold at the break-even point? Round your answers to whole number.
510
280
seats
seats
seats
L
Email Instructor
Save and Exit
Previous
Submit Assignment for Grading
W
00_F_26
EDG5...P
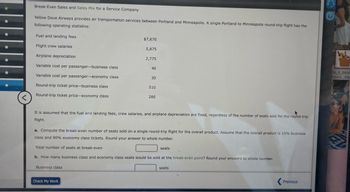
Transcribed Image Text:<
Break-Even Sales and Sales Mix for a Service Company
Yellow Dove Airways provides air transportation services between Portland and Minneapolis. A single Portland to Minneapolis round-trip flight has the
following operating statistics:
Fuel and landing fees
Flight crew salaries
Airplane depreciation
Variable cost per passenger-business class
Variable cost per passenger-economy class
Round-trip ticket price-business class
Round-trip ticket price-economy class
$7,670
Business class
5,875
Check My Work
2,775
40
30
510
It is assumed that the fuel and landing fees, crew salaries, and airplane depreciation are fixed, regardless of the number of seats sold for the round-trip
flight.
280
a. Compute the break-even number of seats sold on a single round-trip flight for the overall product. Assume that the overall product is 10% business
class and 90% economy class tickets. Round your answer to whole number.
Total number of seats at break-even
L
b. How many business class and economy class seats would be sold at the break-even point? Round your answers to whole number.
seats
seats
Previous
?
00_F_2658
EDG5...PQ
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- High-Low Method for a Service Company Boston Railroad decided to use the high-low method and operating data from the past six months to estimate the fixed and variable components of transportation costs The activity base used by Boston Railroad is a measure of railroad operating activity, termed "gross-ton miles," which is the total number of tons multiplied by the miles moved. Transportation Costs Gross-Ton Miles January $1,324,700 294,000 February 1,476,900 329,000 March 1,043,800 213,000 April 1,416,000 318,000 May 1,187,600 256,000 June 1,522,600 346,000 Determine the variable cost per gross-ton mile and the fixed cost. Variable cost (Round to two decimal places.) %$4 per gross-ton mile Total fixed cost Check My Work 4 more Check My Work uses remaining. Previous Next All work saved. Email Instructor Save and Exit Submit Assignment for Gra %24 %24arrow_forwardProduct AG52 has revenues of $748,000, variable cost of goods sold of $640,000, variable selling expenses of $90,000, and fixed costs of $50,000, creating a loss from operations of $32,000. Required: 1. Prepare a differential analysis as of October 7 to determine if Product AG52 should be continued (Alternative 1) or discontinued (Alternative 2), assuming fixed costs are unaffected by the decision. Refer to the lists of Labels and Amount Descriptions for the exact wording of the answer choices for text entries. For those boxes in which you must enter subtracted or negative numbers use a minus sign. If there is no amount or an amount is zero, enter "0". A colon (:) will automatically appear if required. 2. Determine if Product AG52 should be continued (Alternative 1) or discontinued (Alternative 2).arrow_forwardeBook Break-Even Sales and Sales Mix for a Service Company Yellow Dove Airways provides air transportation services between Portland and Minneapolis. A single Portland to Minneapolis round-trip flight has the following operating statistics: Fuel and landing fees $10,331 Flight crew salaries 7,913 Airplane depreciation 3,736 Variable cost per passenger-business class 60 Variable cost per passenger-economy class 50 Round-trip ticket price-business class 590 Round-trip ticket price-economy class 310 It is assumed that the fuel and landing fees, crew salaries, and airplane depreciation are fixed, regardless of the number of seats sold for the round-trip flight. a. Compute the break-even number of seats sold on a single round-trip flight for the overall product. Assume that the overall product is 20% business class and 80% economy class tickets. Round your answer to whole number. Total number of seats at break-even seats b. How many business class and economy class seats would be sold at…arrow_forward
- Product A has revenue of $195,600, variable cost of goods sold of $114,200, variable selling expenses of $33,900, and fixed costs of $59,200, creating a loss from operations of $11,700. Prepare a differential analysis as of May 9, to determine whether Product A should be continued (Alternative 1) or discontinued (Alternative 2), assuming fixed costs are unaffected by the decision. If an amount is zero, enter "O". For those boxes in which you must enter subtracted or negative numbers use a minus sign Differential Analysis Continue Product A (Alt. 1) or Discontinue Product A (Alt. 2) May 9 Differential Effect Continue Product Discontinue Product on Income A (Alternative 1) A (Alternative 2) (Alternative 2) 195,600 -195,600 Revenues Costs: -114,200 X 114,200 X Variable cost of goods sold 33,900 X -33,900 X Variable selling expenses 59,200 X X 59,200 Fixed costs 11,700 -59,200 -47,500 Income (Loss)arrow_forwarduring the past year, the high and low use of three different resources for Fly High Airlines occurred in July and April. The resources are airplane depreciation, fuel, and airplane maintenance. The number of airplane flight hours is the driver. The total costs of the three resources and the related number of airplane flight hours are as follows: Resource Airplane Flight Hours Total Cost Airplane depreciation: High 44,000 $ 18,000,000 Low 28,000 18,000,000 Fuel: High 44,000 445,896,000 Low 28,000 283,752,000 Airplane maintenance: High 44,000 15,792,000 Low 28,000 11,504,000 Required: Use the high-low method to answer the following questions. If an answer is zero, enter "0". 1. What is the variable rate for airplane depreciation? $fill in the blank 1per flight hour What is the fixed cost for airplane depreciation?$fill in the blank 2 2. What is the cost formula for airplane depreciation? Total…arrow_forwardDd.102.arrow_forward
- What would operating income be if only 2,800 snowboards were sold in a quarter? You can assume no change to fixed expenses will occur if sales decline to 2,800 snowboards. Will there be an operating income or Operating loss?arrow_forwardCurrent Attempt in Progress Metlock Express reports the following costs and expenses in June 2022 for its delivery service. Indirect materials used Depreciation on delivery equipment Dispatcher's salary Property taxes on office building CEO's salary Gas and oil for delivery trucks Delivery service (product) costs Period costs $5,510 9,620 (A 4,300 760 Determine the total amount of (a) delivery service (product) costs and (b) period costs. Drivers' salaries Advertising Delivery equipment repairs Office supplies Office utilities 10,320 1,880 Repairs on office equipment $13,760 3,980 258 559 860 162arrow_forwardPlease do not give solution in image format thankuarrow_forward
- High-Low Method for a Service Company Boston Railroad decided to use the high-low method and operating data from the past six months to estimate the fixed and variable components of transportation costs. The activity base used by Boston Railroad is a measure of railroad operating activity, termed “gross-ton miles,” which is the total number of tons multiplied by the miles moved. Transportation Costs Gross-Ton Miles January $1,061,200 303,000 February 1,183,200 338,000 March 836,200 219,000 April 1,134,400 328,000 May 951,400 263,000 June 1,219,800 356,000 Determine the variable cost per gross-ton mile and the fixed cost. Variable cost (Round to two decimal places.) $fill in the blank 1 per gross-ton mile Total fixed cost $fill in the blank 2arrow_forwardRizio Company purchases a machine for $12,300, terms 2/10, n/60, FOB shipping point. Rizio paid within the discount period and took the $246 discount. Transportation costs of $278 were paid by Rizio. The machine required mounting and power connections costing $850. Another $401 is paid to assemble the machine, and $40 of materials are used to get it into operation. During installation, the machine was damaged and $330 worth of repairs were made. Complete the below table to calculate the cost recorded for this machine.arrow_forwardIndirect materials used Depreciation on delivery equipment Dispatcher's salary Property taxes on office building CEO's salary Gas and oil for delivery trucks Delivery service (product) costs $ Period costs $6,940 LA 12,040 5,400 980 12,960 2,320 Drivers' salaries Advertising Delivery equipment repairs Office supplies Determine the total amount of (a) delivery service (product) costs and (b) period costs. Office utilities Repairs on office equipment $17,280 5,080 324 702 1,080 206arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education